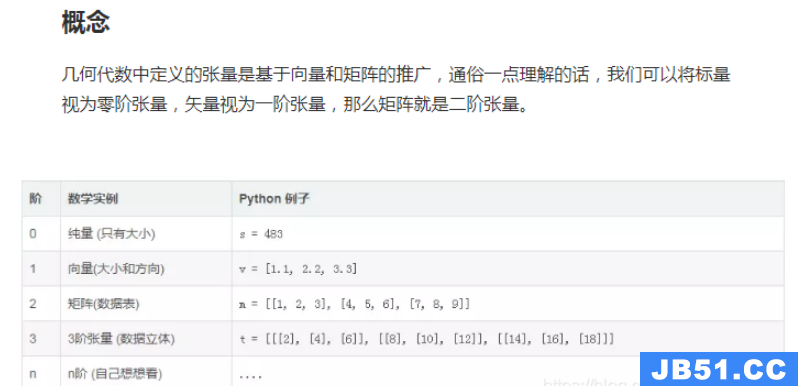
文章目录
1 准备数据
使用 Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry 的天气时间序列数据集。
该数据集包含14个不同的特征,例如气温,大气压力和湿度。从2003年开始,每10分钟收集一次。为了提高效率,本文仅使用2009年至2016年之间收集的数据。
导入需要的库
#导入需要的库
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import pandas as pd
mpl.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8, 6)
mpl.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 150
mpl.rcParams['axes.grid'] = False
导入数据
zip_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
origin='https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras- datasets/jena_climate_2009_2016.csv.zip',
fname='jena_climate_2009_2016.csv.zip',
extract=True)
csv_path, _ = os.path.splitext(zip_path)
df = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
df.head()

10分钟记录一次观测值,一个小时内有6个观测值,一天有144(6x24)个观测值。
给定一个特定的时间,假设要预测未来6小时的温度。为了做出此预测,选择使用5天的观察时间。因此,创建一个包含最后720(5x144)个观测值的窗口以训练模型。
下面的函数返回上述时间窗以供模型训练。参数history_size 是过去信息的滑动窗口大小。target_size 是模型需要学习预测的未来时间步,也作为需要被预测的标签。
下面使用数据的前300,000行当做训练数据集,其余的作为验证数据集。总计约2100天的训练数据。
划分训练特征和标签
def univariate_data(dataset, start_index, end_index, history_size, target_size):
data = []
labels = []
start_index = start_index + history_size
if end_index is None:
end_index = len(dataset) - target_size
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
indices = range(i-history_size, i)
# Reshape data from (history`1_size,) to (history_size, 1)
data.append(np.reshape(dataset[indices], (history_size, 1)))
labels.append(dataset[i+target_size])
return np.array(data), np.array(labels)
for i in range(0,10):
indices = range(i-20, i)
print(indices)
range(-20, 0)
range(-19, 1)
range(-18, 2)
range(-17, 3)
range(-16, 4)
range(-15, 5)
range(-14, 6)
range(-13, 7)
range(-12, 8)
range(-11, 9)
参数设置
TRAIN_SPLIT = 300000
# 设置种子以确保可重复性。
tf.random.set_seed(13)
2 单变量单步
首先,使用一个特征(温度)训练模型,并在使用该模型做预测。
从数据集中提取温度
uni_data = df['T (degC)']
uni_data.index = df['Date Time']
uni_data.head()
Date Time
01.01.2009 00:10:00 -8.02
01.01.2009 00:20:00 -8.41
01.01.2009 00:30:00 -8.51
01.01.2009 00:40:00 -8.31
01.01.2009 00:50:00 -8.27
Name: T (degC), dtype: float64
观察数据随时间变化的情况
uni_data.plot(subplots=True)

#将数据集转换为数组类型
uni_data = uni_data.values
uni_data
标准化
#标准化
uni_train_mean = uni_data[:TRAIN_SPLIT].mean()
uni_train_std = uni_data[:TRAIN_SPLIT].std()
uni_data = (uni_data-uni_train_mean)/uni_train_std
用前history_size个时间点的温度预测第history_size+target_size+1个时间点的温度。start_index和end_index表示数据集datasets起始的时间点,我们将要从这些时间点中取出特征和标签。
每个样本有20个特征(即20个时间点的温度信息),其标签为第21个时间点的温度值,如:
#写函数来划分特征和标签
univariate_past_history = 20
univariate_future_target = 0
x_train_uni, y_train_uni = univariate_data(uni_data, 0, TRAIN_SPLIT, # 起止区间
univariate_past_history,
univariate_future_target)
x_val_uni, y_val_uni = univariate_data(uni_data, TRAIN_SPLIT, None,
univariate_past_history,
univariate_future_target)
可见第一个样本的特征为前20个时间点的温度,其标签为第21个时间点的温度。根据同样的规律,第二个样本的特征为第2个时间点的温度值到第21个时间点的温度值,其标签为第22个时间点的温度……
x_train_uni.shape
>> (299980, 20, 1)
y_train_uni.shape
>> (299980,)
x_val_uni.shape
>> (120531, 20, 1)
print ('Single window of past history')
print (x_train_uni[0])
print ('\n Target temperature to predict')
print (y_train_uni[0])
Single window of past history
[[-1.99766294]
[-2.04281897]
[-2.05439744]
[-2.0312405 ]
[-2.02660912]
[-2.00113649]
[-1.95134907]
[-1.95134907]
[-1.98492663]
[-2.04513467]
[-2.08334362]
[-2.09723778]
[-2.09376424]
[-2.09144854]
[-2.07176515]
[-2.07176515]
[-2.07639653]
[-2.08913285]
[-2.09260639]
[-2.10418486]]
Target temperature to predict
-2.1041848598100876
设置绘图函数
def create_time_steps(length):
return list(range(-length, 0))
def show_plot(plot_data, delta, title):
labels = ['History', 'True Future', 'Model Prediction']
marker = ['.-', 'rx', 'go']
time_steps = create_time_steps(plot_data[0].shape[0]) # 横轴刻度
if delta:
future = delta
else:
future = 0
plt.title(title)
for i, x in enumerate(plot_data):
if i:
plt.plot(future, plot_data[i], marker[i], markersize=10,
label=labels[i])
else:
plt.plot(time_steps, plot_data[i].flatten(), marker[i], label=labels[i])
plt.legend()
plt.xlim([time_steps[0], (future+5)*2])
plt.xlabel('Time-Step')
return plt
show_plot([x_train_uni[0], y_train_uni[0]], 0, 'Sample Example')

def baseline(history):
return np.mean(history)
show_plot([x_train_uni[0], y_train_uni[0], baseline(x_train_uni[0])], 0,
'Baseline Prediction Example')

将特征和标签切片
BATCH_SIZE = 256
BUFFER_SIZE = 10000
train_univariate = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train_uni, y_train_uni))
train_univariate = train_univariate.cache().shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE).repeat()
val_univariate = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val_uni, y_val_uni))
val_univariate = val_univariate.batch(BATCH_SIZE).repeat()
建模
simple_lstm_model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(8, input_shape=x_train_uni.shape[-2:]), # input_shape=(20,1) 不包含批处理维度
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
simple_lstm_model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mae')
训练模型
EVALUATION_INTERVAL = 200
EPOCHS = 10
simple_lstm_model.fit(train_univariate, epochs=EPOCHS,
steps_per_epoch=EVALUATION_INTERVAL,
validation_data=val_univariate, validation_steps=50)
Train for 200 steps, validate for 50 steps
Epoch 1/10
200/200 [==============================] - 5s 27ms/step - loss: 0.4075 - val_loss: 0.1351
Epoch 2/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.1118 - val_loss: 0.0359
Epoch 3/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0489 - val_loss: 0.0290
Epoch 4/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0443 - val_loss: 0.0258
Epoch 5/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0299 - val_loss: 0.0235
Epoch 6/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0317 - val_loss: 0.0224
Epoch 7/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0286 - val_loss: 0.0208
Epoch 8/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0263 - val_loss: 0.0200
Epoch 9/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0254 - val_loss: 0.0182
Epoch 10/10
200/200 [==============================] - 4s 20ms/step - loss: 0.0228 - val_loss: 0.0174
print(val_univariate)
print(val_univariate.take(3))
for x, y in val_univariate.take(3):
plot = show_plot([x[0].numpy(), y[0].numpy(),simple_lstm_model.predict(x)[0]], 0, 'Simple LSTM model')
plot.show()



3 多变量单步
在这里,我们用过去的一些压强信息、温度信息以及密度信息来预测未来的一个时间点的温度。也就是说,数据集中应该包括压强信息、温度信息以及密度信息。
从数据集中划分特征和标签
features_considered = ['p (mbar)', 'T (degC)', 'rho (g/m**3)']
features = df[features_considered]
features.index = df['Date Time']
features.head()

压强、温度、密度随时间变化绘图
features.plot(subplots=True)

将数据集转换为数组类型并标准化
dataset = features.values
data_mean = dataset[:TRAIN_SPLIT].mean(axis=0)
data_std = dataset[:TRAIN_SPLIT].std(axis=0)
dataset = (dataset-data_mean)/data_std
写函数来划分特征和标签
在这里,我们不再像单变量单步中一样用到每个数据,而是在函数中加入step参数,这表明所使用的样本每step个时间点取一次特征和标签。
def multivariate_data(dataset, target, start_index, end_index, history_size,
target_size, step, single_step=False):
data = []
labels = []
start_index = start_index + history_size
if end_index is None:
end_index = len(dataset) - target_size
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
indices = range(i-history_size, i, step) # step表示滑动步长
data.append(dataset[indices])
if single_step:
labels.append(target[i+target_size])
else:
labels.append(target[i:i+target_size])
return np.array(data), np.array(labels)
past_history = 720
future_target = 72
STEP = 6
x_train_single, y_train_single = multivariate_data(dataset, dataset[:, 1], 0,
TRAIN_SPLIT, past_history,
future_target, STEP,
single_step=True)
x_val_single, y_val_single = multivariate_data(dataset, dataset[:, 1],
TRAIN_SPLIT, None, past_history,
future_target, STEP,
single_step=True)
将特征和标签切片
train_data_single = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train_single, y_train_single))
train_data_single = train_data_single.cache().shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE).repeat()
val_data_single = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val_single, y_val_single))
val_data_single = val_data_single.batch(BATCH_SIZE).repeat()
建模
single_step_model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
single_step_model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32,
input_shape=x_train_single.shape[-2:]))
single_step_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1))
single_step_model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop(), loss='mae')
single_step_history = single_step_model.fit(train_data_single, epochs=EPOCHS,
steps_per_epoch=EVALUATION_INTERVAL,
validation_data=val_data_single,
validation_steps=50)
Train for 200 steps, validate for 50 steps
Epoch 1/10
200/200 [==============================] - 31s 155ms/step - loss: 0.3090 - val_loss: 0.2647
Epoch 2/10
200/200 [==============================] - 29s 144ms/step - loss: 0.2623 - val_loss: 0.2444
Epoch 3/10
200/200 [==============================] - 30s 148ms/step - loss: 0.2612 - val_loss: 0.2460
Epoch 4/10
200/200 [==============================] - 31s 157ms/step - loss: 0.2567 - val_loss: 0.2440
Epoch 5/10
200/200 [==============================] - 32s 158ms/step - loss: 0.2263 - val_loss: 0.2362
Epoch 6/10
200/200 [==============================] - 31s 156ms/step - loss: 0.2413 - val_loss: 0.2659
Epoch 7/10
200/200 [==============================] - 30s 149ms/step - loss: 0.2415 - val_loss: 0.2572
Epoch 8/10
200/200 [==============================] - 30s 148ms/step - loss: 0.2410 - val_loss: 0.2380
Epoch 9/10
200/200 [==============================] - 30s 148ms/step - loss: 0.2445 - val_loss: 0.2490
Epoch 10/10
200/200 [==============================] - 30s 149ms/step - loss: 0.2390 - val_loss: 0.2479
def plot_train_history(history, title):
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(len(loss))
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'r', label='Validation loss')
plt.title(title)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
训练模型
plot_train_history(single_step_history,
'Single Step Training and validation loss')

绘制预测图
for x, y in val_data_single.take(3):
plot = show_plot([x[0][:, 1].numpy(), y[0].numpy(),
single_step_model.predict(x)[0]], 12,
'Single Step Prediction')
plot.show()



4 多变量多步
从数据集中划分特征和标签
future_target = 72
x_train_multi, y_train_multi = multivariate_data(dataset, dataset[:, 1], 0,
TRAIN_SPLIT, past_history,
future_target, STEP)
x_val_multi, y_val_multi = multivariate_data(dataset, dataset[:, 1],
TRAIN_SPLIT, None, past_history,
future_target, STEP)
将特征和标签切片
train_data_multi = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train_multi, y_train_multi))
train_data_multi = train_data_multi.cache().shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE).repeat()
val_data_multi = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val_multi, y_val_multi))
val_data_multi = val_data_multi.batch(BATCH_SIZE).repeat()
编写绘图函数
def multi_step_plot(history, true_future, prediction):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
num_in = create_time_steps(len(history))
num_out = len(true_future)
plt.plot(num_in, np.array(history[:, 1]), label='History')
plt.plot(np.arange(num_out)/STEP, np.array(true_future), 'bo',
label='True Future')
if prediction.any():
plt.plot(np.arange(num_out)/STEP, np.array(prediction), 'ro',
label='Predicted Future')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
for x, y in train_data_multi.take(1):
multi_step_plot(x[0], y[0], np.array([0]))
建模
multi_step_model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
multi_step_model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32,
return_sequences=True,
input_shape=x_train_multi.shape[-2:]))
multi_step_model.add(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(16, activation='relu'))
multi_step_model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(72))
multi_step_model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop(clipvalue=1.0), loss='mae')
训练模型
multi_step_history = multi_step_model.fit(train_data_multi, epochs=EPOCHS,
steps_per_epoch=EVALUATION_INTERVAL,
validation_data=val_data_multi,
validation_steps=50)
plot_train_history(multi_step_history, 'Multi-Step Training and validation loss')
绘制温度信息
for x, y in val_data_multi.take(3):
multi_step_plot(x[0], y[0], multi_step_model.predict(x)[0])
参考
https://www.heywhale.com/mw/project/5fe2f3de83e4460030ac7031