1、vuex的定义
1)Vuex 是一个专门为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式,使用插件的形式引进项目中
2)集中存储和管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化
3)每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库),new Vue.store({...}),“store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含应用中大部分的状态 (state)
2、vuex解决的问题
1)多个视图依赖于同一状态
2)来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态
Vuex则是把组件的共享状态抽取出来,以一个全局单例模式管理
同时,通过定义和隔离状态管理中的各种概念并强制遵守一定的规则,代码变得更结构化、易维护
以上就是vuex的思想
3、使用vuex的场景
开发大型单页应用
4、vuex和全局对象的区别
1)Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
2)你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用
5、vuex中的5个核心概念
在index.js引进这5个概念的定义
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import * as actions from './actions'
import * as getters from './getters'
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutations'
import createLogger from 'vuex/dist/logger'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const debug = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,getters,state,mutations,strict: debug,plugins: debug ? [createLogger()] : []
})
然后,在main.js中引进index.js,并在全局Vue实例下注册该store对象,这样所有的组件都可以共享store对象里面的state了
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el: '#app',router,store,render: h => h(App)
})
1)state对象:(在computed中引入)Vuex 使用单一状态树——用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态;每个应用将仅仅包含一个 store 实例
computed: {
localComputed () { /* ... */ },// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}state.js文件的内容 ----定义的states是在getters.js mutations.js actions.js文件调用
import {playMode} from 'common/js/config'
import {loadSearch,loadPlay,loadFavorite} from 'common/js/cache'
const state = {
singer: {},playing: false,fullScreen: false,playlist: [],sequenceList: [],mode: playMode.sequence,currentIndex: -1,disc: {},topList: {},searchHistory: loadSearch(),playHistory: loadPlay(),favoriteList: loadFavorite()
}
export default state
2)getters对象:(可以认为是store的计算属性),在组件中的computed中引入
getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算
Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数,也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount','anotherGetter',// ...
])
}给getter 属性另取一个名字,使用对象形式
mapGetters({
// 把 `this.doneCount` 映射为 `this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount`
doneCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})getters.js文件内容 ---输出states
//获取数据
export const singer = state => state.singer
export const playing = state => state.playing
export const fullScreen = state => state.fullScreen
export const playlist = state => state.playlist
export const sequenceList = state => state.sequenceList
export const mode = state => state.mode
export const currentIndex = state => state.currentIndex
export const currentSong = (state) => {
return state.playlist[state.currentIndex] || {}
}
export const disc = state => state.disc
export const topList = state => state.topList
export const searchHistory = state => state.searchHistory
export const playHistory = state => state.playHistory
export const favoriteList = state => state.favoriteList
在组件里面获取states
// 在组件里面引进states
computed: {
...mapGetters([
'currentIndex','fullScreen','playing'
])
}
//在组件里面调用state
let index = this.currentIndex - 1
3)mutations对象:更改 Vuex 中 store 的状态的唯一方法是commit mutation;
mutation类似于事件,每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler);
回调函数对状态进行更改, state 作为第一个参数
mutation-types.js文件内容----定义一些事件名,用常量表示
export const SET_SINGER = 'SET_SINGER'
export const SET_PLAYING_STATE = 'SET_PLAYING_STATE'
export const SET_FULL_SCREEN = 'SET_FULL_SCREEN'
export const SET_PLAYLIST = 'SET_PLAYLIST'
export const SET_SEQUENCE_LIST = 'SET_SEQUENCE_LIST'
export const SET_PLAY_MODE = 'SET_PLAY_MODE'
export const SET_CURRENT_INDEX = 'SET_CURRENT_INDEX'
export const SET_DISC = 'SET_DISC'
export const SET_TOP_LIST = 'SET_TOP_LIST'
export const SET_SEARCH_HISTORY = 'SET_SEARCH_HISTORY'
export const SET_PLAY_HISTORY = 'SET_PLAY_HISTORY'
export const SET_FAVORITE_LIST = 'SET_FAVORITE_LIST'
mutations.js文件内容-----提交一个state的修改
import * as types from './mutation-types'
//mutations里面存放的是方法名
const mutations = {
[types.SET_SINGER](state,singer) {
//能够获取到当前状态树的state,提交mutation的时候传的参数
state.singer = singer
},[types.SET_PLAYING_STATE](state,flag) {
state.playing = flag
},[types.SET_FULL_SCREEN](state,flag) {
state.fullScreen = flag
},[types.SET_PLAYLIST](state,list) {
state.playlist = list
},[types.SET_SEQUENCE_LIST](state,list) {
state.sequenceList = list
},[types.SET_PLAY_MODE](state,mode) {
state.mode = mode
},[types.SET_CURRENT_INDEX](state,index) {
state.currentIndex = index
}
}
export default mutations
在组件里面commit mutation
methods:{
// 引进一个mutation
...mapMutations({
setFullScreen: 'SET_FULL_SCREEN'
})
// 修改了一个state,然后commit mutation
back() {
this.setFullScreen(false)
}
}不能直接调用mutation,需要使用store.commit(mutation)来调用
提交载荷:可以向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload),作为mutation的第二个参数
对象风格的提交方式:直接使用包含 type 属性的对象
store.commit({
type: 'increment',amount: 10
})mutations需遵守Vue的响应规则:
1)最好提前在 store实例化 中初始化好所有所需属性
2)在对象上添加新的属性的方法:
Vue.set(obj,'newProp',123)//以新对象替换老对象,使用对象展开运算符
state.obj = { ...state.obj,newProp: 123 }使用常量替代mutation类型,通常在mutation-types中定义
mutation是同步函数:实质上任何在回调函数中进行的状态的改变都是不可追踪
在组件中提交mutation:
this.$store.commit('xxx') 提交 mutation使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用(需要在根节点注入 store)methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment',// 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy',amount)`
]),...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}4)actions对象:actions类似mutations,不同之处
action 提交的是 mutation,mutation直接变更状态。
action 可以包含任意异步操作当某个动作触发多个mutation的时候使用action
每一个action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的对象,比如叫做context对象,因此可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters
使用参数结构来简化代码:
actions: {
increment (context,payload) {
commit('increment')
}
}
实际上可以写成类似下面的形式,使用参数结构的方法来简化代码
actions: {
increment ({ commit,state },{m,n}) {
commit('increment')
}
}分发action:store.dispatch,在action内部执行异步操作
actions: {
incrementAsync ({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment')
},1000)
}
}Actions 支持载荷方式和对象方式进行分发
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch('incrementAsync',{
amount: 10
})
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',amount: 10
})在组件中分发action:
this.$store.dispatch('xxx') 分发 action使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用(需要先在根节点注入 store)actions.js文件内容 -----可以同时修改多个states,然后commit 多个states
import * as types from './mutation-types'
import {playMode} from 'common/js/config'
import {shuffle} from 'common/js/util'
import {saveSearch,clearSearch,deleteSearch,savePlay,saveFavorite,deleteFavorite} from 'common/js/cache'
function findIndex(list,song) {
return list.findIndex((item) => {
return item.id === song.id
})
}
export const selectPlay = function ({commit,state},{list,index}) {
commit(types.SET_SEQUENCE_LIST,list)
if (state.mode === playMode.random) {
let randomList = shuffle(list)
commit(types.SET_PLAYLIST,randomList)
index = findIndex(randomList,list[index])
} else {
commit(types.SET_PLAYLIST,list)
}
commit(types.SET_CURRENT_INDEX,index)
commit(types.SET_FULL_SCREEN,true)
commit(types.SET_PLAYING_STATE,true)
}
export const randomPlay = function ({commit},{list}) {
commit(types.SET_PLAY_MODE,playMode.random)
commit(types.SET_SEQUENCE_LIST,list)
let randomList = shuffle(list)
commit(types.SET_PLAYLIST,randomList)
commit(types.SET_CURRENT_INDEX,0)
commit(types.SET_FULL_SCREEN,true)
}
export const insertSong = function ({commit,song) {
let playlist = state.playlist.slice()
let sequenceList = state.sequenceList.slice()
let currentIndex = state.currentIndex
// 记录当前歌曲
let currentSong = playlist[currentIndex]
// 查找当前列表中是否有待插入的歌曲并返回其索引
let fpIndex = findIndex(playlist,song)
// 因为是插入歌曲,所以索引+1
currentIndex++
// 插入这首歌到当前索引位置
playlist.splice(currentIndex,song)
// 如果已经包含了这首歌
if (fpIndex > -1) {
// 如果当前插入的序号大于列表中的序号
if (currentIndex > fpIndex) {
playlist.splice(fpIndex,1)
currentIndex--
} else {
playlist.splice(fpIndex + 1,1)
}
}
let currentSIndex = findIndex(sequenceList,currentSong) + 1
let fsIndex = findIndex(sequenceList,song)
sequenceList.splice(currentSIndex,song)
if (fsIndex > -1) {
if (currentSIndex > fsIndex) {
sequenceList.splice(fsIndex,1)
} else {
sequenceList.splice(fsIndex + 1,1)
}
}
commit(types.SET_PLAYLIST,playlist)
commit(types.SET_SEQUENCE_LIST,sequenceList)
commit(types.SET_CURRENT_INDEX,currentIndex)
commit(types.SET_FULL_SCREEN,true)
}
export const saveSearchHistory = function ({commit},query) {
commit(types.SET_SEARCH_HISTORY,saveSearch(query))
}
export const deleteSearchHistory = function ({commit},deleteSearch(query))
}
export const clearSearchHistory = function ({commit}) {
commit(types.SET_SEARCH_HISTORY,clearSearch())
}
export const deleteSong = function ({commit,song) {
let playlist = state.playlist.slice()
let sequenceList = state.sequenceList.slice()
let currentIndex = state.currentIndex
let pIndex = findIndex(playlist,song)
playlist.splice(pIndex,1)
let sIndex = findIndex(sequenceList,song)
sequenceList.splice(sIndex,1)
if (currentIndex > pIndex || currentIndex === playlist.length) {
currentIndex--
}
commit(types.SET_PLAYLIST,currentIndex)
if (!playlist.length) {
commit(types.SET_PLAYING_STATE,false)
} else {
commit(types.SET_PLAYING_STATE,true)
}
}
export const deleteSongList = function ({commit}) {
commit(types.SET_CURRENT_INDEX,-1)
commit(types.SET_PLAYLIST,[])
commit(types.SET_SEQUENCE_LIST,[])
commit(types.SET_PLAYING_STATE,false)
}
export const savePlayHistory = function ({commit},song) {
commit(types.SET_PLAY_HISTORY,savePlay(song))
}
export const saveFavoriteList = function ({commit},song) {
commit(types.SET_FAVORITE_LIST,saveFavorite(song))
}
export const deleteFavoriteList = function ({commit},deleteFavorite(song))
}
在组件里面调用
methods:{
//引进actions
...mapActions([
'savePlayHistory'
])
//修改多个states
ready() {
this.savePlayHistory(this.currentSong)
}
}
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment',// 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy',...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}5)Module:使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },mutations: { ... },actions: { ... },getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
总结:在使用vuex的时候,如果使用模块化的思想来编程的话,那么通常情况下就需要定义6个js文件,分别是
index.js state.js getters.js mutation-types.js mutation.js actions.js1、index.js:在这里面去引入其他5个JS文件,然后export 一个Vuex.store({})的实例对象,然后再main.js文件里面import该js文件,在Vue实例里面添加store选项,即在根节点下注册该store对象
//index.js文件里面的内容
//store文件夹下,编写vuex的相关代码
//index.js是vuex的入口文件
//vuex中的state只能通过commit修改,不能直接修改
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//起别名是为了像调用对象的方法一样,调用模块里面定义的方法
import * as actions from './actions'
import * as getters from './getters'
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutations'
//使用vuex提供的一些插件
//通过mutation方式修改state的时候,他会在console中输出日志
import createLogger from 'vuex/dist/logger'
//注册插件Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
//npm run dev则process.env.NODE_EN=develop
//npm run builde则process.env.NODE_EN=production
//有性能损耗,所以在开发环境中使用
const debug = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
//输出一个实例化的vuex对象
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,plugins: debug ? [createLogger()] : []
})
2、state.js:在这里面定义一些组件之间的公用状态变量对象,然后export state对象
//所有的状态都放在这个文件夹下管理
//也就是存放数据的对象
//这里要管理的是singer
//playMode对象里面定义了一些常量
import {playMode} from '../common/js/config'
const state = {
singer: {},//播放的状态
playing: false,//歌单展开控制
fullScreen: false,//播放的是一个列表
playlist: [],//播放的歌单是一个有顺序的列表
sequenceList: [],//设置播放模式,顺序播放,随机播放
mode: playMode.sequence,//当前播放的一个索引
currentIndex: -1
}
export default state
3、getters.js:在这里面定义一些常量变量,它的值是函数的返回值,用于获取state.js中的对象的值;或者是当做store对象的计算属性,对state.js的属性对象进行计算,得到一些计算结果的变量,export多个常量
//获取states里面的属性,会做一些映射
//或者作为计算属性,根据states中的属性,计算得到另外一些属性
//代理计算属性,在组件中在computed中可以通过...mapGetters([])引入
//或mapGetters({}),给函数取别名
//getter的第一个参数为state,第二个可选是getter
export const singer = state => state.singer
export const playing = state => state.playing
export const fullScreen = state => state.fullScreen
export const playlist = state => state.playlist
export const sequenceList = state => state.sequenceList
export const mode = state => state.mode
export const currentIndex = state => state.currentIndex
export const currentSong = state => {
return state.playlist[state.currentIndex] || {}
}
4、mutation-types.js:在这里面定义一些操作mutation的字符串常量变量名,这里是定义一些动作名,所以名字一般是set 或者是update,然后再结合state.js中定义的变量对象,export多个常量
//存储mutation的一些相关的名字,也就是一些字符串常量
//即使用常量替代mutation类型
//mutations里面定义一些方法,这里也就是定义mutations里面方法的名字
// 一些动作,所以用set,update
export const SET_SINGER = 'SET_SINGER'
export const SET_PLAYING_STATE = 'SET_PLAYING_STATE'
export const SET_FULL_SCREEN = 'SET_FULL_SCREEN'
export const SET_PLAYLIST = 'SET_PLAYLIST'
export const SET_SEQUENCE_LIST = 'SET_SEQUENCE_LIST'
export const SET_PLAY_MODE = 'SET_PLAY_MODE'
export const SET_CURRENT_INDEX = 'SET_CURRENT_INDEX'
5、mutations.js:在这里面定义一些修改state.js中变量对象的值的方法,这些方法都放在一个常量mutations对象里面,然后export mutations
//输出一个mutations对象,
//每一个mutation的第一个参数state,第二个参数是payload
//用于改变state中的属性的状态
//这些操作都是同步操作
//在组件的methods中通过...mapMutations([])或者...mapMutations({})--用于改别名
import * as types from './mutation-types'
//mutations里面存放的是方法名
const mutations = {
[types.SET_SINGER](state,index) {
state.currentIndex = index
}
}
export default mutations
6、actions.js:在这里面定义一些常量方法,每个常量方法用于提交多个mutation,然后输出多个常量方法名
//当一个动作会触发多个mutation则在actions里面定义一个方法,从而触发这些mutation
import * as types from './mutation-types'
import {playMode} from '../common/js/config'
import {shuffle} from '../common/js/util'
function findIndex(list,song) {
return list.findIndex((item) => {
return item.id === song.id
})
}
export const selectPlay = function ({commit,randomList)
//将在顺序列表中播放的歌,在随机播放列表中的index
//确保点击“随机播放按钮”的时候还是当前这首歌
index = findIndex(randomList,true)
}
//定义一个随机播放的action
export const randomPlay = function ({commit},true)
}

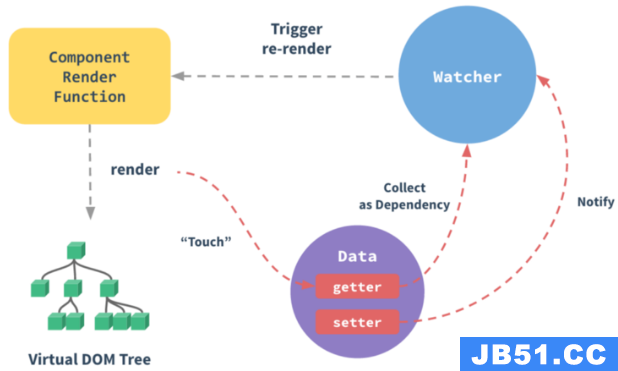 from https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-rc1lYYlsfx-wR4mQmIIQQ V...
from https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-rc1lYYlsfx-wR4mQmIIQQ V... D:\Temp>npm init vite@latest vue3study --temp...
D:\Temp>npm init vite@latest vue3study --temp... 文章浏览阅读1.2k次。最近自己从零撸起的甘特图组件需要子组...
文章浏览阅读1.2k次。最近自己从零撸起的甘特图组件需要子组... 文章浏览阅读3.3k次,点赞3次,收藏16次。静默打印是什么?简...
文章浏览阅读3.3k次,点赞3次,收藏16次。静默打印是什么?简...