我试着证实我的怀疑:
grub> find /grub/stage1 find /grub/stage1 (hd0,0)
所以我将设备地图更新为:
(fd0) /dev/fd0 (hd0) /dev/sda (hd1) /dev/sdb
(注意(hd1)条目是我添加的
所以我试着在/ dev / sdb上安装grub
我得到:
grub> root (hd1,0) root (hd1,0) Filesystem type is ext2fs,partition type 0x83 grub> setup (hd1) setup (hd1) Checking if "/boot/grub/stage1" exists... no Checking if "/grub/stage1" exists... no Error 15t: File not found
所以我做了一些谷歌搜索(可悲的谷歌刚刚做了一个很好的工作,并拿起100个grub安装示例,这在这里没有帮助)
在找到一些线索后我尝试了:
# grub-install --recheck /dev/sdb Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time. Installation finished. No error reported. This is the contents of the device map /boot/grub/device.map. Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'. (fd0) /dev/fd0 (hd0) /dev/sda (hd1) /dev/sdb # grub-install /dev/sdb Installation finished. No error reported. This is the contents of the device map /boot/grub/device.map. Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'. (fd0) /dev/fd0 (hd0) /dev/sda (hd1) /dev/sdb
哪种建议grub现在也安装在/ dev / sdb上,但是如果再看看我仍然会得到:
grub> find /grub/stage1 find /grub/stage1 (hd0,0)
2个驱动器的分开输出:
SDA
Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 500MB 500MB ext3 1 boot 2 500MB 81.0GB 80.5GB 2 raid 3 81.0GB 85.0GB 4000MB 3 raid 4 85.0GB 3001GB 2916GB 4 raid
SDB
Partition Table: gpt Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 17.4kB 500MB 500MB ext3 1 2 500MB 81.0GB 80.5GB 2 raid 3 81.0GB 85.0GB 4000MB 3 raid 4 85.0GB 3001GB 2916GB 4 raid
和mdadm mdstat:
Personalities : [raid1]
md1 : active raid1 sdb3[1] sda3[0]
3905218 blocks super 1.1 [2/2] [UU]
md2 : active raid1 sdb4[1] sda4[0]
2847257598 blocks super 1.1 [2/2] [UU]
md0 : active raid1 sda2[0] sdb2[1]
78612189 blocks super 1.1 [2/2] [UU]
有没有人能够对这种情况有所了解,感觉就像我现在99%那样并且遗漏了一些明显的东西.
谢谢.
编辑更新:
# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/md0 74G 18G 53G 25% / tmpfs 580M 0 580M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 462M 98M 341M 23% /boot xenstore 580M 64K 580M 1% /var/lib/xenstored
/在md0上,它由sda2和sdb2组成
swap是md1,即sda3和sdb3
md2是LVM
但是/ boot仅在/ sda1上
我想这就是问题所在,决议是创建md4并让它包含sda1和sdb1
也许我的东西在我的头脑中有点混乱,但我认为grub没有安装在分区上,而是驱动器的前几个块,即sda或hd0 / 1
任何澄清和建议表示赞赏.
解决方法
root (hd1,partition type 0x83
采取以下步骤:
>在/ dev / sda1和/ dev / sdb1上创建2 / boot分区 – 键入fd(Linux自动检测raid) – 使用您喜欢的工具(fdisk,cfdisk,gparted,…)(GPD为fd00)
>记得打开两个分区sda1和sdb1上的可引导标志(不适用于GPT)
>强制磁盘成为全新的raid:
mdadm --zero-superblock /dev/sda1 mdadm --zero-superblock /dev/sdb1
>创建将成为/ boot分区的raid元数据时,请使用0.9版. Linux无法自动检测更新的版本(没有ramdisk).
mdadm --create /dev/md0 --level=1 --raid-disks=2 /dev/sda1 /dev/sdb1 --metadata=0.9
>使用ext2或ext3格式化
>安装您选择的Linux,不要形成/ boot
你的发行版首次启动后:
>修复/ etc / fstab指向/启动到/ dev / md0(可能没有必要)
>在2个磁盘MBR上安装grub
# grub /dev/sda grub> root (hd0,0) grub> setup (hd0) grub> quit quit # grub /dev/sdb grub> root (hd1,0) grub> setup (hd1) grub> quit quit
>编辑引导程序(对Grub1的说明)
>搜索“默认”行并在下面添加“后备”选项
vi /boot/grub/menu.lst default 0 fallback 1
>在引导加载程序中添加另一个条目(再次,在我的情况下,我选择了grub1,因为它不那么复杂,并且它足以满足我的需要),其中一个指向作为raid成员的不同引导分区:
title Debian GNU/Linux,kernel 2.6.32-5-686 (default) root (hd0,0) kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-5-686 root=/dev/mapper/vg-root ro quiet initrd /initrd.img-2.6.32-5-686 title Debian GNU/Linux,kernel 2.6.32-5-686 (fallback) root (hd1,0) kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-5-686 root=/dev/mapper/vg-root ro quiet initrd /initrd.img-2.6.32-5-686
>请注意,我的/ md raid上有一个LVM层.
完成.这应该足以让你拥有一个“冗余”的引导加载程序.

 linux常用进程通信方式包括管道(pipe)、有名管道(FIFO)、...
linux常用进程通信方式包括管道(pipe)、有名管道(FIFO)、... Linux性能观测工具按类别可分为系统级别和进程级别,系统级别...
Linux性能观测工具按类别可分为系统级别和进程级别,系统级别...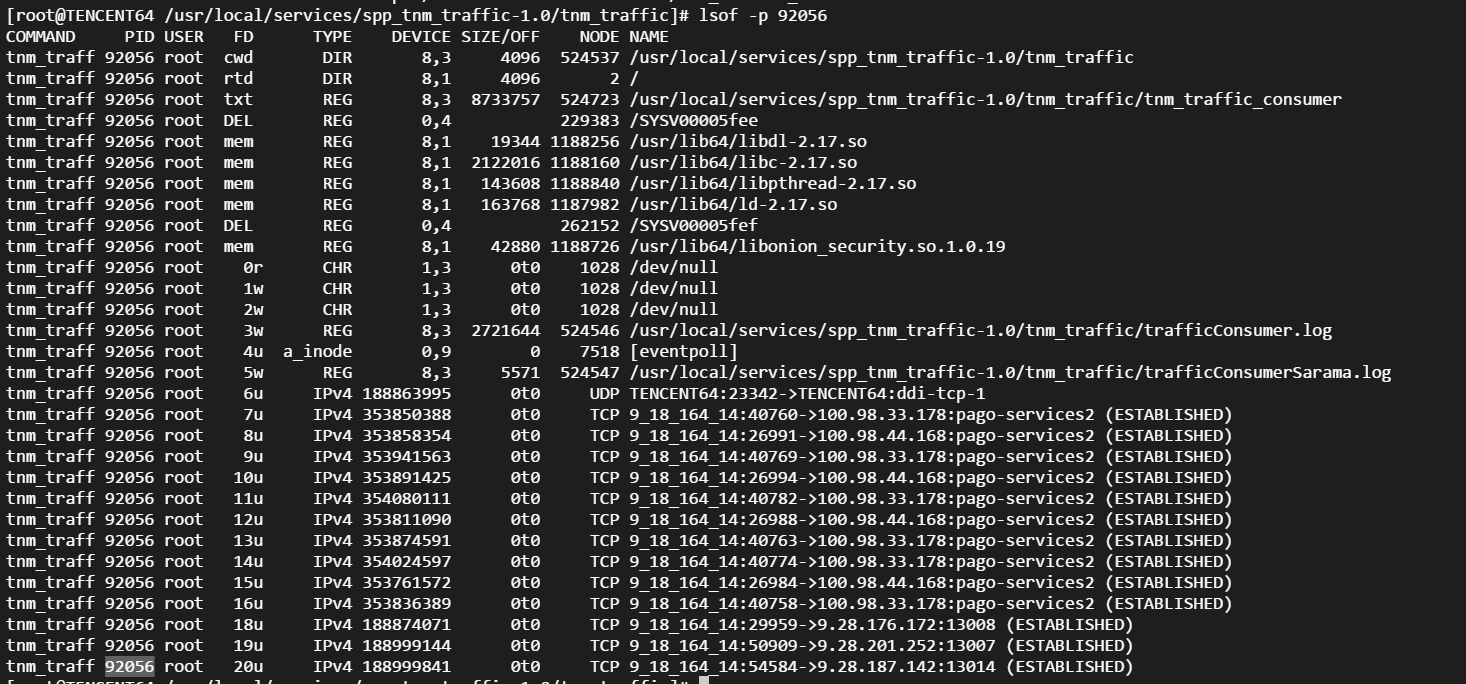 本文包含作者工作中常用到的一些命令,用于诊断网络、磁盘占满...
本文包含作者工作中常用到的一些命令,用于诊断网络、磁盘占满... linux的平均负载表示运行态和就绪态及不可中断状态(正在io)的...
linux的平均负载表示运行态和就绪态及不可中断状态(正在io)的... CPU上下文频繁切换会导致系统性能下降,切换分为进程切换、线...
CPU上下文频繁切换会导致系统性能下降,切换分为进程切换、线...