目录
1.关系运算符重载
当我们自定义数据类型时,使用关系运算符做比较,编译器不会内部做比较,这时我们就需要对关系运算符进行重载。
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
bool operator==(Person & p)//返回值为bool类型好做比较
{
if (this->m_name == p.m_name && this->m_age == p.m_age)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator!=(Person& p)
{
if (this->m_name == p.m_name && this->m_age == p.m_age)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
string m_name;
int m_age;
};
2.函数调用运算符重载
函数调用运算符就是()这个运算符
class MyPrint
{
public:
void operator()(string text)
{
cout << text << endl;
}
};
void test()
{
MyPrint myPrint;
//对象当做函数来调用
myPrint("nihao"); // 仿函数
}
class MyAdd
{
public:
int operator()(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 + v2;
}
};
void test1()
{
//MyAdd myAdd;
//两种调用方式
//一种是直接将对象当中函数来调用
cout << myAdd(1, 2) << endl;
//另一种是不用创建对象,直接用类名创建无名的对象来调用
cout << MyAdd()(1, 1) << endl;//匿名对象
}
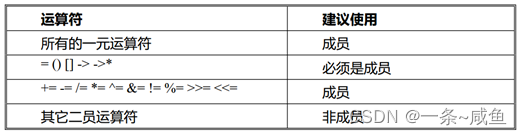
3.运算符重载总结
1. =, [], () 和 -> 操作符只能通过成员函数进行重载
2. << 和 >>只能通过全局函数配合友元函数进行重载
3. 不要重载 && 和 || 操作符,因为无法实现短路规则
常规的运算符重载建议
4.强化训练-字符串类的封装
**cout 输入自定义的字符串**
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, MyString& str)
{
cout << str.pString;
return cout;
}
**cin 让用户输入字符串内容**
istream& operator>>(istream& cin, MyString& str)
{
//先判断原始是否有内容,有的话清空
if (str.pString != NULL)
{
delete[] str.pString;
str.pString = NULL;
}
char buff[1024];//用户输入的内容
cin >> buff;
//把用户输入的内容赋值给str
str.pString = new char[strlen(buff) + 1];
strcpy(str.pString, buff);
str.m_Size = strlen(buff);
return cin;
}
**重载 = 运算符**
MyString& MyString::operator=(const char* str)//字符串
{
if (this->pString != NULL)
{
delete[] this->pString;
this->pString = NULL;
}
this->pString = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(this->pString, str);
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const MyString& str)//自定义类型
{
if (this->pString != NULL)
{
delete[] this->pString;
this->pString = NULL;
}
this->pString = new char[strlen(str.pString) + 1];
strcpy(this->pString, str.pString);
return *this;
}
**重载 + 运算符**
MyString MyString::operator+(const char* str)//字符串相加
{
//计算返回的字符串开辟的大小
int newSize = this->m_Size + strlen(str) + 1;
char* temp = new char[newSize];
memset(temp, 0, newSize);
//拼接字符串
strcat(temp, this->pString);
strcat(temp, str);
MyString newStr(temp);
delete[] temp;
return newStr;
}
MyString MyString::operator+(const MyString& str)//自定义数据类型相加
{
//计算返回的字符串开辟的大小
int newSize = this->m_Size + strlen(str.pString) + 1;
char* temp = new char[newSize];
memset(temp, 0, newSize);
//拼接字符串
strcat(temp, this->pString);
strcat(temp, str.pString);
MyString newStr(temp);
delete[] temp;
return newStr;
}
**重载 [] 运算符**
char& MyString::operator[](int index)
{
return this->pString[index];
}
**重载 == 运算符**
bool MyString::operator==(const char* str)
{
if (strcmp(this->pString , str)== 0 && this->m_Size == strlen(str))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool MyString::operator==(const MyString& str)
{
if (strcmp(this->pString, str.pString) == 0 && this->m_Size == strlen(str.pString))
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
5.继承的引出

//继承写法
//抽象一个基类的网页,重复的部分都写在这个网页上
class BasePage
{
public:
void header()
{
cout << "公共头部" << endl;
}
void footer()
{
cout << "公共底部" << endl;
}
void left()
{
cout << "左侧列表" << endl;
}
};
class News :public BasePage // 继承 News类继承BasePage类
{
public:
void content()
{
cout << "Neww" << endl;
}
};
class YULE :public BasePage
{
public:
void content()
{
cout << "Play" << endl;
}
};
class Game :public BasePage
{
public:
void content()
{
cout << "gameover" << endl;
}
};
//继承减少代码的重复性
//BasePage 基类(父类)
//News 派生类(子类)
6.继承的方式
首先继承的方式有三种:公有继承、私有继承和保护继承
**基类**
class Base1
{
public:
int m_a = 1;
protected:
int m_b = 1;
private:
int m_c = 0;
};
//公有继承
class Son1 :public Base1
{
public:
void func()
{
//cout << m_c << endl;基类中私有的属性不可继承
cout << m_a << endl;//基类中公共的属性可以继承,且还是public
cout << m_b << endl;//基类中保护的属性可以继承,且还是protected,类外不可访问
}
};
//保护继承
class Son2 :protected Base1
{
public:
void func()
{
//cout << m_c << endl;基类中私有的属性不可继承
cout << m_a << endl;//基类中公有的属性可以继承,且变为protected,类外不可访问
cout << m_b << endl;//基类中保护的属性可以继承,且还是protected,类外不可访问
}
};
//私有继承
class Son3 :private Base1
{
public:
void func()
{
//cout << m_c << endl;基类中私有的属性不可继承
cout << m_a << endl;//基类中公有的属性可以继承,且变为private,类外不可访问
cout << m_b << endl;//基类中保护的属性可以继承,且变为private,类外不可访问
}
};
公有继承
--父类中的protected 在子类中是 protected
--父类中的public 在子类中是 public
保护继承
--父类中的protected 在子类中是 protected
--父类中的public 在子类中是 protected
私有继承
--父类中的protected 在子类中是 private
--父类中的public 在子类中是 private
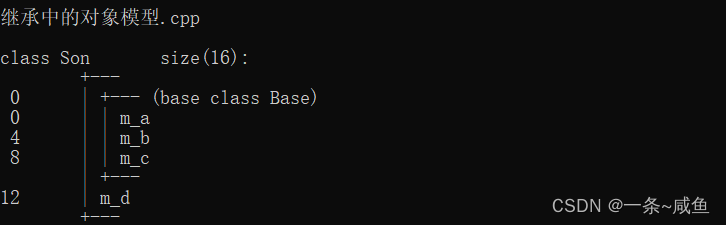
7.继承中的对象模型
子类会继承父类中所有的内容 ,包括了 私有属性,只是我们访问不到,编译器给隐藏了
class Base
{
public:
int m_a;
protected:
int m_b;
private:
int m_c;
};
//子类中会继承父类的私有成员,只是被编译器给隐藏起来,访问不到私有成员
class Son :public Base
{
public:
int m_d;
};
void test()
{
cout << sizeof(Son) << endl;//16
}
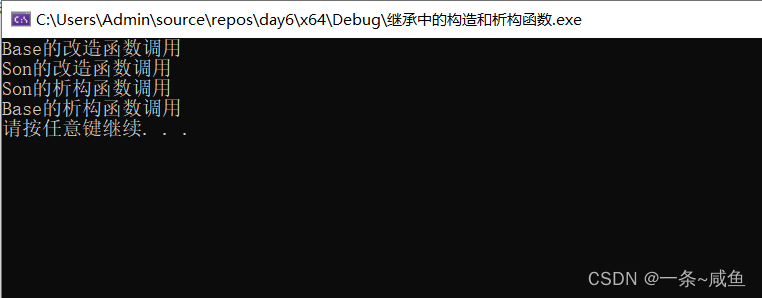
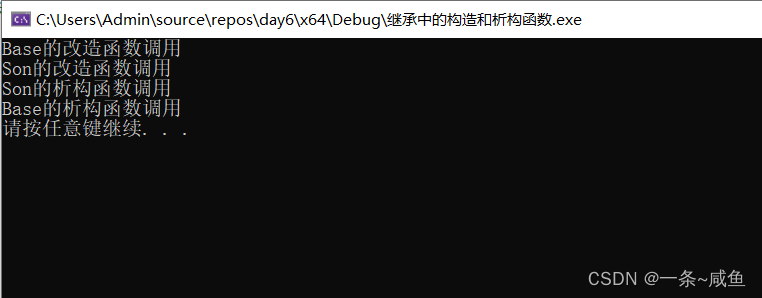
8.继承中的构造和析构顺序
子类会继承父类的成员属性和成员函数
但是子类不会继承父类的构造函数和析构函数
只有父类自己知道构造和析构自己的属性,而子类不知道
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
m_a = 10;
cout << "Base的改造函数调用" << endl;
}
~Base()
{
cout << "Base的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_a;
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
Son()
{
cout << "Son的改造函数调用" << endl;
}
~Son()
{
cout << "Son的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
};
如果父类中没有合适默认构造,那么子类可以利用初始化列表的方式显示的调用父类的其他构造
class Base2
{
public:
Base2(int a)
{
this->m_a = a;
cout << "有参构造调用" << endl;
cout << this->m_a << endl;
}
int m_a;
};
class Son2:public Base2
{
public:
Son2(int a) : Base2(a)//利用初始化列表的方式显示电影有参构造
{
}
};
9.继承中的同名处理
如果子类和父类拥有同名的属性和函数,子类并不会覆盖父类的成员,输出时按照就近原则输出子类,要想输出父类,需要按照结构–对象.父类名::属性/函数名
如果子类与父类的成员函数名称相同,子类会把父类的所有的同名版本都隐藏掉
如果想调用父类的方法,必须加作用域
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
m_a = 100;
}
void func()
{
cout << "Base.func" << endl;
}
void func(int a)
{
cout << "Base.func.a" << endl;
}
int m_a;
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
Son()
{
m_a = 200;
}
void func()
{
cout << "Son.func" << endl;
}
int m_a;
};
**成员属性--直接调用先调用子类,如果想调用父类 需要作用域**
**成员函数--直接调用先调用子类,父类的所有版本都会被隐藏,除非显示用作用域运算符去调用**
void test()
{
Son s1;
//调用子类中的m_a
cout << s1.m_a << endl;
//调用父类中的m_a
cout << s1.Base::m_a << endl;
//调用子类中的func
s1.func();
//调用父类中的func
s1.Base::func();
}
10.继承中静态成员的处理
class Base
{
public:
static void func()
{
cout << "Base.func" << endl;
}
static void func(int a)
{
cout << "Base.func.a" << endl;
}
static int m_a;
};
int Base::m_a = 18;
class Son :public Base
{
public:
static void func()
{
cout << "Son.func" << endl;
}
static int m_a;
};
int Son::m_a = 20;
//静态成员属性在子类中可以继承下来
//如果想访问父类中的成员,加作用域即可
void test()
{
cout << Son::m_a << endl;
//访问父类的属性
cout << Base::m_a << endl;
Son::func();
//访问父类的同名函数
Son::Base::func(12);
}
11.多继承的概念以及问题
派生类同时继承多个基类
class Base1
{
public:
Base1()
{
m_a = 10;
}
int m_a;
};
class Base2
{
public:
Base2()
{
m_a = 11;
}
int m_a;
};
//多继承
class Son :public Base1, public Base2
{
public:
int m_c;
int m_d;
};
//多继承中很容易引发二义性,想解决二义性问题,就需要通过作用域来进行区分
void test()
{
//cout << sizeof(Son) << endl;
//cout << s1.m_a << endl;//二义性
Son s1;
cout << s1.Base1::m_a << endl;
cout << s1.Base2::m_a << endl;
}
12.菱形继承问题以及解决
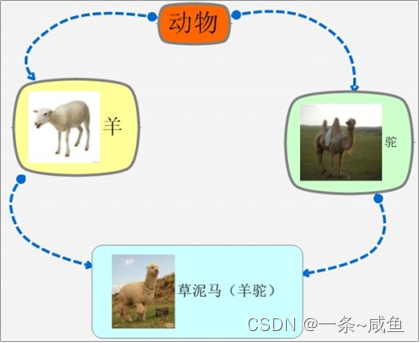
这种继承所带来的问题:
- 羊继承了动物的数据和函数,鸵同样继承了动物的数据和函数,当草泥马调用函数或者数据时,就会产生二义性。
- 草泥马继承自动物的函数和数据继承了两份,其实我们应该清楚,这份数据我们只需要一份就可以。
class Animal
{
public:
int m_age = 18;
};
class Sheep :public Animal
{
};
class Tuo :public Animal
{
};
class SheepTuo :public Sheep, public Tuo
{
};
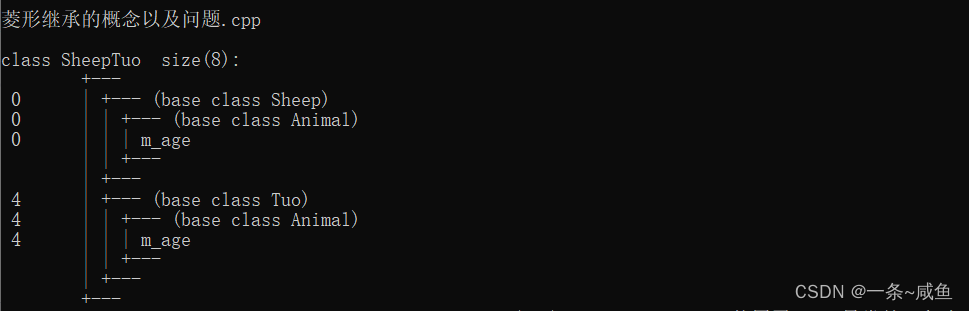
占据不必要的内存,解决方案是利用虚继承
class Animal
{
public:
int m_age = 18;
};
//虚基类Sheep
class Sheep :virtual public Animal
{
};
//虚基类Tuo
class Tuo :virtual public Animal
{
};
class SheepTuo :public Sheep, public Tuo
{
};
此时可以直接访问m_age了,因为没有了二义性
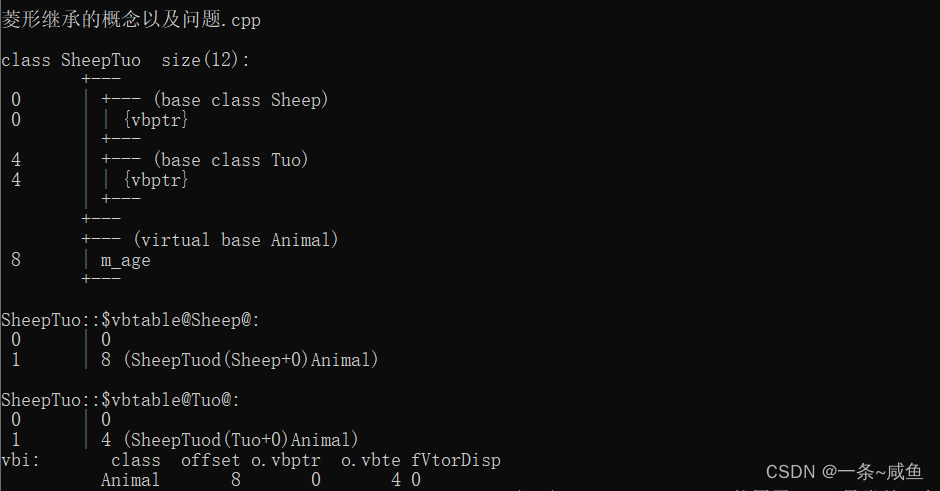
vbptr是虚基类指针,指向一张虚基类表,通过表找到偏移量(0+8/0+4),找到共有的数据
