ListView作为一个经常被用来显示一组信息的控件,熟练掌握其用法显得尤为重要。这篇文章我们将从两个方面,介绍 ListView的用法。
ListView无非也就是多个控件的多次重复显示,ListView将Android中MVC模式很好的展示出来。MVC模式中最重要的就是控制器,Adapter很好的担任了这个角色。所以本片文章主要从Adapter的角度来讲解ListView的用法。本篇文章将从两个方面介绍Adapter,SimpleAdapter和自定义Adapter。
Ⅰ、SimpleAdapter。SimpleAdapter已经可以加载较为丰富的内容,知识内容形式比较单一罢了。
①、准备数据源。这里我随便列了一组数据
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>private String[] mtitle = {"姓名","性别","年龄","居住地","邮箱"};
private String[] mdetailinfo = {"总有些草民想害朕","男","23","广东深圳","1178065943@qq.com"};
我们还需要一个集合来存放这些数据
List<Map<String,Object>> mdata = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
for(int i=0; i<mtitle.length; i++){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("titletv",mtitle[i]);
map.put("detailtv",mdetailinfo[i]);
mdata.add(map);
}
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
③、总的布局有了,要显示当然缺不了每个item的布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iconiv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/icon_img" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#B3EC64"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/titletv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#E51A23"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/detailtv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#E51A23"
android:textSize="14sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
④、好了,准备工作做好了,我们只需要使用SimpleAdapter准备的数据关联起来即可。下面是SimpleAdapter
SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this,mdata,R.layout.list_item_layout,new String[]{
"titletv","detailtv"
},new int[]{
R.id.titletv,R.id.detailtv});
listView.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
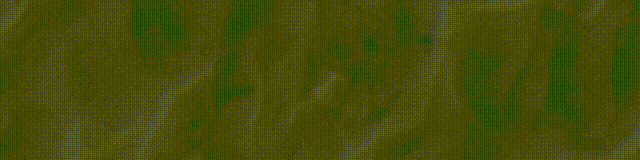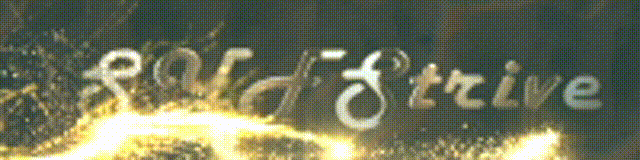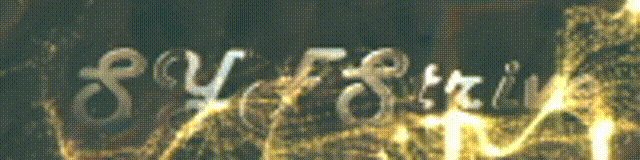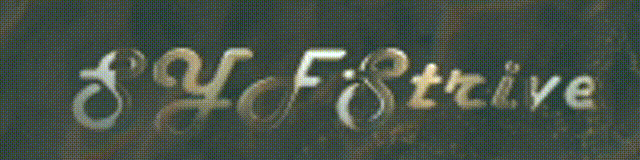
大功告成,看看效果
嘿嘿,看着还不错,ListView的使用是不是很简单呢,当然不是的,在开发过程中,我们经常需要自定义Adapter来加载我们多需要的数据,让我们的界面什么的看起来更好一些,下面我们就来介绍一下自定义Adapter。
II、我选取的例子是用ListView加载搜索到的蓝牙设备,并将设备的名字与地址都展示出来。
这个小Demo主要用到了四个类。BluetoothDeviceDB.java,DeviceInfo.java,DeviceInfoAdaper.java以及MainActivity.java.下面我将一一介绍各个类的用途。
①、BluetoothDeviceDB.主要是数据库的创建,表格的创建,以及增删查改几个方法,目的是用来存放匹配的蓝牙设备信息。代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import android.content.ContentValues; import android.content.Context; import android.database.Cursor; import android.database.sqlite.sqliteDatabase; import android.database.sqlite.sqliteDatabase.CursorFactory; import android.database.sqlite.sqliteOpenHelper; import android.util.Log; public class BluetoothDeviceDB extends sqliteOpenHelper { public static final String DATABASE_NAME = "BluetoothDB"; public static final String TABLE_NAME = "bluetoothrecord"; public static final String TITLE = "title"; public static final String ADDRESS = "address"; public static final String STATUS = "statue"; public static final int STATUE_CONNECTED = 1; public static final int STATUE_NOCONNECT = 0; public static String _id = "_id"; public static final String TABLE_CREATE = "create table " + TABLE_NAME + "(" + _id + " INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT," + TITLE + " TEXT," + ADDRESS + " TEXT," + STATUS + " INTEGER" + ");"; private static final String TAG = "BluetoothDeviceDB"; private static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 2; public BluetoothDeviceDB(Context context){ super(context,DATABASE_NAME,null,DATABASE_VERSION); } public BluetoothDeviceDB(Context context,String name,CursorFactory factory,int version) { super(context,name,factory,version); } //当数据库首次被创建时 @Override public void onCreate(sqliteDatabase db) { db.execsql(TABLE_CREATE); } @Override public void onUpgrade(sqliteDatabase db,int oldVersion,int newVersion) { String sql = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + TABLE_NAME; db.execsql(sql); } public long insert(sqliteDatabase db,String title,String address,int statue){ Log.d(TAG,"BluetoothDeviceDB-----insert()"); if(checkIsExist(db,address)){ Log.d(DATABASE_NAME,address+ " the device is exist"); } ContentValues cv = new ContentValues(); long row; cv.put(TITLE,title); cv.put(ADDRESS,address); cv.put(STATUS,statue); row = db.insert(TABLE_NAME,cv); return row; } public long update(sqliteDatabase db,int statue,int position){ ContentValues cv = new ContentValues(); long row; cv.put(TITLE,statue); row = db.update(TABLE_NAME,cv,_id + "=" + position,null); return row; } //查询记录的总数 public int getCount(sqliteDatabase db){ String sql = "select count(*) from " + TABLE_NAME; Cursor c = db.rawQuery(sql,null); c.movetoFirst(); int length = c.getInt(0); c.close(); return length; } private boolean checkIsExist(sqliteDatabase db,String address) { ArrayList<CompanionData> list = selectAll(db); for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++){ if(list.get(i).compare(address)){ return true; } } return false; } public CompanionData getCompanionData(sqliteDatabase db,String address){ ArrayList<CompanionData> list = selectAll(db); for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++){ if(list.get(i).compare(address)){ return list.get(i); } } return null; } private ArrayList<CompanionData> selectAll(sqliteDatabase db) { ArrayList<CompanionData> arrayList = new ArrayList<CompanionData>(); Cursor cursor = db.query(TABLE_NAME,null); if(cursor != null && cursor.getCount() > 0){ cursor.movetoFirst(); } for(cursor.movetoFirst(); !cursor.isAfterLast();cursor.movetoNext()){ CompanionData data = new CompanionData(); data.setmId(cursor.getInt(0)); data.setmTitle(cursor.getString(1)); data.setmAddress(cursor.getString(2)); data.setmStatue(cursor.getInt(3)); arrayList.add(data); } cursor.close(); return arrayList; } public class CompanionData{ private int mId; private String mAddress; private String mTitle; private int mStatue; public int getmId() { return mId; } public void setmId(int mId) { this.mId = mId; } public String getmAddress() { return mAddress; } public void setmAddress(String mAddress) { this.mAddress = mAddress; } public String getmTitle() { return mTitle; } public void setmTitle(String mTitle) { this.mTitle = mTitle; } public int getmStatue() { return mStatue; } public void setmStatue(int mStatue) { this.mStatue = mStatue; } public boolean compare(String address){ if(mAddress.equals(address)){ return true; }else { return false; } } } }②、DeviceInfo.java顾名思义就是用来存放设备各种信息的分装类。代码如下:
public class DeviceInfo {
private int imageId;
private String deviceName;
private String deviceAddress;
public DeviceInfo(){
imageId = R.drawable.ic_bluetooth;
}
public int getimageId() {
return imageId;
}
public void setimageId(int imageId) {
this.imageId = imageId;
}
public String getDeviceName() {
return deviceName;
}
public void setDeviceName(String deviceName) {
this.deviceName = deviceName;
}
public String getDeviceAddress() {
return deviceAddress;
}
public void setDeviceAddress(String deviceAddress) {
this.deviceAddress = deviceAddress;
}
}
③、好了,数据准备工作做好了,我们这篇文章的重头戏来了,DeviceInfoAdapter.java,他是用来把DeviceInfo加载到ListView中的。自定义Adapter,其实就是继承BaseAdapter,然后重写它其中的四个方法,getCount(),getItem(),getItemId(),和getView();各个方法具体是干什么的,代码中都有注释了,我就不在这里重复描述了。自定义Adapter的关键就在此,只要把这四个方法理顺了,你就可以定制任何自己想要的Adapter了。ok,让我们来观摩观摩代码:
package com.gajsh.bluetoothcommunication; import java.util.List; import com.gajsh.mybluetooth.R; import android.annotation.SuppressLint; import android.content.Context; import android.util.Log; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.BaseAdapter; import android.widget.TextView; @SuppressLint("ViewHolder") public class DeviceInfoAdapter extends BaseAdapter { private static final String TAG = "DeviceInfoAdapter"; private Context context; List<DeviceInfo> devices; public DeviceInfoAdapter(Context context,List<DeviceInfo> mPairedList) { super(); this.context = context; this.devices = mPairedList; } @Override public int getCount() {// 获取数据长度 Log.d(TAG,"size:"+devices.size()); return devices.size(); } @Override public Object getItem(int position) {// 获取Item中的数据源组 return devices.get(position); } @Override public long getItemId(int position) {// 用于item的定位--系统内部调用 return position; } @Override public View getView(int position,View contentView,ViewGroup group) { if (devices != null) // 实例获取item控件 // 为该控件管理布局并填充数据 if (contentView == null) { LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context); contentView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item_layout,null); TextView devicename = (TextView) contentView .findViewById(R.id.titletv); TextView address = (TextView) contentView .findViewById(R.id.addresstv); devicename.setText(devices.get(position).getDeviceName()); address.setText(devices.get(position).getDeviceAddress()); } return contentView; } }
④、最后一个类当然是让我们写的这些东西组织起来,让我们能够达到最终的目的—ListView显示所有匹配蓝牙设备的信息。
有几个要强调的地方。
1、蓝牙核心类BlueAdapter,它是通过getDefaultAdapter()来得到,而不是New出来,通过它可以进行蓝牙的搜索、匹配等。
2、addSystemPairedDevicesToDB(),这个类是将匹配的设备添加到数据库中,其中涉及蓝牙设备是否存在于数据库的检查类ExistOnSystemDB();
3、将数据库中的设备信息取出来存放到List中,addPairedDevicetoList()
4、最终我们是在OnResume()这个生命周期的方法中完成数据的适配的。
下面是MainActivity.java的代码
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; import com.gajsh.mybluetooth.R; import android.annotation.SuppressLint; import android.app.Activity; import android.app.AlertDialog; import android.app.ProgressDialog; import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter; import android.bluetooth.BluetoothDevice; import android.content.broadcastReceiver; import android.content.Context; import android.content.DialogInterface; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.IntentFilter; import android.database.Cursor; import android.database.sqlite.sqliteDatabase; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuInflater; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.widget.ListView; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; private BluetoothAdapter mBtAdapter; BluetoothDeviceDB dbhelper; DeviceInfoAdapter mPairedAdapter; sqliteDatabase sql; Cursor cursor; List<DeviceInfo> mPairedList; ListView mPairedListView; Set<BluetoothDevice> pairedDevices; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); mPairedList = new ArrayList<DeviceInfo>(); mPairedListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.pairedlv); dbhelper = new BluetoothDeviceDB(this); sql = dbhelper.getWritableDatabase(); mBtAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter(); // 向数据库中提交匹配的蓝牙设备 addSystemPairedDevicesToDB(); }; @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); Log.d(TAG,"-------------"); addPairedDevicetoList(); mPairedAdapter = new DeviceInfoAdapter(this,mPairedList); mPairedListView.setAdapter(mPairedAdapter); for (DeviceInfo device : mPairedList) { String devicename = device.getDeviceName(); String address = device.getDeviceAddress(); Log.d(TAG,"list的内容" + devicename + address); } } private void addPairedDevicetoList() { Cursor cursor = sql.rawQuery("select * from " + BluetoothDeviceDB.TABLE_NAME + " order by " + BluetoothDeviceDB._id,null); mPairedList.clear(); if (cursor != null && cursor.movetoFirst()) { for (int i = 0; i < cursor.getCount(); i++) { Log.d(TAG,"这是添加第---" + i + "---个元素"); DeviceInfo deviceInfo = new DeviceInfo(); deviceInfo.setDeviceAddress(cursor.getString(cursor .getColumnIndex(BluetoothDeviceDB.ADDRESS))); deviceInfo.setDeviceName(cursor.getString(cursor .getColumnIndex(BluetoothDeviceDB.TITLE))); mPairedList.add(deviceInfo); cursor.movetoNext(); } } if (cursor != null) { cursor.close(); cursor = null; } Log.d(TAG,"---添加完成---"); } private void addSystemPairedDevicesToDB() { pairedDevices = mBtAdapter.getBondedDevices(); if (pairedDevices.size() > 0 && !ExistOnSystemDB(pairedDevices)) { for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) { String address = device.getAddress(); String devicename = device.getName(); if (address != null && devicename != null) { dbhelper.insert(sql,device.getName(),device.getAddress(),0); } } } Log.d(TAG,"数据库元素添加完成"); } private boolean ExistOnSystemDB(Set<BluetoothDevice> pairedDevices) { Cursor cursor = sql.rawQuery("select address from " + BluetoothDeviceDB.TABLE_NAME,null); if (cursor != null && cursor.movetoFirst()) { for (int j = 0; j < cursor.getCount(); j++) { String dbaddress = cursor.getString(cursor .getColumnIndex(BluetoothDeviceDB.ADDRESS)); for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) { String pairedaddress = device.getAddress(); if (pairedaddress.equalsIgnoreCase(dbaddress)) { return true; } } } } return false; } }基本代码都有了,下面我把布局文件也列来,相当简单,首先是主布局
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/grey"
android:text="@string/bondeddevices" />
<ListView
android:id="@+id/pairedlv"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>由于布局相对简单,我就不给大家介绍布局的实现思路了,下面是list_item_layout
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/grey"
android:text="@string/bondeddevices" />
<ListView
android:id="@+id/pairedlv"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>由于我都是练习Demo,所以采用的都是线性布局,建议大家多用用相对布局,在开发中相对布局应用相对来说比较多些。
不知不觉,自定义Adapter也讲完了,其中也涉及到了sqlite数据库,有兴趣的朋友可以多研究一下。当然我加载的信息比较简单,大家有兴趣可以弄得复杂些,最后把效果图给大家看下: