散点图的应用很广泛,以前介绍过很多画图方法:Python画图(直方图、多张子图、二维图形、三维图形以及图中图),漏掉了这个,现在补上,用法很简单,我们可以help(plt.scatter)看下它的用法:
Help on function scatter in module matplotlib.pyplot:
scatter(x,y,s=None,c=None,marker=None,cmap=None,norm=None,vmin=None,vmax=None,alpha=None,linewidths=None,verts=None,edgecolors=None,hold=None,data=None,**kwargs)
Make a scatter plot of `x` vs `y`
Marker size is scaled by `s` and marker color is mapped to `c`
Parameters
----------
x,y : array_like,shape (n,)
Input data
s : scalar or array_like,),optional
size in points^2. Default is `rcParams['lines.markersize'] ** 2`.
c : color,sequence,or sequence of color,optional,default: 'b'
`c` can be a single color format string,or a sequence of color
specifications of length `N`,or a sequence of `N` numbers to be
mapped to colors using the `cmap` and `norm` specified via kwargs
(see below). Note that `c` should not be a single numeric RGB or
RGBA sequence because that is indistinguishable from an array of
values to be colormapped. `c` can be a 2-D array in which the
rows are RGB or RGBA,however,including the case of a single
row to specify the same color for all points.
marker : `~matplotlib.markers.MarkerStyle`,default: 'o'
See `~matplotlib.markers` for more information on the different
styles of markers scatter supports. `marker` can be either
an instance of the class or the text shorthand for a particular
marker.
cmap : `~matplotlib.colors.Colormap`,default: None
A `~matplotlib.colors.Colormap` instance or registered name.
`cmap` is only used if `c` is an array of floats. If None,defaults to rc `image.cmap`.
norm : `~matplotlib.colors.Normalize`,default: None
A `~matplotlib.colors.Normalize` instance is used to scale
luminance data to 0,1. `norm` is only used if `c` is an array of
floats. If `None`,use the default :func:`normalize`.
vmin,vmax : scalar,default: None
`vmin` and `vmax` are used in conjunction with `norm` to normalize
luminance data. If either are `None`,the min and max of the
color array is used. Note if you pass a `norm` instance,your
settings for `vmin` and `vmax` will be ignored.
alpha : scalar,default: None
The alpha blending value,between 0 (transparent) and 1 (opaque)
linewidths : scalar or array_like,default: None
If None,defaults to (lines.linewidth,).
verts : sequence of (x,y),optional
If `marker` is None,these vertices will be used to
construct the marker. The center of the marker is located
at (0,0) in normalized units. The overall marker is rescaled
by ``s``.
edgecolors : color or sequence of color,default: None
If None,defaults to 'face'
If 'face',the edge color will always be the same as
the face color.
If it is 'none',the patch boundary will not
be drawn.
For non-filled markers,the `edgecolors` kwarg
is ignored and forced to 'face' internally.
Returns
-------
paths : `~matplotlib.collections.PathCollection`
Other parameters
----------------
kwargs : `~matplotlib.collections.Collection` properties
See Also
--------
plot : to plot scatter plots when markers are identical in size and
color
Notes
-----
* The `plot` function will be faster for scatterplots where markers
don't vary in size or color.
* Any or all of `x`,`y`,`s`,and `c` may be masked arrays,in which
case all masks will be combined and only unmasked points will be
plotted.
Fundamentally,scatter works with 1-D arrays; `x`,and `c`
may be input as 2-D arrays,but within scatter they will be
flattened. The exception is `c`,which will be flattened only if its
size matches the size of `x` and `y`.
我们可以看到参数比较多,平时主要用到的就是大小、颜色、样式这三个参数
s:形状的大小,默认 20,也可以是个数组,数组每个参数为对应点的大小,数值越大对应的图中的点越大。
c:形状的颜色,"b":blue "g":green "r":red "c":cyan(蓝绿色,青色) "m":magenta(洋红色,品红色) "y":yellow "k":black "w":white
marker:常见的形状有如下
".":点 ",":像素点 "o":圆形
"v":朝下三角形 "^":朝上三角形 "<":朝左三角形 ">":朝右三角形
"s":正方形 "p":五边星 "*":星型
"h":1号六角形 "H":2号六角形"+":+号标记 "x":x号标记
"D":菱形 "d":小型菱形
"|":垂直线形 "_":水平线形
我们来看几个示例(在一张图显示了)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
x=np.array([3,5])
y=np.array([7,8])
x1=np.random.randint(10,size=(25,))
y1=np.random.randint(10,))
plt.scatter(x,c='r')
plt.scatter(x1,y1,s=100,c='b',marker='*')
#使用pandas来读取
x2=[]
y2=[]
rdata=pd.read_table('1.txt',header=None)
for i in range(len(rdata[0])):
x2.append(rdata[0][i].split(',')[0])
y2.append(rdata[0][i].split(',')[1])
plt.scatter(x2,y2,s=200,c='g',marker='o')
plt.show()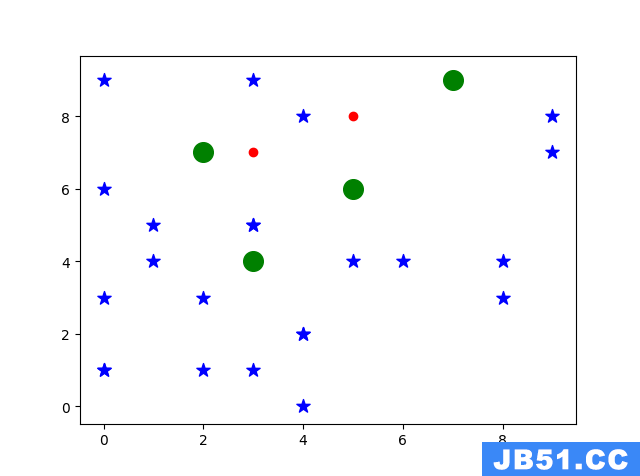
其中文档1.txt内容如下(上面图中的4个绿色大点)
5,6
7,9
3,4
2,7

 XML轻松学习手册
XML轻松学习手册