问题描述
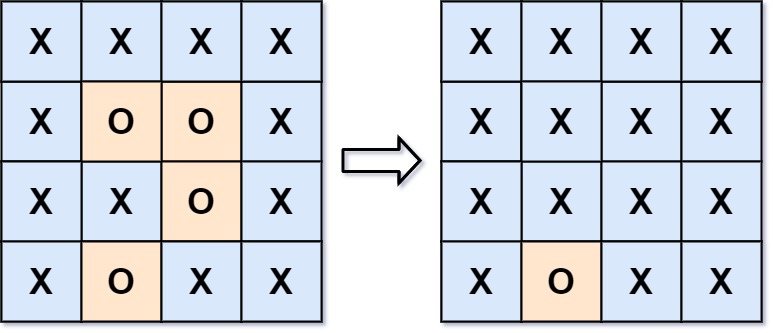
130,被围绕的区域
题目:给你一个
m x n的矩阵board,由若干字符'X'和'O',找到所有被'X'围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的'O'用'X'填充。思路:从边是'O'的字符处开始dfs, 先给标记成其他符号,代表着非包围字符, 那么剩下的'O'就都是被包围的字符了, 然后遍历矩阵, 将被包围的字符置为'X', 未被包围的字符置回'O'即可。如果直接顺序遍历,会出现全部O的情况下仍然修改。
class Solution { int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0}; int[] dy = {0, 0, 1, -1}; public void solve(char[][] board) { int n = board.length; if (n == 0) { return; } int m = board[0].length; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (board[i][0] == 'O') { queue.offer(new int[]{i, 0}); board[i][0] = 'A'; } if (board[i][m - 1] == 'O') { queue.offer(new int[]{i, m - 1}); board[i][m - 1] = 'A'; } } for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) { if (board[0][i] == 'O') { queue.offer(new int[]{0, i}); board[0][i] = 'A'; } if (board[n - 1][i] == 'O') { queue.offer(new int[]{n - 1, i}); board[n - 1][i] = 'A'; } } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int[] cell = queue.poll(); int x = cell[0], y = cell[1]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int mx = x + dx[i], my = y + dy[i]; if (mx < 0 || my < 0 || mx >= n || my >= m || board[mx][my] != 'O') { continue; } queue.offer(new int[]{mx, my}); board[mx][my] = 'A'; } } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { if (board[i][j] == 'A') { board[i][j] = 'O'; } else if (board[i][j] == 'O') { board[i][j] = 'X'; } } } } }
200,岛屿的数量
题目:给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
class Solution { int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; public int numIslands(char[][] grid) { ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(); Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); int heigh = grid.length; int width = grid[0].length; int max = 0; for (int i = 0; i <heigh; i++) { queue.clear(); for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == '1') { if (!arrayList.contains(new int[]{i, j})) { max++; queue.add(new int[]{i, j}); arrayList.add(new int[]{i, j}); grid[i][j]=0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int middle[] = queue.poll(); for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int newX = middle[0] + dx[k]; int newY = middle[1] + dy[k]; int[] newPoint = new int[]{newX, newY}; if (newX >= 0 && newX < heigh && newY >= 0 && newY < width && grid[newX][newY] == '1') { arrayList.add(newPoint); queue.add(newPoint); grid[newX][newY]='0'; } } } } } } } return max; } }
542,01矩阵
题目:给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵 mat ,请输出一个大小相同的矩阵,其中每一个格子是 mat 中对应位置元素到最近的 0 的距离。两个相邻元素间的距离为 1 。
class Solution { static int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; static int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] matrix) { // 首先将 0 边上的 1 入队 int[] dx = new int[] {-1, 1, 0, 0}; int[] dy = new int[] {0, 0, -1, 1}; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>(); int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length; int[][] res = new int[m][n]; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (matrix[i][j] == 0) { for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int x = i + dx[k]; int y = j + dy[k]; if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && matrix[x][y] == 1 && res[x][y] == 0) { // 这是在 0 边上的1。需要加上 res[x][y] == 0 的判断防止重复入队 res[x][y] = 1; queue.offer(new int[] {x, y}); } } } } } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int[] point = queue.poll(); int x = point[0], y = point[1]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int newX = x + dx[i]; int newY = y + dy[i]; if (newX >= 0 && newX < m && newY >= 0 && newY < n && matrix[newX][newY] == 1 && res[newX][newY] == 0) { res[newX][newY] = res[x][y] + 1; queue.offer(new int[] {newX, newY}); } } } return res; } }
547,省份数量
题目:有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
class Solution { int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; public int findCircleNum(int[][] grid) { Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); int heigh = grid.length; int width = grid[0].length; int max = 0; for (int i = 0; i < heigh; i++) { queue.clear(); //没有被访问过 if (grid[i][i] == 1) { //System.out.println(i); max++; queue.add(new int[]{i, i}); grid[i][i] = 0; for (int j = i; j < width; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == 1) { queue.add(new int[]{j, j}); grid[i][j] = 0; grid[j][j] = 0; grid[j][i] = 0; } } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int middle[] = queue.poll(); for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) { if (grid[middle[0]][j] == 1) { queue.add(new int[]{j, j}); grid[middle[0]][j] = 0; grid[j][j] = 0; grid[j][middle[0]] = 0; } } } } } return max; } }
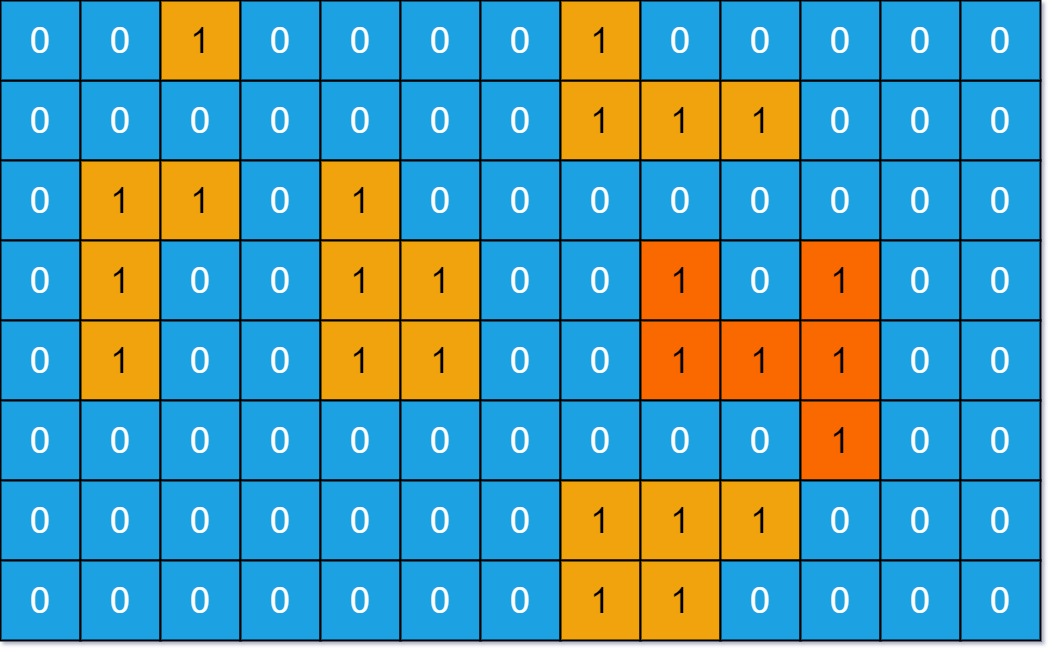
695,岛屿最大面积
题目:给你一个大小为 m x n 的二进制矩阵 grid 。岛屿 是由一些相邻的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合,这里的「相邻」要求两个 1 必须在 水平或者竖直的四个方向上 相邻。你可以假设 grid 的四个边缘都被 0(代表水)包围着。岛屿的面积是岛上值为 1 的单元格的数目。计算并返回 grid 中最大的岛屿面积。如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为 0 。
class Solution { static int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; static int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) { ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(); Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); int heigh = grid.length; int width = grid[0].length; int max = 0; for (int i = 0; i <heigh; i++) { queue.clear(); for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) { int temp = 0; if (grid[i][j] == 1) { if (!arrayList.contains(new int[]{i, j})) { queue.add(new int[]{i, j}); arrayList.add(new int[]{i, j}); grid[i][j]=0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int middle[] = queue.poll(); temp += 1; for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int newX = middle[0] + dx[k]; int newY = middle[1] + dy[k]; int[] newPoint = new int[]{newX, newY}; if (newX >= 0 && newX < heigh && newY >= 0 && newY < width && grid[newX][newY] == 1) { arrayList.add(newPoint); queue.add(newPoint); grid[newX][newY]=0; } } } if (max<temp){ max = temp; } } } } } return max; } }
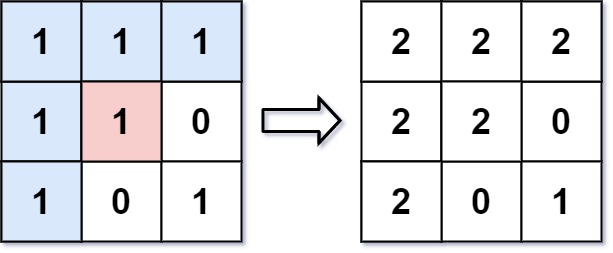
733,图像渲染
题目:有一幅以 m x n 的二维整数数组表示的图画 image ,其中 image[i][j] 表示该图画的像素值大小。你也被给予三个整数 sr , sc 和 newColor 。你应该从像素 image[sr][sc] 开始对图像进行 上色填充 。为了完成 上色工作 ,从初始像素开始,记录初始坐标的 上下左右四个方向上 像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,接着再记录这四个方向上符合条件的像素点与他们对应 四个方向上 像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,……,重复该过程。将所有有记录的像素点的颜色值改为 newColor 。最后返回 经过上色渲染后的图像 。
class Solution { int[] dx = {1, 0, 0, -1}; int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0}; public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int color) { //没有换色 int currColor = image[sr][sc]; if (currColor == color) return image; int oldColor = image[sr][sc]; int heigh = image.length; int width = image[0].length; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.add(new int[]{sr, sc}); image[sr][sc] = color; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int middle[] = queue.poll(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int newX = middle[0] + dx[i]; int newY = middle[1] + dy[i]; int[] newPoint = new int[]{newX, newY}; if (newX>=0&&newX<heigh&&newY>=0&&newY<width&&image[newX][newY]==oldColor){ queue.add(newPoint); image[newX][newY]=color; } } } return image; } }
797,所有可能的路径
题目:给你一个有 n 个节点的 有向无环图(DAG),请你找出所有从节点 0 到节点 n-1 的路径并输出(不要求按特定顺序) graph[i] 是一个从节点 i 可以访问的所有节点的列表(即从节点 i 到节点 graph[i][j]存在一条有向边)。
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>(); public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) { stack.offerLast(0); dfs(graph, 0, graph.length - 1); return ans; } public void dfs(int[][] graph, int x, int n) { if (x == n) { ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(stack)); return; } for (int y : graph[x]) { stack.offerLast(y); dfs(graph, y, n); stack.pollLast(); } } }
841,钥匙和房间
题目:有 n 个房间,房间按从 0 到 n - 1 编号。最初,除 0 号房间外的其余所有房间都被锁住。你的目标是进入所有的房间。然而,你不能在没有获得钥匙的时候进入锁住的房间。当你进入一个房间,你可能会在里面找到一套不同的钥匙,每把钥匙上都有对应的房间号,即表示钥匙可以打开的房间。你可以拿上所有钥匙去解锁其他房间。给你一个数组 rooms 其中 rooms[i] 是你进入 i 号房间可以获得的钥匙集合。如果能进入 所有 房间返回 true,否则返回 false。
class Solution { public boolean canVisitAllRooms(List<List<Integer>> rooms) { Queue<List> queue = new LinkedList(); boolean[] visited = new boolean[rooms.size()]; queue.add(rooms.get(0)); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { ArrayList<Integer> temp = (ArrayList) queue.poll(); for (int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++) { if (!visited[temp.get(i)]) { queue.add(rooms.get(temp.get(i))); visited[temp.get(i)]=true; } } } for (int i = 1; i < visited.length; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) { return false; } } return true; } }
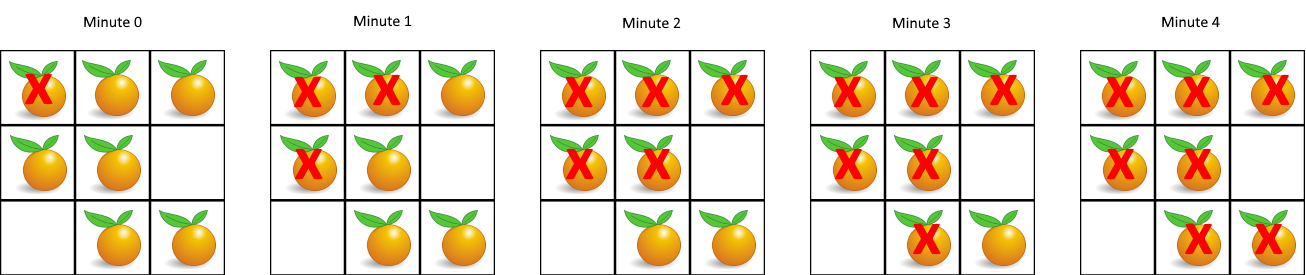
994,腐烂的橘子
题目:在给定的 m x n 网格 grid 中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
- 值 0 代表空单元格;
- 值 1 代表新鲜橘子;
- 值 2 代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,腐烂的橘子 周围 4 个方向上相邻 的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。返回 直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1 。
class Solution { int[] dr = new int[]{-1, 0, 1, 0}; int[] dc = new int[]{0, -1, 0, 1}; public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) { int R = grid.length, C = grid[0].length; Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<Integer>(); Map<Integer, Integer> depth = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for (int r = 0; r < R; ++r) { for (int c = 0; c < C; ++c) { if (grid[r][c] == 2) { int code = r * C + c; queue.add(code); depth.put(code, 0); } } } int ans = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int code = queue.remove(); int r = code / C, c = code % C; for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) { int nr = r + dr[k]; int nc = c + dc[k]; if (0 <= nr && nr < R && 0 <= nc && nc < C && grid[nr][nc] == 1) { grid[nr][nc] = 2; int ncode = nr * C + nc; queue.add(ncode); depth.put(ncode, depth.get(code) + 1); ans = depth.get(ncode); } } } for (int[] row: grid) { for (int v: row) { if (v == 1) { return -1; } } } return ans; } }
997,找到小镇的法官
题目:小镇里有 n 个人,按从 1 到 n 的顺序编号。传言称,这些人中有一个暗地里是小镇法官。如果小镇法官真的存在,那么:
- 小镇法官不会信任任何人。
- 每个人(除了小镇法官)都信任这位小镇法官。
- 只有一个人同时满足属性 1 和属性 2 。
给你一个数组 trust ,其中 trust[i] = [ai, bi] 表示编号为 ai 的人信任编号为 bi 的人。
如果小镇法官存在并且可以确定他的身份,请返回该法官的编号;否则,返回 -1 。
思路:在法官存在的情况下,法官不相信任何人,每个人(除了法官外)都信任法官,且只有一名法官。因此法官这个节点的入度是 n-1, 出度是 0。遍历每个节点的入度和出度,如果找到一个符合条件的节点,由于题目保证只有一个法官,我们可以直接返回结果;如果不存在符合条件的点,则返回 -1。
class Solution { public int findJudge(int n, int[][] trust) { int[] inDegrees = new int[n + 1]; int[] outDegrees = new int[n + 1]; for (int[] edge : trust) { int x = edge[0], y = edge[1]; ++inDegrees[y]; ++outDegrees[x]; } for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if (inDegrees[i] == n - 1 && outDegrees[i] == 0) { return i; } } return -1; } }
1091,二进制矩阵中的最短路径
题目:给你一个 n x n 的二进制矩阵 grid 中,返回矩阵中最短 畅通路径 的长度。如果不存在这样的路径,返回 -1 。二进制矩阵中的 畅通路径 是一条从 左上角 单元格(即,(0, 0))到 右下角 单元格(即,(n - 1, n - 1))的路径,该路径同时满足下述要求:
路径途经的所有单元格都的值都是 0 。路径中所有相邻的单元格应当在 8 个方向之一 上连通(即,相邻两单元之间彼此不同且共享一条边或者一个角)。畅通路径的长度 是该路径途经的单元格总数。
思路:广义优先遍历,每层步数+1。
class Solution { int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0, 1, -1, -1, 1}; int[] dy = {0, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1}; public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) { Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); int heigh = grid.length; int width = grid[0].length; int start = grid[0][0]; if (heigh == 1) { if (grid[0][0]==1){ return -1; }else { return 1; } } else if (heigh == 0) { return -1; } else if (start == 1) { return -1; } else if (grid[heigh - 1][heigh - 1] == 1) { return -1; } else { queue.add(new int[]{0, 0}); } int min = 1; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { min++; int levelNum = queue.size();//获取当前层的节点数. for (int j = 0; j < levelNum; j++) { int[] cell = queue.poll(); for (int i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) { int newX = cell[0] + dx[i]; int newY = cell[1] + dy[i]; if (newX == heigh - 1 && newY == newX&&grid[newX][newY]==0) { return min; } if (newX >= 0 && newX < heigh && newY >= 0 && newY < width && grid[newX][newY] == 0) { queue.add(new int[]{newX, newY}); grid[newX][newY]=1; } } } } return -1; } }
1557,可以到达所有点的最少点数
题目:给你一个 有向无环图 , n 个节点编号为 0 到 n-1 ,以及一个边数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [fromi, toi] 表示一条从点 fromi 到点 toi 的有向边。找到最小的点集使得从这些点出发能到达图中所有点。题目保证解存在且唯一。你可以以任意顺序返回这些节点编号。
思路:所有出节点和入节点的集合,如果一个出节点不在入节点集合中,说明出度为0,符合结果。相反,一个节点可以没有出节点,当叶子节点,但不能没有入节点,否则出度为0,这也是为啥用hash找hasSet的原因。
class Solution { public List<Integer> findSmallestSetOfVertices(int n, List<List<Integer>> edges) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>(); HashSet<Integer> hash = new HashSet<>(); for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) { hash.add(edges.get(i).get(0)); hashSet.add(edges.get(i).get(1)); } for (Integer a : hash) { if(!hashSet.contains(a)){ res.add(a); } } return res; } }
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)