交换排序的基本思想是:两两比较待排序记录的关键字,发现两个记录的次序相反时即进行交换,直到没有反序的记录为止。应用交换排序基本思想的主要排序方法有:冒泡排序和快速排序。
一、下面我们来认识一下此方法在T-SQL中的实际使用:
declare @date datetime
declare @endDate datetime
declare @termID int
set @termID=46 --在此设置机器号
set @date='2008-8-8' --在此设置开始日期
set @endDate='2008-8-27' --在此设置结束日期
select t1.rownumber,t1.termid,t1.termrecordid,t2.rownumber,t2.termrecordid,t1.tcrdate,t2.termRecordid-t1.termRecordid as 差值
from(
select ROW_NUMBER() OVER (order by termid,termRecordID)as RowNumber,termid,termRecordID,tcrdate
from TE_TermCollectRecords
where tcrdate>=@date and tcrdate<@enddate
) t1,(
select ROW_NUMBER() OVER (order by termid,tcrdate
from TE_TermCollectRecords
where tcrdate>=@date and tcrdate<@enddate
) t2
where t2.rowNumber=t1.rowNumber+1 AND t2.termRecordid-t1.termRecordid>1
order by t1.tcrdate,t1.termid
1、其实上面首先是利用了子查询,查询出了两个带参数的完全一样的表,利用了SQL2005中带有的一个函数ROW_NUMBER()查询出了相应的行号,使用第二个去跟第一个进行较,若之差大于1则表示此数据前后的两条数据不连续有断号现象,也就实现了我查找丢失流水的信息。
当然,我们在SQL2000中则可以利用Identity(int,1,1)这个函数来实现查询每行流水。
2、由此想到了另外一些有关于子查询的事情也利用这个行号来解决。遇到一个客户的数据库时间跳变太无规率的跳变,只能将大致的时间调整回来。其整个表结构有两个字段Termrecordid和consumedate两个栏位应该是一直递增的,因为时间跳得已经完全没有任何可寻解后,想直接利用现存的时候将时间按照Termrecordid进行一个一个的更新
具体操作法如下:
select *,identity(int,1) as rowindex into #tempp from econsumedata where
deviceid=6 and recordid>111 order by recordid ---将所有异常数据都查询出来,且生成了一列以行号为值的列
go
select recordid,consumedate,rowindex from #tempp ---将两个标志栏位查询出来以及行号
go
update a
set a.consumedate=b.consumedate
from #tempp a inner join #temp1 b on a.rowindex=b.rowdex --利用行号作为联接条件进行更新
go
update a
set a.consumedate=b.consumedate
from econsumedata a inner join #tempp b on a.recordid=b.recordid
where a.deviceid=6 and a.recordid>111 ---更新正式表
drop table #tempp
drop table #temp1

 本篇内容主要讲解“sqlalchemy的常用数据类型怎么使用”,感...
本篇内容主要讲解“sqlalchemy的常用数据类型怎么使用”,感... 今天小编给大家分享一下sqlServer实现分页查询的方式有哪些的...
今天小编给大家分享一下sqlServer实现分页查询的方式有哪些的... 这篇文章主要介绍“sqlmap之osshell怎么使用”,在日常操作中...
这篇文章主要介绍“sqlmap之osshell怎么使用”,在日常操作中... 本篇内容介绍了“SQL注入的知识点有哪些”的有关知识,在实际...
本篇内容介绍了“SQL注入的知识点有哪些”的有关知识,在实际...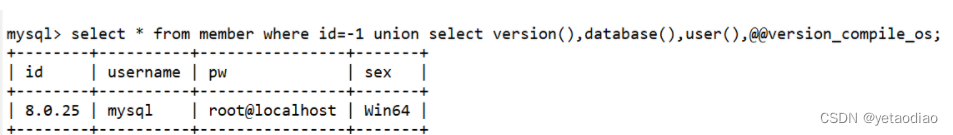 1. mssql权限sa权限:数据库操作,文件管理,命令执行,注册...
1. mssql权限sa权限:数据库操作,文件管理,命令执行,注册... sql执行计划如何查看?在SPL庞大的数据中我们不知道如何查看...
sql执行计划如何查看?在SPL庞大的数据中我们不知道如何查看...