异常的讲解
一、习题的引入
代码
public class Test {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实现一个功能:键盘录入两个数,求商:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第一个数:");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入第二个数:");
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("商:"+num1/num2);
}
}运行结果:

测试过程发现问题
录入的数据应为int类型,但是录入非int类型数据的时候,出异常:

除数为0的时候:

异常:Exception:在程序的运行过程中,发生了不正常的现象,阻止了程序的运行,我们称之为发生异常。
二、通过if-else解决异常
package com.lanson.test01;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Auther: lanson
*/
public class Test {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实现一个功能:键盘录入两个数,求商:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第一个数:");
if(sc.hasNextInt()){
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入第二个数:");
if(sc.hasNextInt()){
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
if(num2 == 0){
System.out.println("对不起,除数不能为0");
}else{
System.out.println("商:"+num1/num2);
}
}else{
System.out.println("对不起,你录入的不是int类型的数据!");
}
}else{
System.out.println("对不起,你录入的不是int类型的数据!");
}
}
}用if-else堵漏洞的缺点:
(1)代码臃肿,业务代码和处理异常的代码混在一起。
(2)可读性差
(3)程序员需要花费大量的经历来维护这个漏洞
(4)程序员很难堵住所有的漏洞。
三、try-catch
【1】基于if-else处理异常缺点太多,所以java中专门出了一个异常处理机制:
“异常三连” try-catch-finally
【2】异常出现了以后怎么看:
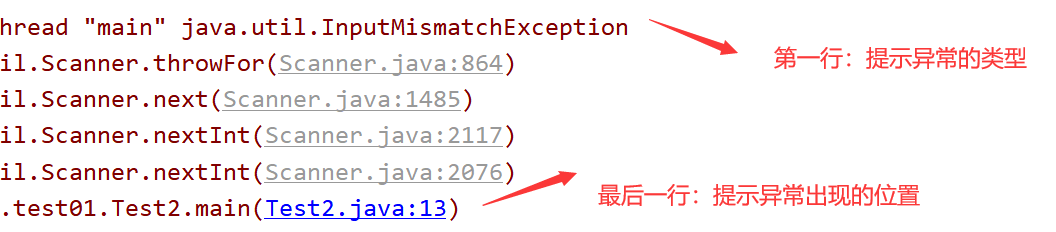
【3】捕获异常: try-catch
对应代码:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实现一个功能:键盘录入两个数,求商:
try{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第一个数:");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入第二个数:");
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("商:"+num1/num2);
}catch(Exception ex){
System.out.println("对不起,程序出现异常!");
}
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器111");
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器222");
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器333");
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器444");
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器555");
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器666");
}
}原理:
把可能出现异常的代码放入try代码块中,然后将异常封装为对象,被catch后面的()中的那个异常对象接收,接收以后:执行catch后面的{}里面的代码,然后try-catch后面的代码,该怎么执行就怎么执行。
详细说一下:
(1)try中没有异常,catch中代码不执行。
(2)try中有异常,catch进行捕获:
如果catch中异常类型和你出的异常类型匹配的话:走catch中的代码--》进行捕获
如果catch中异常类型和你出的异常类型不匹配的话:不走catch中的代码--》没有捕获成功,程序相当于遇到异常了,中断了,后续代码不执行
注意:
(1)try中如果出现异常,然后用catch捕获成功的话,那么try中后续的代码是不会执行的。
(2)如果catch捕获异常成功,那么try-catch后面的代码该执行还是执行没有影响。
四、catch中如何处理异常
package com.lanson.test01;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Auther: lanson
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实现一个功能:键盘录入两个数,求商:
try{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第一个数:");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入第二个数:");
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("商:"+num1/num2);
}catch(Exception ex){
//第一种处理:什么都不写,什么都不做
//第二种处理:输出自定义异常信息
//System.out.println("对不起,你的代码有问题!");
//第三种处理:打印异常信息:
/*(1)调用toString方法,显示异常的类名(全限定路径)*/
/*System.out.println(ex);
System.out.println(ex.toString());*/
/*(2)显示异常描述信息对应的字符串,如果没有就显示null
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());*/
/*(3)显示异常的堆栈信息:将异常信息捕获以后,在控制台将异常的效果给我们展示出来,方便我们查看异常*/
/* ex.printStackTrace();*/
//第四种处理:抛出异常:
throw ex;
}
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器111");
}
}五、try-catch-finally
【1】在什么情况下,try-catch后面的代码不执行?
(1)throw抛出异常的情况
(2)catch中没有正常的进行异常捕获
(3)在try中遇到return
【2】怎么样才可以将 try-catch后面的代码 必须执行?
只要将必须执行的代码放入finally中,那么这个代码无论如何一定执行。
【3】return和finally执行顺序?
先执行finally最后执行return
【4】什么代码会放在finally中呢?
关闭数据库资源,关闭IO流资源,关闭socket资源。
【5】有一句话代码很厉害,它可以让finally中代码不执行!
System.exit(0);//终止当前的虚拟机执行 代码:
package com.lanson;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Auther: lanson
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实现一个功能:键盘录入两个数,求商:
try{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第一个数:");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入第二个数:");
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("商:"+num1/num2);
System.exit(0);//终止当前的虚拟机执行
return;
}catch(ArithmeticException ex){
//throw ex;
}finally {
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器111");
}
}
}六、多重catch
【1】try中出现异常以后,将异常类型跟catch后面的类型依次比较,按照代码的顺序进行比对,执行第一个与异常类型匹配的catch语句
【2】一旦执行其中一条catch语句之后,后面的catch语句就会被忽略了!
【3】在安排catch语句的顺序的时候,一般会将特殊异常放在前面(并列),一般化的异常放在后面。
先写子类异常,再写父类异常。
【4】在JDK1.7以后,异常新处理方式:可以并列用|符号连接:

package com.lanson.test01;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Auther: lanson
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer
//实现一个功能:键盘录入两个数,求商:
try{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第一个数:");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入第二个数:");
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("商:"+num1/num2);
}catch(ArithmeticException ex){
System.out.println("对不起,除数不可以为0");
}catch(InputMismatchException ex){
System.out.println("对不起,你录入的数据不是int类型的数据");
}catch(Exception ex){
System.out.println("对不起,你的程序出现异常");
}finally {
System.out.println("----谢谢你使用计算器111");
}
}
}七、异常的分类
【1】层次结构:

注意:程序中语法错误,逻辑错误 都不属于上面的Error,Exception
【2】运行时异常:
public class Test5 {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//运行时异常:
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(arr.length);
/*int[] arr2 = null;
System.out.println(arr2.length);*/
System.out.println(arr[10]);
}
}【3】检查异常:
处理方式1:try-catch嵌套try-catch
public class Test6 {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//检查异常:
try {
try {
Class.forName("com.lanson.test01.Test").newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}处理方式2:多重catch
public class Test6 {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//检查异常:
try {
Class.forName("com.lanson.test01.Test").newInstance();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}处理方式3:throws
public class Test6 {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
//检查异常:
Class.forName("com.lanson.test01.Test").newInstance();
}
}throw和throws的区别
package com.lanson.test01;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Auther: lanson
*/
public class Test7 {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//实现一个功能:两个数相除,当除数为0的时候,程序出现异常。
/*try {
devide();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
devide();
}
public static void devide() throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第一个数:");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入第二个数:");
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
if(num2 == 0 ){//除数为0 ,制造异常。
//制造运行时异常:
/*throw new RuntimeException();*/
//制造检查异常:
/*try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
throw new Exception();
}else{
System.out.println("商:"+num1/num2);
}
}
}总结:
throw和throws的区别:
(1)位置不同:
throw:方法内部
throws: 方法的签名处,方法的声明处
(2)内容不同:
throw+异常对象(检查异常,运行时异常)
throws+异常的类型(可以多个类型,用,拼接)
(3)作用不同:
throw:异常出现的源头,制造异常。
throws:在方法的声明处,告诉方法的调用者,这个方法中可能会出现我声明的这些异常。然后调用者对这个异常进行处理:
要么自己处理要么再继续向外抛出异常
练习:
package com.lanson.test02;
/**
* @Auther: lanson
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) throws Exception {
if(sex.equals("男")||sex.equals("女")){
this.sex = sex;
}else{//非男非女
//解决办法1:
/*this.sex = "男";*/
//解决办法2:给个友好型提示,但是打印结果为默认的null效果
/*System.out.println("对不起,你的性别错误了");*/
//解决办法3:
//制造运行时异常:
/*throw new RuntimeException("性别不对!");*/
//制造检查异常
/*try {
throw new Exception();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}*/
throw new Exception();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
//this.sex = sex;
try {
this.setSex(sex);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}package com.lanson.test02;
/**
* @Auther: lanson
*/
public class Test {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个Student的对象:
/*Student s = new Student();
s.setName("菲菲");
s.setAge(19);
try {
s.setSex("asdfasdfasdf");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(s);*/
Student s2 = new Student("娜娜",21,"asdfasdfasdf");
System.out.println(s2);
}
}八、重载和重写的异常
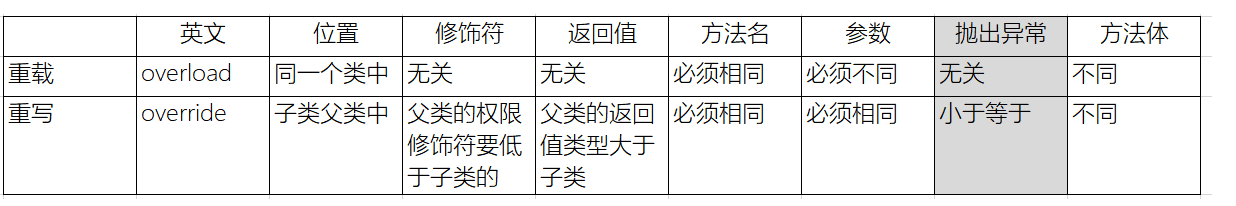
【1】重载:
public class Demo {
public void a() throws Exception{
}
public void a(int age) throws ArithmeticException{
}
}【2】重写:


子类 <= 父类
九、自定义异常
自定义的异常可以继承:运行时异常
public class MyException extends RuntimeException {
static final long serialVersionUID = -70348971907L;
public MyException(){
}
public MyException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}也可以继承检查异常:
public class MyException extends Exception {
static final long serialVersionUID = -70348971907L;
public MyException(){
}
public MyException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}如果继承的是运行时异常,那么在使用的时候无需额外处理
如果继承的是检查异常,那么使用的时候需要try-catch捕获或者throws向上抛
