第五章 Lua学习笔记之函数
函数有两个用途
1. 完成指定功能,函数作为调用语句使用
2. 计算并返回值,函数作为赋值语句的表达式使用
function unpack(t,i)
i = i or 1
if t[i] then
return t[i],unpack(t,i + 1)
end
Lua 中的函数和 Javascript 中的有些相似,函数在书写的时候,前面都需要加上 function 这个关键字, 上篇文章中提过 function 这个关键字,他在 Lua 中也是一种类型。下面我们来看看 Lua 中的一个简单函数是怎么写的。
- function printHello(a,b) --a,b为参数
- print(a,b);
- print("Hello")
- end
在上面的一段函数中,函数的开头需要function 关键字来修饰它,表明它是一个“函数类型” ,当然既然成为“类型” 我们在程序中也可以这样写:
- testFuction=function (a,b) return a+b end
- --testFuction就相当于这个函数的函数名了
所以说,Lua 的函数是很灵活的。
在C/C++中我们总是用"{ }" 来括起一个函数,但是Lua中有所不同,大家也注意到了上边的代码,最后跟随着一个 "end" ,这个 end 就是来表明一个函数的结尾的。好了对于Lua中函数的初步认识就到这里,更深入的我们要留在以后实践中来体会。
lua函数接受可变参数,lua讲函数的参数放在一个叫arg的表中,除了参数之外,表中还有一个域n表示参数个数
function g(a,b,…)end
g(3) a = 3,b = nil,arg = {n = 0}
g(3,4) a = 3,b = 4,arg = {n=0}
如果只想要string.find返回的第二个值:
一个典型的方法是使用虚变量(下划线)
s = "12345678"
p = "3456"
local _,x = string.find(s,p)
print(x)
命名参数
Lua的函数参数和位置相互关联,调用时实参安顺序依次传给形参。
有时候用名字指定参数是很有用的。
比如用rename函数给一个文件重新命名,有时候我们记不得命名前后两个参数的顺序了
Return os.rename(arg.old,arg.new)
Rename{old = “temp.lua”,new=”temp1.lua”}
当函数参数很多时,这样处理就比较方便,简单。例如窗口创建函数;
w = Window {
x = 0,y = 0,width = 300,height = 200,
title = "lua",background = "blue",43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> border = true
}
function Window(options)
if type(options.title) ~= "string" then
error("no title")
elseif type(options.width) ~= "number" then
error("no width")
elseif type(options.height) ~= "number" then
error("no height")
_Window(options.title,43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> options.x or 0,43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> options.y or 0,43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> options.width,options.height,43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> options.background or "white",43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> options.border
)
End
第六章再论函数
Lua中的函数有以下两个特点:
1. lua中的函数和其他变量(string,number) 一样,可以赋值,可以放在变量中,可以放在表中。可以作为函数参数,可以作为函数返回值。
2. 被嵌套的内部函数可以访问他外面的数据成员
3. Lua函数可以是匿名的,当我们提到函数名(比如print),其实是print这个变量指向打印输出这个函数,当然,打印输出函数也可以由其他变量指向。例如:
a = { p = print}
a.p("hello world")
print = math.sin
a.p(print(1))
sin = a.p
sin(10,20)
没错,函数就是变量,就是值。
function foo(x)
return 2*x
foo = function (x)
return 2*x end
函数定义就是把function这个值赋值给foo这个变量。
我们使用function(x)…end 创建函数和 {}创建表是一个道理。
Table标准库有一个排序函数,接受一个表作为参数对标中的元素进行排序。
这个函数必须对不同类型的元素进行升降排序,Lua不是尽可能多的传入参数解决这种问题,而是接受一个排序函数作为参数,(类似c++的函数指针)排序函数作为输入参数,并且返回两个参数比较后的大小关系(用c++可以实现这个万能的排序算法)
例如:
name = { "peter","paul","mary"}
grades = { mary = 10,paul = 7,peter = 13 }
table.sort(name,function (n1,n2) return grades[n1] > grades[n2] end )
在lua中,其他函数作为函数的参数,成这个函数为高级函数,没有什么特殊的地方。
function sortbygrade (name,grades)
table.sort(name,n2) return grades[n1] > grades[n2] end)
闭包
包含在sortbygrade中的sort的参数匿名function 可以访问sortbygrade的grades在匿名function 内部grades既不是全局变量,也不是局部变量。他别称为外部的局部变量或upvalue
function newCounter()
local i = 0
return function ()
i = i + 1
return i
end
ca = newCounter()
cb = newCounter()
print(ca())
print(cb())
匿名函数使用upvalue i保存他的计数
当我们调用匿名函数的时候I已经超出了他的适用范围,因为创建i的函数newCounter已经返回了。简单滴说闭包是一个函数加上他可以正确访问的upvalues,如果我们再次调用newCOunter,将创建一个新的局部变量i
因此我们得到了一个作用在新建的i上的新闭包。
技术上讲,闭包是值而不是函数。函数仅仅是闭包的一个原形声明;我们继续使用术语函数代替闭包。
闭包的功能:
作为高级函数的参数。
作为函数嵌套的函数。
作为回调函数。
创建沙箱。
do
local oldOpen = io.open
io.open = function (filename,mode)
if access_OK(filename,mode) then
return oldOpen(filename.mode)
else
return nil,"access denied"
end
非全局函数
Lua中函数分为全局和非全局
大部分作为table的域(math.sin io.read)
--1.表和函数在一起
Lib = {}
Lib.foo = function (x,y) return x + y end
Lib.goo = function (x,y) return x - y end
--2.使用表构造函数
Lib = {
foo = function (x,y) return x + y end,43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> goo = function (x,43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> --3.Lua提供另一种语法方式
function Lib.foo (x,y)
return x + y
function Lib.go0 (x,43); font-family:Arial; font-size:14px; line-height:26px"> return x - y
当我们把函数赋值给局部变量时,函数成了局部的,就是说局部函数像局部变量一样在一定范围内有效。声明局部函数的方式:
Local f = function(…)
…
Local function f (…)
….
需要注意声明递归局部函数
Local face—声明和定义必须分开
face = function(n)
If(n==1)
Return 1
Else
Return n*face(n-1)
尾调用:
如果函数最后一句执行的是函数调用,我们称这种调用为尾调用
Function f(x)
Return g(x)
--g(x)即为尾调用
例子中f调用g之后不会做任何事情
这时候,g不需要返回到f,所以尾调用之后,栈不保存f的任何信息。
由于尾调用不需要栈空间,所以尾调用递归可以无限次进行
Function foo(n)
If(n>0)then
Return foo(n-1)
需要注意:为调用之后确实不做什么事,不做什么事的调用不一定是尾巴调用
G(x)
R
return
--不是尾调用
下面的例子也不是尾调用
Return g(x)+1
Return(g(x))
Return x or g(x)
以上表达式的最后一步计算的不是g(x)本身,所以不是尾函数
- local function languageTest()
- -- table test
- local names = {"Peter", "Paul",54); background-color:inherit">"Mary"}
- local grades = {Mary=10, Paul=7, Peter=8}
- table.sort(names, function(n1, n2)
- return grades[n1] > grades[n2]
- end)
- for i=1, #names do
- print(names[i])
- end
- -- function test
- local function newCounter(name)
- local i = 0
- return function()
- i = i+1
- name .. ":" .. i
- end
- end
- local c1 = newCounter("c1")
- local c2 = newCounter("c2")
- print(c1())
- print(c1())
- print(c2())
- print(c1())
- print(c2())
- -- for test
- function values(t)
- local i = 0;
- function() i=i+1; return t[i] for elm in values(names) do
- print(elm)
- -- -- for test2
- -- for k in pairs(names) do
- -- print(k)
- -- end
- function tableTest()
- Set = {}
- local mt = {}
- -- create a new set with teh values of the given list
- Set.new = function(l)
- set = {}
- setmetatable(set, mt)
- for _, v in ipairs(l) do set[v] = true set;
- Set.union = function(a, b)
- if getmetatable(a) ~= mt or getmetatable(b) ~= mt then
- error("attempt to 'add' a set with a non-set value", 2);
- end
- local res = Set.new {}
- for k in pairs(a) do res[k] = in pairs(b) do res[k] = return res
- Set.intersection = Set.new {}
- in pairs(a) do
- res[k] = b[k]
- Set.tostring = function(set)
- local l = {}
- for e in pairs(set) do
- l[#l+1] = e
- return "{" .. table.concat(l,54); background-color:inherit">", ") .. "}"
- Set.print = function(s)
- print(Set.tostring(s))
- mt.__add = union
- mt.__mul = Set.intersection
- mt.__tostring = Set.tostring
- mt.__le = if not b[k] then false true
- mt.__lt = return a<=b and not (b<=a)
- end
- mt.__eq = and b<=a
- local s1 = Set.new {10, 20, 30, 50}
- local s2 = Set.new {30, 1}
- local s3 = s1+s2+s2
- -- local s3 = s1+s2+s2 + 8
- Set.print(s3)
- Set.print((s1+s2)*s1)
- s1 = Set.new{2, 4}
- s2 = Set.new{4, 10, 2}
- print(s1<=s2)
- print(s1<s2)
- print(s1>=s2)
- print(s1>s2)
- print(s1==s2*s1)
- print(s1)
- -- mt.__metatable = "not your business"
- -- print(getmetatable(s1))
- -- setmetatable(s1, {})
- local Window = {} -- create a namespace
- --create teh prototype with default values.
- Window.prototype = {x=0, y=0, width=100, height=100}
- Window.mt = {} -- create a metatable
- --declare the constructor function
- function Window.new(o)
- setmetatable(o, Window.mt)
- return o
- end
- Window.mt.__index = table,255); font-weight:bold; background-color:inherit">key)
- return Window.prototype[key]
- -- Window.mt.__index = Window.prototype
- w = Window.new {x=10, y=20}
- print(w.x)
- -- Tables with default values
- function setDefault(t, d)
- local mt = {__index = function() return d end}
- setmetatable(t, mt)
- local tab = {x=10, y=20}
- print(tab.x, tab.z)
- setDefault(tab, 0)
- print(tab.x,255); font-weight:bold; background-color:inherit">function(t) return t.___ end }
- t.___ = d
- -- Tracking table accesses
- local t = {} -- original table (created somewhere)
- -- keep a private access to the original table
- local _t = t
- -- create proxy
- t = {}
- -- create metatable
- local mt = {
- __index = function(t, k)
- print("*access to element " .. tostring(k))
- return _t[k]
- end,
- __newindex = print("*update of element " .. tostring(k) .. " to " .. tostring(v))
- _t[k] = v -- update original table
- }
- setmetatable(t, mt)
- t[2] = "hello"
- print(t[2])
- -- Read-only tables
- function readOnly(t)
- local proxy = {}
- local mt = {
- __index = t,
- __newindex = error("attempt to update a read-only table", 2)
- end
- }
- setmetatable(proxy,255); font-weight:bold; background-color:inherit">return proxy
- end
- days = readOnly {"Sunday",54); background-color:inherit">"Monday",54); background-color:inherit">"Tuesday",54); background-color:inherit">"Wednesday",54); background-color:inherit">"Thursday",54); background-color:inherit">"Friday",54); background-color:inherit">"Saturday"}
- print(days[1])
- -- days[2] = "Noday"
- end
- function objectTest()
- local Account = {
- balance = 0,
- new = function(self, o)
- o = o or {} -- create table is user does not provide one
- setmetatable(o, self)
- self.__index = self
- withdraw = if v>self.balance then error"insufficient funds" end
- self.balance = self.balance - v
- deposit = self.balance = self.balance + v
- }
- local a = Account:new {balance = 0}
- a:deposit(100.00)
- print(a.balance)
- local b = Account:new()
- print(b.balance)
- b.balance = 123
- print(b.balance)
- b:withdraw(100)
- print(b.balance)
- print(a.balance)
- -- inheritance
- local SpecialAccount = Account:new({
- withdraw = if v - self.balance >= self:getLimit() then
- error"insufficient funds"
- self.balance = self.balance - v
- getLimit = function(self)
- return self.limit or 0
- end
- })
- local s = SpecialAccount:new {limit=1000.00}
- s:deposit(100.00)
- s:withdraw(200.00)
- print("s:", s.balance)
- function main()
- languageTest();
- tableTest();
- objectTest();
- end
- main()
- -- table test
- local names = {"Peter",54); background-color:inherit">"Paul",54); background-color:inherit">"Mary"}
- local grades = {Mary=10, Peter=8}
- table.sort(names,255); font-weight:bold; background-color:inherit">function(n1, n2)
- return grades[n1] > grades[n2]
- end)
- for i=1, #names do
- print(names[i])
- end
- -- function test
- function newCounter(name)
- local i = 0
- return function()
- i = i+1
- name .. ":" .. i
- end
- end
- local c1 = newCounter("c1")
- local c2 = newCounter("c2")
- -- for test
- function values(t)
- local i = 0;
- function() i=i+1; return t[i] for elm in values(names) do
- print(elm)
- -- -- for test2
- -- for k in pairs(names) do
- -- print(k)
- -- end
- function tableTest()
- Set = {}
- local mt = {}
- -- create a new set with teh values of the given list
- Set.new = function(l)
- set = {}
- setmetatable(set, mt)
- for _,153); background-color:inherit">in ipairs(l) do set[v] = true set;
- Set.union = function(a, b)
- if getmetatable(a) ~= mt or getmetatable(b) ~= mt then
- error("attempt to 'add' a set with a non-set value", 2);
- end
- local res = Set.new {}
- for k in pairs(a) do res[k] = in pairs(b) do res[k] = return res
- Set.intersection = Set.new {}
- in pairs(a) do
- res[k] = b[k]
- Set.tostring = function(set)
- local l = {}
- for e in pairs(set) do
- l[#l+1] = e
- return "{" .. table.concat(l, ") .. "}"
- Set.print = function(s)
- print(Set.tostring(s))
- mt.__add = union
- mt.__mul = Set.intersection
- mt.__tostring = Set.tostring
- mt.__le = if not b[k] then false true
- mt.__lt = return a<=b and not (b<=a)
- end
- mt.__eq = and b<=a
- local s1 = Set.new {10, 50}
- local s2 = Set.new {30, 1}
- local s3 = s1+s2+s2
- -- local s3 = s1+s2+s2 + 8
- Set.print(s3)
- Set.print((s1+s2)*s1)
- s1 = Set.new{2, 4}
- s2 = Set.new{4, 2}
- print(s1<=s2)
- -- mt.__metatable = "not your business"
- -- print(getmetatable(s1))
- local Window = {} -- create a namespace
- --create teh prototype with default values.
- Window.mt = {} -- create a metatable
- --declare the constructor function
- function Window.new(o)
- return o
- end
- Window.mt.__index = table,255); font-weight:bold; background-color:inherit">key)
- return Window.prototype[key]
- -- Window.mt.__index = Window.prototype
- w = Window.new {x=10,119); background-color:inherit">-- Tables with default values
- function setDefault(t, d)
- local mt = {__index = function() return d end}
- local tab = {x=10, y=20}
- print(tab.x,255); font-weight:bold; background-color:inherit">function(t) return t.___ end }
- t.___ = d
- -- Tracking table accesses
- local t = {} -- original table (created somewhere)
- -- keep a private access to the original table
- local _t = t
- -- create proxy
- t = {}
- -- create metatable
- local mt = {
- __index = function(t, k)
- print("*access to element " .. tostring(k))
- return _t[k]
- end,
- __newindex = print("*update of element " .. tostring(k) .. " to " .. tostring(v))
- _t[k] = v -- update original table
- t[2] = "hello"
- print(t[2])
- -- Read-only tables
- function readOnly(t)
- local proxy = {}
- local mt = {
- __index = t,248)"> __newindex = error("attempt to update a read-only table", 2)
- end
- }
- return proxy
- end
- days = readOnly {"Sunday",54); background-color:inherit">"Monday",54); background-color:inherit">"Tuesday",54); background-color:inherit">"Wednesday",54); background-color:inherit">"Thursday",54); background-color:inherit">"Friday",54); background-color:inherit">"Saturday"}
- print(days[1])
- -- days[2] = "Noday"
- end
- function objectTest()
- local Account = {
- new = function(self, o)
- o = o or {} -- create table is user does not provide one
- setmetatable(o,248)"> self.__index = self
- withdraw = if v>self.balance then error"insufficient funds" end
- self.balance = self.balance - v
- deposit = self.balance = self.balance + v
- local a = Account:new {balance = 0}
- a:deposit(100.00)
- print(a.balance)
- local b = Account:new()
- -- inheritance
- local SpecialAccount = Account:new({
- withdraw = if v - self.balance >= self:getLimit() then
- error"insufficient funds"
- self.balance = self.balance - v
- getLimit = function(self)
- return self.limit or 0
- end
- })
- local s = SpecialAccount:new {limit=1000.00}
- print("s:", s.balance)
- function main()
- languageTest();
- end
- main()

 1.github代码实践源代码是lua脚本语言,下载th之后运行thmai...
1.github代码实践源代码是lua脚本语言,下载th之后运行thmai... 此文为搬运帖,原帖地址https://www.cnblogs.com/zwywilliam/...
此文为搬运帖,原帖地址https://www.cnblogs.com/zwywilliam/... Rime输入法通过定义lua文件,可以实现获取当前时间日期的功能...
Rime输入法通过定义lua文件,可以实现获取当前时间日期的功能...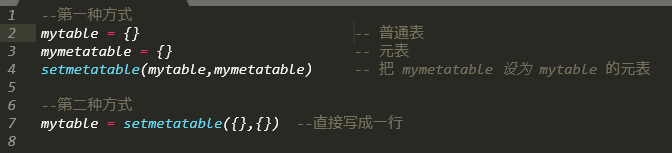 在Lua中的table(表),就像c#中的HashMap(哈希表),key和...
在Lua中的table(表),就像c#中的HashMap(哈希表),key和...