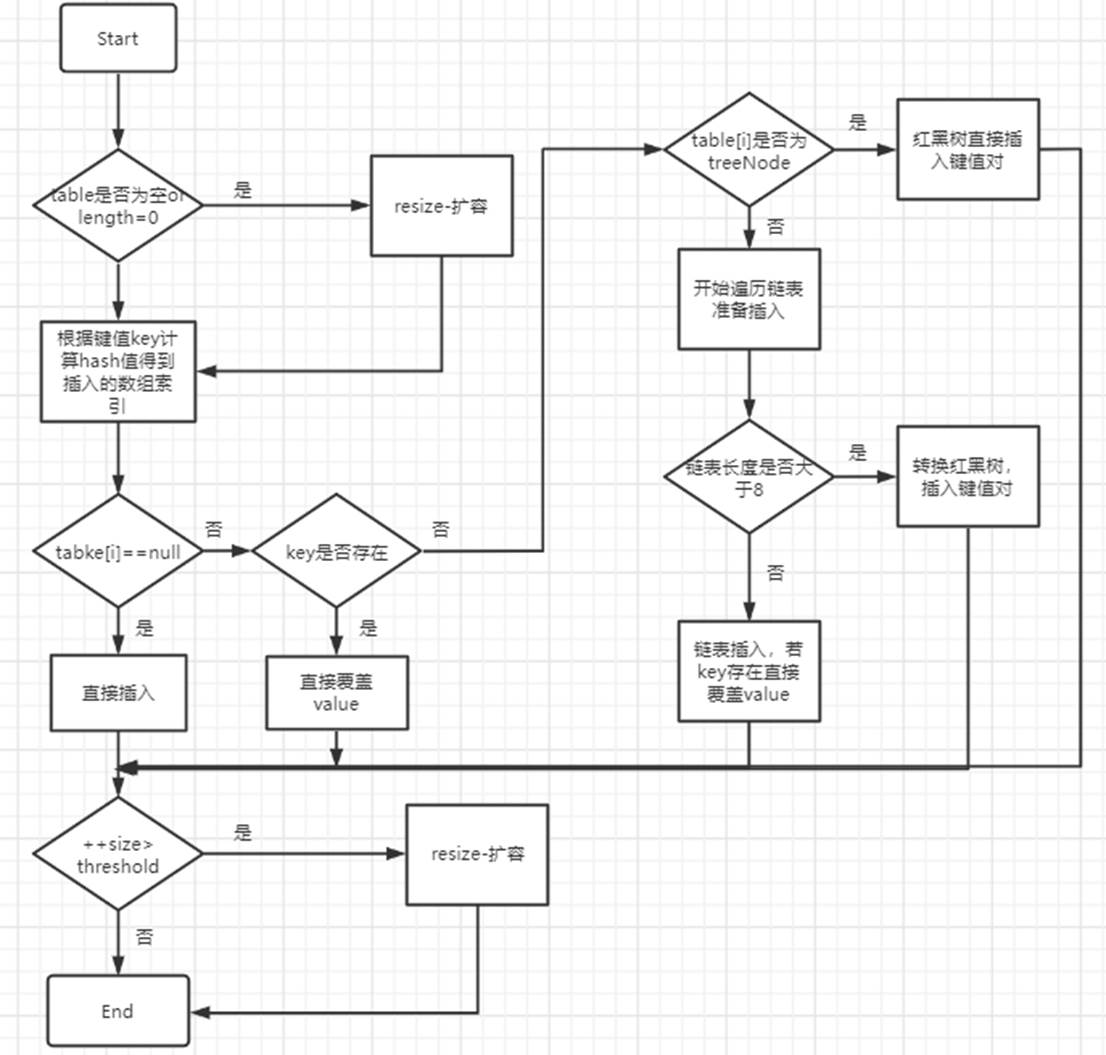
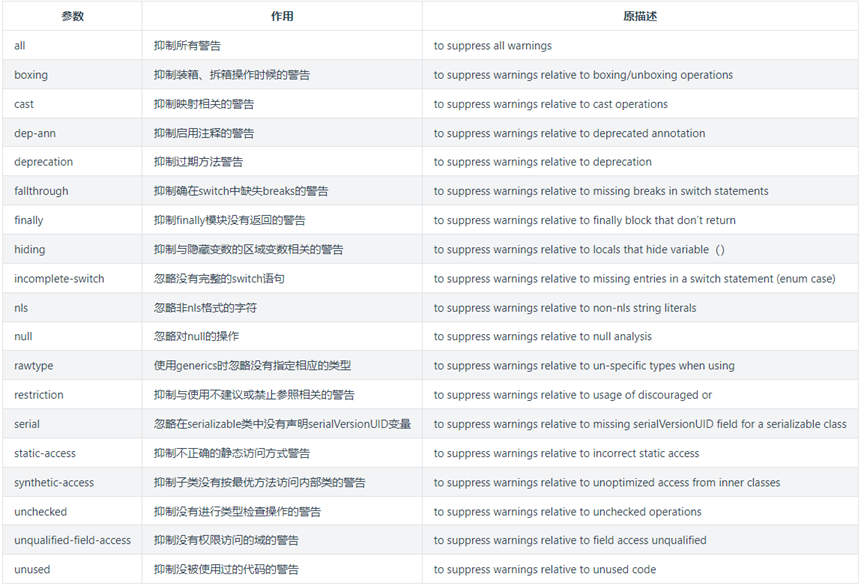
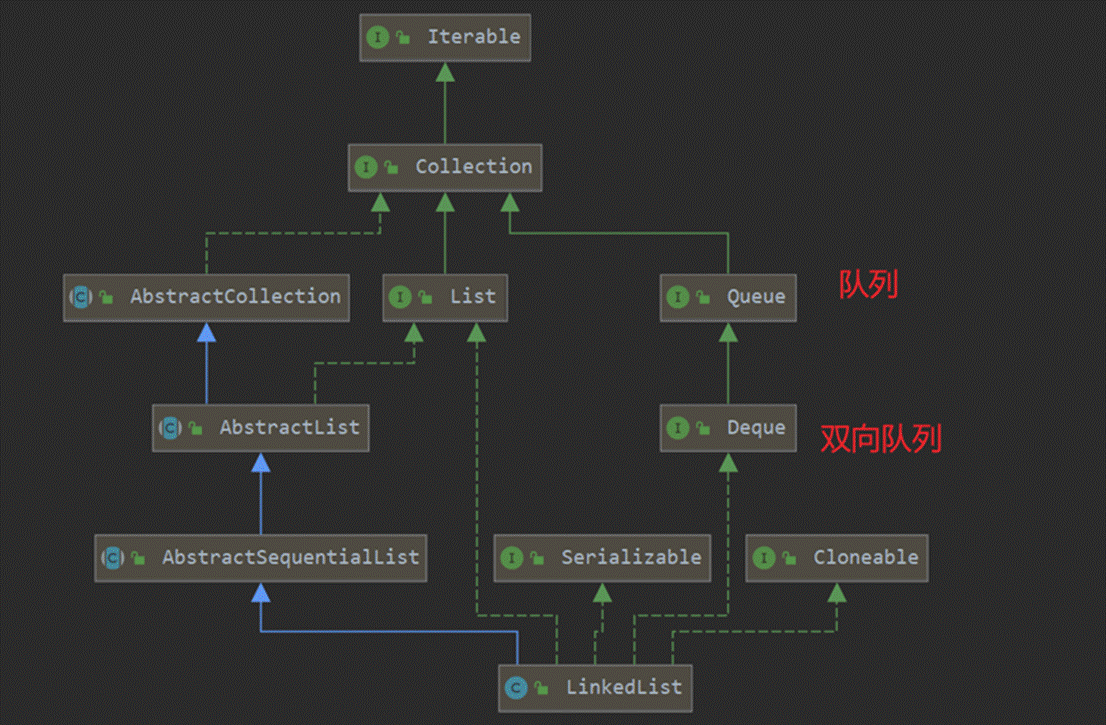
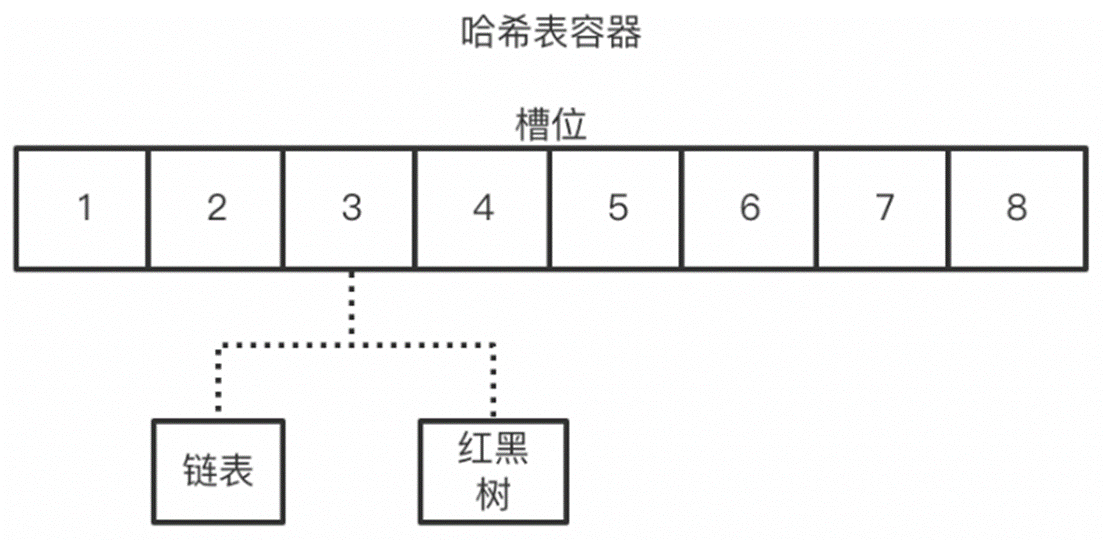
/** * Generates a "pre-ordered" list of the nodes contained in this object's subtree * Note: This is counterclockwise pre-order traversal * * @param clockwise set to true for clockwise traversal and false for counterclockwise traversal * * @return Iterator<Tree> list iterator */ public Iterator<Tree> PreOrder(boolean clockwise) { LinkedList<Tree> list = new LinkedList<Tree>(); if(!clockwise) PreOCC(this,list); else PreO(this,list); count = 0; return list.iterator(); } private void PreOCC(Tree rt,LinkedList<Tree> list) { list.add(rt); rt.setVirtual_y(count); count++; Iterator<Tree> ci = rt.ChildrenIterator(); while(ci.hasNext()) PreOCC(ci.next(),list); } private void PreO(Tree rt,LinkedList<Tree> list,int count) { list.add(rt); rt.setX_vcoordinate(count); Iterator<Tree> ci = rt.ReverseChildrenIterator(); while(ci.hasNext()) PreO(ci.next(),list,++count); }
Tree root = new Tree(new Integer(0)); root.addChild(new Tree(new Integer(1),root)); root.addChild(new Tree(new Integer(2),root)); root.addChild(new Tree(new Integer(3),root)); Iterator<Tree> ci = root.ChildrenIterator(); ci.next(); Tree select = ci.next(); select.addChild(new Tree(new Integer(4),select)); select.addChild(new Tree(new Integer(5),select));
当我打印遍历节点的顺序以及它分配给相应节点的坐标时,这是我的输出.
0 3 2 5 4 1
0 1 2 3 4 3
0 1 2 4 5 3
0 1 2 3 4 3
注意:前两行是顺时针预先遍历遍历和x坐标的分配.接下来的两行是逆时针预先遍历遍历并分配它们的y坐标.
我的问题是如何让第二行阅读:
0 1 2 3 4 5
编辑1:这是我用来打印我访问节点的顺序和我指定的坐标的代码.
Iterator<Tree> pre = root.PreOrder(true); System.out.println(" \t"); while(pre.hasNext()) System.out.print(pre.next() + "\t"); pre = root.PreOrder(true); System.out.println(); System.out.println("x-coordinates:\t"); while(pre.hasNext()) System.out.print(pre.next().getVirtual_x() + "\t"); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); Iterator<Tree> preCC = root.PreOrder(false); System.out.println(" \t"); while(preCC.hasNext()) System.out.print(preCC.next() + "\t"); preCC = root.PreOrder(false); System.out.println(); System.out.println("x-coordinates:\t"); while(preCC.hasNext()) System.out.print(preCC.next().getVirtual_y() + "\t");
这里还有一个引用,以更好地解释x,y坐标.
顶点.顶点的y坐标.
Compute the counterclockwise
pre-ordering of the vertices of T (the
ordering are numbered from 0 to n −
1),use them as the x-coordinates for
the vertices.Compute the clockwise pre-ordering of
the vertices of T (the ordering are
numbered from 0 to n − 1),use them as
the y-coordinates for the vertices.
解决方法
来自James Gosling的“Java编程语言”:
“…There is exactly one parameter
passing mode in Java – pass by value –
and that keeps things simple. ..”
我认为这是对此的最终权威.
I realize this is a hotly debated,controversial topic for Java programmers
不,没有辩论.詹姆斯·戈斯林(James Gosling)从一开始就将这种语言融入到语言中.如果你认为这是有争议的,你会被遗憾或无知.