全部代码 https://github.com/Joshmomel/Princeton_Algorithms/tree/wordnet/src
背景
这次作业需要先构造一个wordnet, 然后在此基础上找出两组次的最短距离
wordnet是单词指向上位词的一个网络
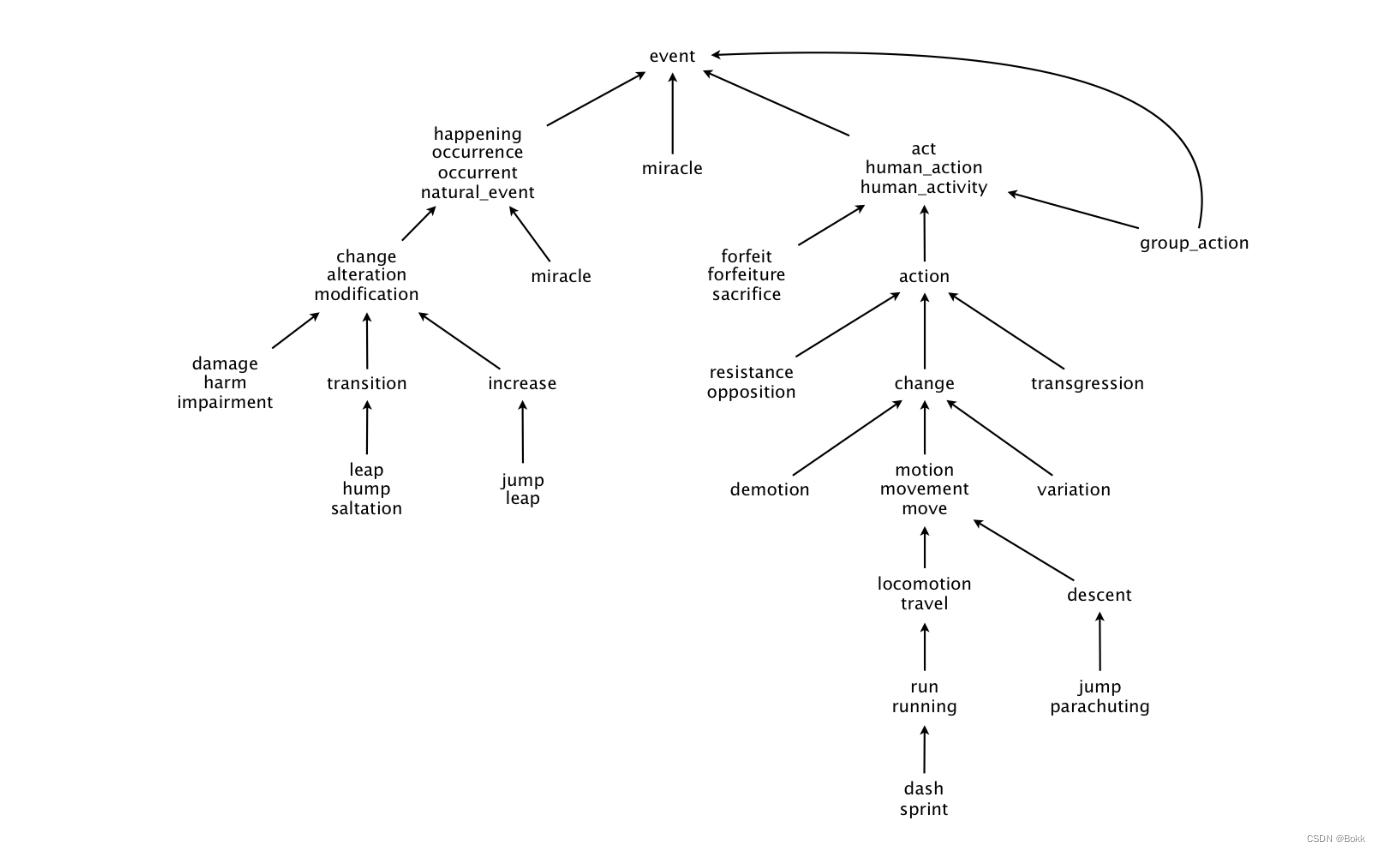
SAP
需求
根据FAQ 的Possible progress steps, 我们先要完成SAP. 也就是输入一个Digraph, 点v, 点w, 就算出最短共同祖先 (shortest ancestral path), 以及最短距离.
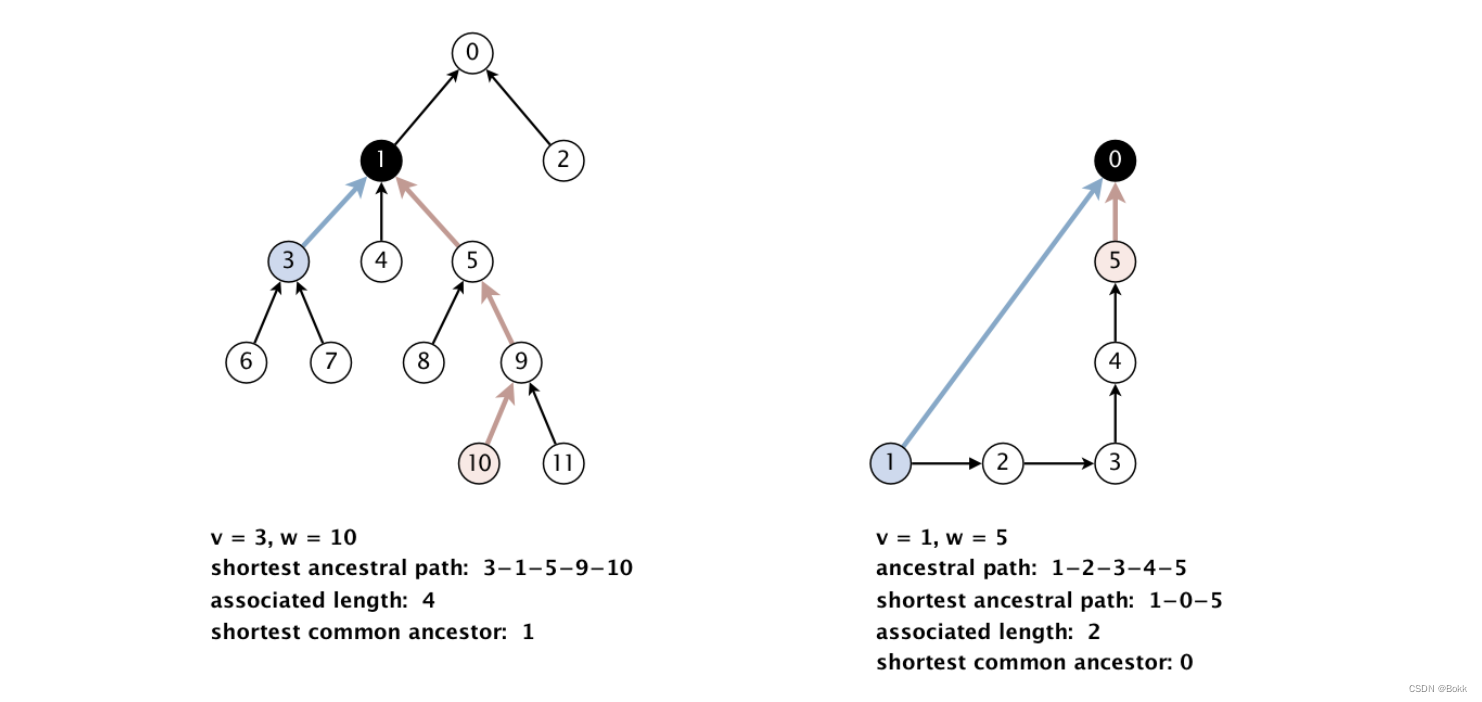
比如左图, 点3跟10的最短共同祖先就是1, 他们的距离是4
比如右图, 点1跟点5的最短共同祖先就是0, 他们的距离是2
算法分析
- 对点v做一次BFS, 使用mapV记录下经过的点以及其距离, {vertices: distance}
- 设置两个variable, node以及count, 初始值为-1, 用于储存下面的最短距离以及祖先用
- 对点w做一次BFS, 如果点n同时也经过mapV, 那么计算一下点v跟w的距离, 如果比count少, 则跟新count, 并且把node指向n
BreadthFirstDirectedPaths bfsFromV = new BreadthFirstDirectedPaths(G, v);
BreadthFirstDirectedPaths bfsFromW = new BreadthFirstDirectedPaths(G, w);
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < G.V(); i++) {
if (bfsFromW.hasPathTo(i)) {
map.put(i, bfsFromW.distTo(i));
}
}
int node = -1;
int count = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < G.V(); i++) {
var find = map.get(i);
if (find != null && bfsFromV.hasPathTo(i)) {
var total = find + bfsFromV.distTo(i);
if (count == -1 || total < count) {
count = total;
node = i;
}
}
}
上面的count就是lenght, node就是ancestor
性能提升
当然, 除了算法这个SAP还需要考虑在call length(int v, int w), ancestor(int v, int w) 怎么不用重复调用BFS, 毕竟调用一次就能同时算出length以及ancestor 我的方法是通过map存起来
具体来说, 构建一个VwPair类
private static class VwPair {
int v;
int w;
public VwPair(int v, int w) {
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
}
}
构建一个VwData类
private static class VwData {
int length;
int ancestor;
public VwData(int length, int ancestor) {
this.length = length;
this.ancestor = ancestor;
}
}
然后map是
private final HashMap<VwPair, VwData> db = new HashMap<>();
流程就是
ancestor(int v, int w) -> getSAP(v, w) -> 如果db没有 -> setSAP()
length(int v, int w) -> getSAP(v, w) -> 如果db没有 -> setSAP()
那么如果先ancestor(int v, int w), 则在length(int v, int w)的时候就db已经有记录了, 直接getSAP(v, w)中会, 不需要setSAP()
完整代码可以参考这里
Wordnet
需求
Wordnet就是把输入的文件转成Digraph的格式, 其中输入包括了synsets以及hypernyms
synsets: 词的id, 词, 词的定义

hypernyms: 词id, 上位词

要构成Wordnet的Graph是这样的
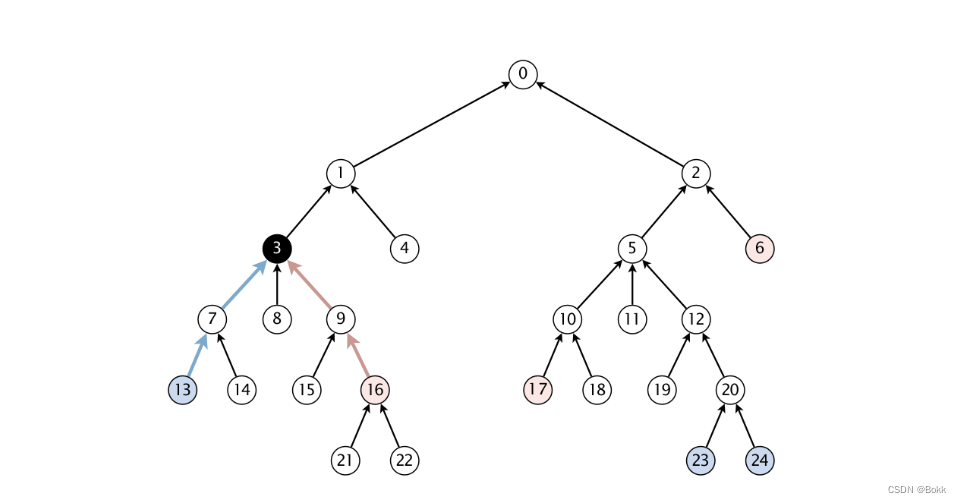
基本思路就是通过hypernyms构造Graph, 然后通过synsets找对应id的词
当然还要注意构造出来的Digraph的root不要有outdegree
代码
private int v = 0;
private final Digraph G;
private final SAP sap;
private final Map<String, List<Integer>> nounMap = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<Integer, String> idMap = new HashMap<>();
public WordNet(String synsets, String hypernyms) {
readSynsets(synsets);
G = new Digraph(this.v);
buildDigraph(hypernyms);
if (!isRootedDAG()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.sap = new SAP(this.G);
}
readSynsets 就是读取Synsets并存在nounMap中,要注意一个id是可以对应多个词的, 所以是Map<String, List>
isRootedDAG 就是看是否有一个outdegree为1的node就行
buildDigraph 就是读取hypernyms,然后调用Gigraph的addEdge方法
private void readSynsets(String synsets) {
In in = new In(synsets);
while (!in.isEmpty()) {
String s = in.readLine();
var fields = s.split(",");
var nouns = fields[1].split(" ");
int id = Integer.parseInt(fields[0]);
List<String> nounList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(nounList, nouns);
for (String noun : nounList) {
List<Integer> idList = nounMap.get(noun);
if (idList == null) {
ArrayList<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(id);
nounMap.put(noun, ids);
} else {
idList.add(id);
}
}
idMap.put(Integer.valueOf(fields[0]), fields[1]);
v += 1;
}
}
private boolean isRootedDAG() {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < G.V(); i++) {
if (G.outdegree(i) == 0)
count++;
}
return count == 1;
}
private void buildDigraph(String hypernyms) {
In in = new In(hypernyms);
while (!in.isEmpty()) {
String s = in.readLine();
var fields = s.split(",");
for (int i = 1; i < fields.length; i++) {
G.addEdge(Integer.parseInt(fields[0]), Integer.parseInt(fields[i]));
}
}
}
其它方法基本上调用SAP即可
public Iterable<String> nouns() {
return nounMap.keySet();
}
// is the word a WordNet noun?
public boolean isNoun(String word) {
if (word == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
return nounMap.get(word) != null;
}
// distance between nounA and nounB (defined below)
public int distance(String nounA, String nounB) {
if (!isNoun(nounA) || !isNoun(nounB)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
return this.sap.length(nounMap.get(nounA), nounMap.get(nounB));
}
// a synset (second field of synsets.txt) that is the common ancestor of nounA and nounB
// in a shortest ancestral path (defined below)
public String sap(String nounA, String nounB) {
if (!isNoun(nounA) || !isNoun(nounB)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
int id = this.sap.ancestor(nounMap.get(nounA), nounMap.get(nounB));
return idMap.get(id);
}
完整代码可以参考这里
Outcast
需求
作业已经把算法给了, 基本上就是照着写就行. 需要做的就是计算每个词跟其他词的距离di,找出di中最大的距离

代码
// given an array of WordNet nouns, return an outcast
public String outcast(String[] nouns) {
String outcast = null;
int maxDistance = -2;
for (String noun : nouns) {
int distance = 0;
for (String s : nouns) {
distance += wordNet.distance(noun, s);
}
if (maxDistance == -2 || distance > maxDistance) {
maxDistance = distance;
outcast = noun;
}
}
return outcast;
}
完整代码可以参考这里
总结
这个作业主要难度在于SAP的类,我花了很多时间思考这么计算最短共同祖先 (shortest ancestral path), 后来发现其实Algorithm书上的作业给了参考!就是做两次BFS, 后来研究了一下algs4中的BreadthFirstDirectedPaths是怎么用的, 基本就做出来了。但是后面需要拿100%适当的抛出Exception也是花了点时间。 总的来说这个作业还是很有意思的,通过基本的算法实现了一个看着高大上的问题 - 找词的相似度
