数据类型
数据类型,也是一种约束
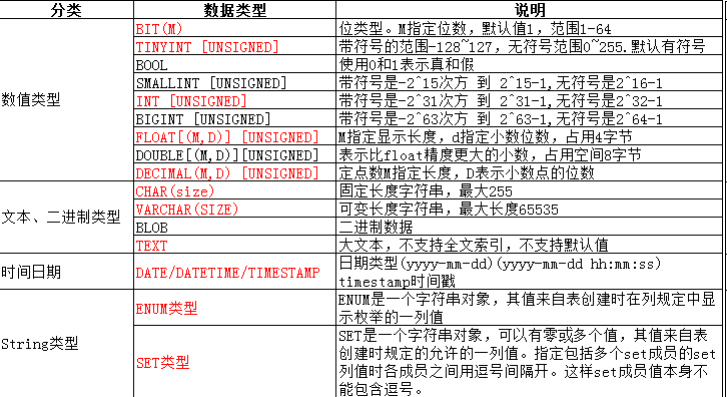
数据类型分类

数值类型

-
数值类型+unsigned 就是无符号类型
-
MysqL中类型与C/C++定义变量方式反过来
C/C++:
unsigned int a;
a int unsigned;
-
为什么有这么多种类型: 在节省空间与满足应用场景之间的平衡
以tinyint认识整型族
先建个简单的只有一个字段表
MysqL> create database test_db charset=utf8 collate=utf8_general_ci engine=InnoDB;
create table t1(num tinyint);
MysqL> desc t1;
+-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| num | tinyint(4) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MysqL> show create table t1\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t1
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`num` tinyint(4) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
tinyint(4) 括号内数字后面说
有符号边界范围测试
- 边界内能够正常插入
MysqL> insert into t1(num) values(-128);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t1(num) values(127);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t1(num) values(0);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t1(num) values(-1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t1(num) values(1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MysqL> select * from t1;
+------+
| num |
+------+
| -128 |
| 127 |
| 0 |
| -1 |
| 1 |
+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 边界外无法插入
MysqL> insert into t1(num) values(-129);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num' at row 1
MysqL> insert into t1(num) values(128);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num' at row 1
无符号边界测试
建一个只有无符号tiny类型的表
MysqL> create table t2(num tinyint unsigned);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
- 范围内正常插入
MysqL> insert into t2(num) values(0);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t2(num) values(1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t2(num) values(255);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
- 范围外不允许插入
MysqL> insert into t2(num) values(256);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num' at row 1
MysqL> insert into t2(num) values(-1);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num' at row 1
说明
MysqL中,所有数值类型数据范围不匹配时,MysqL一般会直接拦截,不允许写入;
反过来,已经存在MysqL中的数据,一定是合法的;
例如,修改表字段时,如果原有数据不满足新数据类型规则时,不允许进行修改
MysqL> alter table t1 modify num tinyint unsigned;
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num' at row 1
MysqL> alter table t2 modify num tinyint;
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num' at row 3
这也说明,MysqL中数据类型也是一种约束
约束:约束程序员/使用者 尽可能正确的存取数据
另外,尽量不使用unsigned,对于int类型可能存放不下的数据,int unsigned同样可能存放不下,与其如此,还不如设计时,将int类型提升为bigint类型。
BIT类型
基本语法:
bit[(M)] : 比特位/位图。M表示位数,范围从1到64。如果M被忽略,默认为1。
用法举例:
MysqL> create table t3(id int, online bit(1));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
MysqL> insert into t3(id,online) values(1,0);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t3(id,online) values(2,1);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MysqL> insert into t3(id,online) values(3,2);
ERROR 1406 (22001): Data too long for column 'online' at row 1
MysqL> select * from t3; #### 字符回显是以ascii码表示的,此时online的值属于不回显字符;
+------+--------+
| id | online |
+------+--------+
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select id,bin(online) from t3;
+------+-------------+
| id | bin(online) |
+------+-------------+
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 |
+------+-------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
如何证明是ascii码,把bit调整更大(到10),然后插入'a',之后就能看到回显的'a'了;
FLOAT类型
建一个小数精度为2,总有效长度为4的表
MysqL> create table t4 (id int ,salary float(4,2))charset=utf8, collate=utf8_general_ci,engine=InnoDB;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
MysqL> desc t4;
+--------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| salary | float(4,2) | YES | | NULL | |
+--------+------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 常规插入
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(1,99.99);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(2,-99.99);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
- 错误插入
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,100.00);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'salary' at row 1
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,100.0);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'salary' at row 1
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,99.999);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'salary' at row 1
- 占位插入
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,1.000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,1.0000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,1.00000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,99.00000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,099.00);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,000099.9900);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 (id,salary) values(4,10.0);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
- 舍入插入
MysqL> insert into t4 values(3, 99.994);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MysqL> insert into t4 values(3, 99.995);
ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'salary' at row 1
舍入后,如果范围超过精度,则不允许插入;在精度范围内,则允许插入
查看插入的数据
MysqL> select * from t4;
+------+--------+
| id | salary |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 99.99 |
| 2 | -99.99 |
| 4 | 1.00 |
| 4 | 1.00 |
| 4 | 1.00 |
| 4 | 99.00 |
| 4 | 99.00 |
| 4 | 99.99 |
| 4 | 10.00 |
| 4 | 1.00 |
+------+--------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
说明: 约束有效数字范围不能超过指定范围. 无效数字是可以超过的,无效数字不保留,只保留有效数字部分; 不满足的小数部分会自动补齐
无符号Float
无符号float直接把负数部分砍掉
默认的Float
默认的float即不输入范围的float,用户能够输入的精度范围很大,结果精度不太准确
修约规则
采用的修约规则:“四舍六入五成双”,也即“4舍6入5凑偶”,这里“四”是指≤4 时舍去,"六"是指≥6时进上,"五"指的是根据5后面的数字来定,当5后有数时,舍5入1;当5后无有效数字时,需要分两种情况来讲:
(1)5前为奇数,舍5入1;
(2)5前为偶数,舍5不进(0是偶数)。
评价
总的来说float精度不算太高。如果对存储精度要求不高或计算结果不需要高精度,可以使用FLOAT或DOUBLE。如果需要保持高精度,例如在财务系统中存储金额,建议使用DECIMAL。但需要注意,DECIMAL相比于FLOAT和DOUBLE会占用更多的存储空间。因此,在存储大量数值时,需要平衡精度和存储空间的需求。
精度不同版本可能不一样
高精度浮点decimal
浮点语法都一样
decimal(m, d) [unsigned] : 定点数m指定长度,d表示小数点的位数
与float精度对比
MysqL> create table tt8 ( id int, salary float(10,8), salary2
decimal(10,8));
MysqL> insert into tt8 values(100,23.12345612, 23.12345612);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select * from tt8;
+------+-------------+-------------+
| id | salary | salary2 |
+------+-------------+-------------+
| 100 | 23.12345695 | 23.12345612 | # 发现decimal的精度更准确,因此如果我们希望某个数据表示高精度,选择decimal
+------+-------------+-------------+
精度不同版本可能不一样
float表示的精度大约是7位。
decimal整数最大位数m为65。支持小数最大位数d是30。如果d被省略,默认为0.如果m被省略,默认是10。
- FLOAT: FLOAT是一种单精度浮点数类型,可以存储大约7位有效数字。它占用4个字节(32位)的存储空间。FLOAT适用于存储结果或计算结果不需要高精度、但需要较大范围的情况。但需要注意的是,由于使用近似值表示,FLOAT数据类型可能会导致一些舍入误差,在某些情况下,无法精确表示某些小数。
- DOUBLE: DOUBLE是一种双精度浮点数类型,可以存储大约15位有效数字。它占用8个字节(64位)的存储空间。DOUBLE适用于存储结果或计算结果需要高精度的情况。与FLOAT一样,DOUBLE也使用近似值表示,可能存在舍入误差。
- DECIMAL: DECIMAL是一种精确数值类型,用于存储具有非常高精度要求的数值。DECIMAL可以精确地保存用户定义的小数位数,并且不会发生近似值。DECIMAL的存储空间大小取决于定义的精度和范围。例如,DECIMAL(10, 2)可以存储10位数字,其中有2位小数。由于精确性较高,DECIMAL数据类型适用于存储金融领域的金额或其他精确计算。
char类型
char类型是定长字符类型,长度固定;
语法:
char(L): 固定长度字符串,L是可以存储的长度,单位为字符,最大长度值可以为255
测试
MysqL> create table t6(id int, name char(2));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
MysqL> insert into t6 values(1,'a');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t6 values(1,'ab');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t6 values(1,'abc');
ERROR 1406 (22001): Data too long for column 'name' at row 1
MysqL> insert into t6 values(1,'中');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t6 values(1,'中国');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into t6 values(1,'中国人');
ERROR 1406 (22001): Data too long for column 'name' at row 1
MysqL> select * from t6;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | a |
| 1 | ab |
| 1 | 中 |
| 1 | 中国 |
+------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
说明:
char允许设置的最大范围为255;
varchar类型
语法
varchar(L): 可变长度字符串,L表示最大字符长度,最大长度65535个字节,
## 换算成utf8(3字节) 就是 21845个字符;
注意,最大长度是字节不是字符
说明
关于varchar(len),len到底是多大,这个len值,和表的编码密切相关:
- varchar长度可以指定为0到65535之间的值,但是有1 - 3 个字节用于记录数据大小,所以说有效字
节数是65532。 - 当我们的表的编码是utf8时,varchar(n)的参数n最大值是65532/3=21844[因为utf中,一个字符占
用3个字节],如果编码是gbk,varchar(n)的参数n最大是65532/2=32766(因为gbk中,一个字符
占用2字节)。
char和varchar的区别
varchar括号的数值表示能够容纳的最大字符数,varchar实际装了多少字符就开多大空间.
类似C++中的string能够自动扩容,varchar是用多少空间就实际申请多少空间.

如何选择定长或变长字符串?
- 如果数据确定长度都一样,就使用定长(char),比如:身份证,手机号,md5
- 如果数据长度有变化,就使用变长(varchar), 比如:名字,地址,但是你要保证最长的能存的进去。
- 定长的磁盘空间比较浪费,但是效率高。
- 变长的磁盘空间比较节省,但是效率低。
- 定长的意义是,直接开辟好对应的空间
- 变长的意义是,在不超过自定义范围的情况下,用多少,开辟多少。
日期与时间类型
概念:
日期通常表示:年月日, 时间表示:时分秒, 所以日期时间就是:年月日时分秒
MysqL中常用的日期有如三个
-
date: 日期,格式yyyy-mm-dd,占用三个字节 -
datetime: 日期时间,格式yyyy-mm-dd HH:ii::ss,表示范围: 从1000到9999, -
timestamp:时间戳, 从1970年开始的yyyy-mm-dd HH:ii:ss格式和datatime完全一致,占用四字节
举例:
MysqL> insert into t7 values('2000-1-1','2001-1-1 12:34:56');
MysqL> select * from t7;
+------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| d | dt | ts |
+------------+---------------------+---------------------+
| 2000-01-01 | 2001-01-01 12:34:56 | 2024-09-06 12:55:28 |
+------------+---------------------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
说明
- 日期类型常用存放例如生日;更精确场景时就用日期时间,例如注册时间,历史登录时间等;主要用于维护一个不会轻易发生改变的时间
- 时间戳类型在首次插入数据/或更新数据时,会自动生成/更新(一般都不用管),结果与datetime一样,可以理解为插入当前时间;(例如评论功能,发表评论时记录当前时间,当更新评论时,时间也会跟着改变)
注意
-
时间戳类型存在时,不能用全列插入(不指定列插入);
MysqL> insert into t7 values('2000-1-1','2001-1-1 12:34:56'); ERROR 1136 (21S01): Column count doesn't match value count at row 1 MysqL> insert into t7(d,dt) values('2000-1-1','2001-1-1 12:34:56'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) -
时间类型插入时需要加引号
MysqL> insert into t7(d,dt) values(2000-1-1,2001-1-1 12:34:56); ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your sql Syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MysqL server version for the right Syntax to use near '12:34:56)' at line 1
enum和set
- enum:枚举,“单选”类型(多选一)
定义语法:
enum('选项1','选项2','选项3',...);
该设定只是提供了若干个选项的值,最终一个单元格中,实际只存储了其中一个值;而且出于效率考虑,这些值实际存储的是“数字”,因为这些选项的每个选项值依次对应如下数字:1,2,3,....最多65535个;当我们添加枚举值时,也可以添加对应的数字编号。
- set:集合,“多选”类型;
定义语法:
set('选项值1','选项值2','选项值3', ...);
该设定只是提供了若干个选项的值,最终一个单元格中,设计可存储了其中任意多个值;而且出于效率考虑,这些值实际存储的是“数字”,因为这些选项的每个选项值依次对应如下数字:1,2,4,8,16,32,.... 最多64个。
MysqL实际存储set还是将其存为数字,占用1、2、4、8个字节。
但和enum不同,set实际是以位图结构对每个位一一映射对应的选项值;
enum类型不可插入0,不可插入空串'',而set类型在严格模式下可以插入0和空串;
MysqL规定set类型最多占用8个字节(64个bit位)
测试
MysqL> create table Votes (id int, gender enum('男','女'), hobby set('a','b','c','d','e'));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
举例
hobby一共有5个选项值,则有效位图为5位,举例
00001 === 'a'
00010 === 'b'
00011 === 'a','b'
...
- 枚举与set常规插入
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,'男','a'); # 正常插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes(id) values(2); # 只插入id,枚举和集合不插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(3,1,'a'); # 枚举值为1
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(3,2,'a'); # 枚举值为2
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(5,0,'a'); # 枚举值为0
ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'gender' at row 1
MysqL> insert into Votes values(5,3,'a'); # 枚举值为3
ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'gender' at row 1
MysqL> select * from Votes;
+------+--------+-------+
| id | gender | hobby |
+------+--------+-------+
| 1 | 男 | a |
| 2 | NULL | NULL |
| 3 | 男 | a |
| 3 | 女 | a |
+------+--------+-------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- set空串测试
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,0); # set插入0
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes(id) values(1); # 枚举,set空插入
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select * from Votes;
+------+--------+-------+
| id | gender | hobby |
+------+--------+-------+
| 1 | 男 | |
| 1 | NULL | NULL |
+------+--------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
对比发现,当set值为0时,set对应的字符串是空串,不是NULL
- set位图测试
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,1); # 00001
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,2); # 00010
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,3); # 00011
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,4); # 00100
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,5); # 00101
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select * from Votes;
+------+--------+-------+
| id | gender | hobby |
+------+--------+-------+
| 1 | 男 | a |
| 1 | 男 | b |
| 1 | 男 | a,b |
| 1 | 男 | c |
| 1 | 男 | a,c |
+------+--------+-------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
根据验证结果也证明了set是位图结构映射.
- set边界测试
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,16); # 10000
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,17); # 10001
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,31); # 11111
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MysqL> insert into Votes values(1,1,32); #100000
ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'hobby' at row 1
MysqL> select * from Votes;
+------+--------+-----------+
| id | gender | hobby |
+------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | 男 | e |
| 1 | 男 | a,e |
| 1 | 男 | a,b,c,d,e |
+------+--------+-----------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
集合查询函数 find_in_set
MysqL> select 9*2;;
+-----+
| 9*2 |
+-----+
| 18 |
+-----+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified
MysqL> select 9/2;;
+--------+
| 9/2 |
+--------+
| 4.5000 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified
MysqL> select 9%2;;
+------+
| 9%2 |
+------+
| 1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
举例find_in_set
MysqL> select find_in_set("a","a,b,c");
+--------------------------+
| find_in_set("a","a,b,c") |
+--------------------------+
| 1 |
+--------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select find_in_set("b","a,b,c");
+--------------------------+
| find_in_set("b","a,b,c") |
+--------------------------+
| 2 |
+--------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select find_in_set("c","a,b,c");
+--------------------------+
| find_in_set("c","a,b,c") |
+--------------------------+
| 3 |
+--------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select find_in_set("d","a,b,c");
+--------------------------+
| find_in_set("d","a,b,c") |
+--------------------------+
| 0 |
+--------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MysqL> select find_in_set("a,b","a,b,c");
+----------------------------+
| find_in_set("a,b","a,b,c") |
+----------------------------+
| 0 |
+----------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
语法
FIND_IN_SET(str, strlist)
-
str是要查找的字符串。 -
strlist是包含逗号分隔的字符串的列表。
如果 str 在 strlist 中,FIND_IN_SET 返回 str 在 strlist 中的位置(从1开始计数)。如果 str 不在 strlist 中,则返回0。
例如:
SELECT FIND_IN_SET('b','a,b,c,d');
将返回 2,因为 'b' 是列表 'a,b,c,d' 中的第二个元素。(从1开始,方便只要存在返回值都为真)
注:该函数大小写不敏感,所以 'B' 和 'b' 会被认为是相同的。
在set中的应用
表中有以下数据
MysqL> select * from Votes ;
+------+--------+-----------+
| id | gender | hobby |
+------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | 男 | |
| 1 | NULL | NULL |
| 1 | 男 | a |
| 1 | 男 | b |
| 1 | 男 | a,b |
| 1 | 男 | c |
| 1 | 男 | a,c |
| 1 | 男 | e |
| 1 | 男 | a,e |
| 1 | 男 | a,b,c,d,e |
+------+--------+-----------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查找存在有爱好a的记录/行
MysqL> select * from Votes where find_in_set('a',hobby);
+------+--------+-----------+
| id | gender | hobby |
+------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | 男 | a |
| 1 | 男 | a,b |
| 1 | 男 | a,c |
| 1 | 男 | a,e |
| 1 | 男 | a,b,c,d,e |
+------+--------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查找存在爱好a和爱好b的记录
MysqL> select * from Votes where find_in_set('a',hobby) and find_in_set('b',hobby);
+------+--------+-----------+
| id | gender | hobby |
+------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | 男 | a,b |
| 1 | 男 | a,b,c,d,e |
+------+--------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)