目录
A - 数塔问题
A - 数塔问题
思路:
- 数字三角形模型
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define fast ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr)
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LL_INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-9;
const int N = 210, M = 2e5 + 10;
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int T, cases;
int n, m;
int f[N][N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ )
cin >> f[i][j];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ )
f[i][j] += max(f[i - 1][j - 1], f[i - 1][j]);
int res = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
res = max(res, f[n][i]);
cout << res << endl;
return;
}
signed main()
{
//fast;
T = 1;
//cin >> T;
while(T -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
B - 最长上升子序列
思路:
- 最长上升子序列模型( l o n g e s t i n c r e a s i n g s e q u e n c e longest~increasing~sequence longest increasing sequence ),又称 L I S LIS LIS 模型
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define fast ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr)
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LL_INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-9;
const int N = 2100, M = 2e5 + 10;
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int T, cases;
int n, m;
int a[N];
int f[N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
f[i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j ++ )
if(a[j] < a[i]) f[i] = max(f[i], f[j] + 1);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
res = max(res, f[i]);
cout << res << endl;
return;
}
signed main()
{
//fast;
T = 1;
//cin >> T;
while(T -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
C - 最长公共子序列 ( L C S LCS LCS ): O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)做法
全称:( l o n g e s t c o m m o n s e q u e n c e longest~common~sequence longest common sequence )
前提:
- 最长公共子序列至少有一个序列元素不重复
思路:
- 最长公共子序列( 转化为 最长上升子序列
- 按照 最长上升子序列的优化方案一 (点此链接看详细证明):贪心 + 二分 优化为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)
具体步骤:
- 将元素不重复的序列的元素映射到其下标
- 在第二个序列中找到每个元素在第一个序列中的下标,构造新序列,
- 我们要求的结果即为新序列的 最长上升子序列( L I S LIS LIS )
证明:
- 找 最长公共子序列 只需维护数据的相对位置关系即可
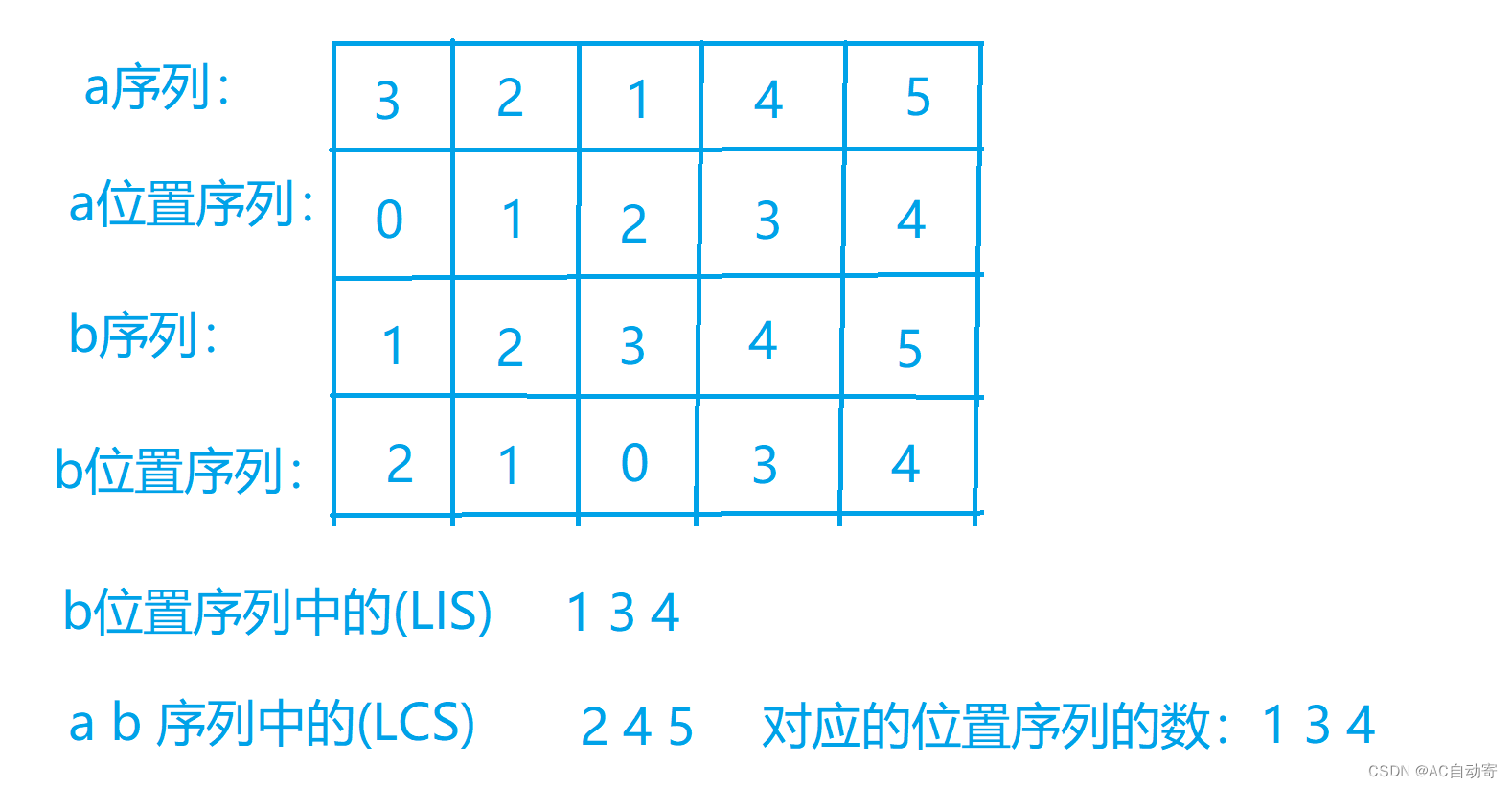
举例:
-
input:
5 3 2 1 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 -
output:
3 - 如图:
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n;
int id[N], q[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(id, -1, sizeof id);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
id[x] = i;
}
int len = 0;
q[0] = -1;
// 位置序列中最小值为 0 ,所以设置一个比最小值还小的值 -1 作为哨兵,
// 防止数组越界,保证了在二分的时候一定能找到结果
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
if(id[x] == -1) continue;
int k = id[x];
int l = 0, r = len;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if(q[mid] < k) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
q[r + 1] = k;
len = max(len, r + 1);
}
printf("%d\n", len);
return 0;
}
D - 摘花生
思路:
- 模拟,,水题
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define fast ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr)
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LL_INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-9;
const int N = 110, M = 1e5 + 10;
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int T, cases;
int n, m, times;
struct Points
{
int x, y, w;
bool operator < (const Points &W)const
{
return W.w < w;
}
}g[M];
int idx;
void solve()
{
memset(g, 0, sizeof g);
idx = 0;
cin >> n >> m >> times;
int x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
{
cin >> x;
if(x > 0) g[idx ++ ] = {i, j, x};
}
sort(g, g + idx);
int res = 0;
int lastx = 0, lasty;
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i ++ )
{
if(!i) lasty = g[i].y;
int t = abs(g[i].x - lastx) + abs(g[i].y - lasty);
if(times >= g[i].x + t + 1)
{
times -= t + 1;
res += g[i].w;
lastx = g[i].x, lasty = g[i].y;
}
else break;
}
cout << res << endl;
return;
}
signed main()
{
//fast;
T = 1;
cin >> T;
while(T -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
E - Boxes of Chocolates Again
思路:
- 完全背包求方案数 + 高精度加法
问: 高精度用 v e c t o r vector vector 慢的一批,不管了(这题没啥意思,,)思路就是这样,有高人救一下否 ? ? ?
答: 高精度压位即可, i n t int int类型 只存 0~9 的一位数实在是浪费,并且速度还慢, i n t int int 类型习惯压 4 4 4 或 8 8 8 位,最多可以压 9 9 9 位。
注: 想学习高精度压位的,参考此博客:【算法专题】高精度之压位
写的确实不错啊,膜拜 dalao ! ! !
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define fast ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr)
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LL_INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-9;
const int N = 5500, M = N * 2;
const int YB = 8, YM = 1e8;
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int T, cases;
int n, m, times;
vector<int> f[N];
vector<int> add(vector<int> &A, vector<int> &B)
{
if(A.size() < B.size()) return add(B, A);
vector<int> C;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i ++ )
{
t += A[i];
if(i < B.size()) t += B[i];
C.push_back(t % YM);
t /= YM;
}
if(t) C.push_back(t);
return C;
}
void print(vector<int> f)
{
printf("%d", f.back());
for (int i = f.size() - 2; i >= 0; i -- )
printf("%08d", f[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void init()
{
f[0].push_back(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= 5010; i ++ )
for (int j = i; j <= 5010; j ++ )
f[j] = add(f[j], f[j - i]);
return;
}
void solve()
{
print(f[n]);
}
signed main()
{
//fast;
T = 1;
//cin >> T;
init();
while(cin >> n)
solve();
return 0;
}
F - Road Optimization
思路:
- 直接枚举 f [ i ] [ j ] f[i][j] f[i][j] 是从哪一次转移过来的即可
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define fast ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr)
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LL_INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-9;
const int N = 510, M = N * 2;
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int T, cases;
int n, m, allow;
int dist[N];
int speed[N];
int f[N][N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m >> allow;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> dist[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> speed[i];
dist[ ++ n] = m;
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof f);
f[1][1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ )
for (int k = 1; k < i; k ++ )
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[k][j - 1] + (dist[i] - dist[k]) * speed[k]);
int res = INF;
for (int i = 0; i <= allow; i ++ ) res = min(res, f[n][n - i]);
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main()
{
//fast;
T = 1;
//cin >> T;
while(T -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
G - Hasan and his lazy students
G - Hasan and his lazy students
思路:
- 最长上升子序列求方案数
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <bitset>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define fast ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr)
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LL_INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-9;
const int N = 2010, M = N * 2;
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int T, cases;
int n, m, allow;
int a[N];
int f[N];
int g[N];
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> a[i];
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
memset(g, 0, sizeof g);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
f[i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j ++ )
if(a[j] < a[i]) f[i] = max(f[i], f[j] + 1);
g[i] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j ++ )
if(a[j] < a[i] && f[i] == f[j] + 1)
g[i] =(g[i] + g[j]) % mod;
if(!g[i]) g[i] = 1;
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) res = max(res, f[i]);
int num = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if(f[i] == res) num = (num + g[i]) % mod;
cout << res << " " << num << endl;
return;
}
signed main()
{
fast;
T = 1;
cin >> T;
while(T -- )
solve();
return 0;
}
