Python OS模块
1. 访问文件
1.1 os.open(path, flags)
os.open(path, flags) 的功能是打开文件:
参数 path,要打开的文件
参数 flags,可能取值如下
返回值
1.2 os.read(fd, count)
参数 fd,使用 open 打开的文件描述
参数 count,至多读取 count 个字节
返回值
1.3 os.write(fd, binary)
1.4 os.close
os.close(fd) 的功能是关闭文件描述符,使用 open 打开文件后,需要使用 close 关闭。
1.5 例子:复制文件
import osdef copy(sourcePath, targetPath):sourceFd = os.open(sourcePath, os.O_RDONLY)targetFd = os.open(targetPath, os.O_WRONLY | os.O_CREAT)while (True):binary = os.read(sourceFd, )if len(binary) == :returnos.write(targetFd, binary)copy('test.txt', 'text.bak')
运行程序,输出如下:
C:\> python copy.py C:\> dir2001/10/01 10:40 <DIR> .2001/10/01 10:40 <DIR> ..2001/10/01 10:40 333 copy.py 2001/10/01 09:48 19 test.txt 2001/10/01 10:40 19 text.bak
2. 访问目录
2.1 os.getcwd()
os.getcwd 的功能是获取当前工作目录。该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.getcwd()'C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Downloads'
注意,在 windows 中,路径分隔符 \ 和 Python 的转义字符 \ 相同,需要对路径中的字符 \ 进行转义。
2.2 os.chdir(path)
os.chdir(path) 的功能切换当前工作目录。该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.chdir('C:\\Windows')>>> os.getcwd()'C:\\Windows'2.3 os.listdir(path)
os.listdir(path) 的功能是列出指定目录下的文件名:
该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.listdir('C:\\Program Files')['Common Files', 'desktop.ini', 'Git', 'IIS', 'Intel', 'Internet Explorer', 'JetBrains', 'Microsoft Help Viewer', 'Microsoft Office', 'Microsoft sql Server', 'Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0', 'Microsoft.NET', 'Mozilla Firefox', 'Office', 'Oracle', 'PuTTY', 'Sublime Text 2', 'tcc', 'Typora', 'Uninstall @R_304_4045@ion', 'Windows admin', 'Windows Identity Foundation', 'Windows Kits', 'Windows Mail', 'Windows Media Player']2.4 os.mkdir(path)
os.mkdir(path) 的功能是创建目录,该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.mkdir('test')3. 路径名
3.1 os.path 模块
os.path 模块是 os 模块的子模块,用于处理文件路径名。
路径名由两部分构成:目录名和文件名。例如:路径 C:\Windows\Readme.txt,目录名为 C:\Windows,文件名为 Readme.txt。
3.2 os.path.basename(path)
os.path.basename 的功能是获取路径名中的文件名,该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.basename('C:\\Windows\\Readme.txt')'Readme.txt'3.3 os.path.dirname(path)
os.path.dirname 的功能是获取路径名中的目录名,该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.dirname('C:\\Windows\\Readme.txt')'C:\\Windows'3.4 os.sep
os.sep 是 os 模块的导出变量,定义了文件路径名的分割符:
在 linux 中,os.sep 等于 /
在 windows 中,os.sep 等于 \
os.sep 的用法如下:
>>> import os>>> os.sep'\\'>>> 'C:\\Windows' + os.sep + 'Readme.txt''C:\\Windows\\Readme.txt'
在第 4 行,使用 os.sep 将 ‘C:\Windows’ 和 ‘Readme.txt’ 连接形成一个新的路径。
3.5 os.path.join(*args)
os.path.join(*args) 接受可变数量的参数,将所有的输入参数使用路径分隔符连接,形成一个新的路径名。
参数 *args,args 是可变参数
返回值,返回由输入参数组成的新路径
该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.path.join('C:\\Windows', 'Readme.txt')'C:\\Windows\\Readme.txt'>>> os.path.join('C:\\Windows', 'System32', 'Kernel.dll')'C:\\Windows\\System32\\Kernel.dll'
3.6 os.path.exists(path)
os.path.exists(path) 检查文件是否存在:
该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.path.exists('C:\\Windows')True>>> os.path.exists('C:\\non-exist-file')False
4. 文件属性
4.1 os.path.getsize(path)
os.path.getsize(path) 获取指定路径的文件的大小,该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.path.getsize('C:\\Users\\desktop.ini')
4.2 os.path.isfile(path)
操作系统中,常见的文件类型有两种:
os.path.isfile(path) 判断文件是否为普通文件,该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.path.isfile('C:\\Windows\\notepad.exe')True>>> os.path.isfile('C:\\Windows')False
4.3 os.path.isdir(path)
os.path.isdir(path) 判断文件是否为目录文件,该函数的使用示例:
>>> import os>>> os.path.isdir('C:\\Windows\\notepad.exe')False>>> os.path.isdir('C:\\Windows')True
4.4 例子:递归列出目录
假设存在 test 目录,test 目录下的子文件和子目录如下图所示:
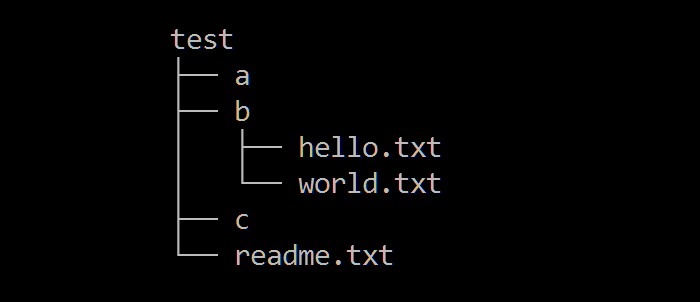
现在要求编写程序 listDir.py,列出 test 目录下所有的文件,listDir.py 的内容如下:
import osdef listDir(dir):entries = os.listdir(dir)for entry in entries:path = os.path.join(dir, entry)print(path)if os.path.isdir(path):listDir(path)listDir('test')
运行程序,输出结果如下:
test\a test\b test\b\x.txt test\b\y.txt test\c test\readme.txt
