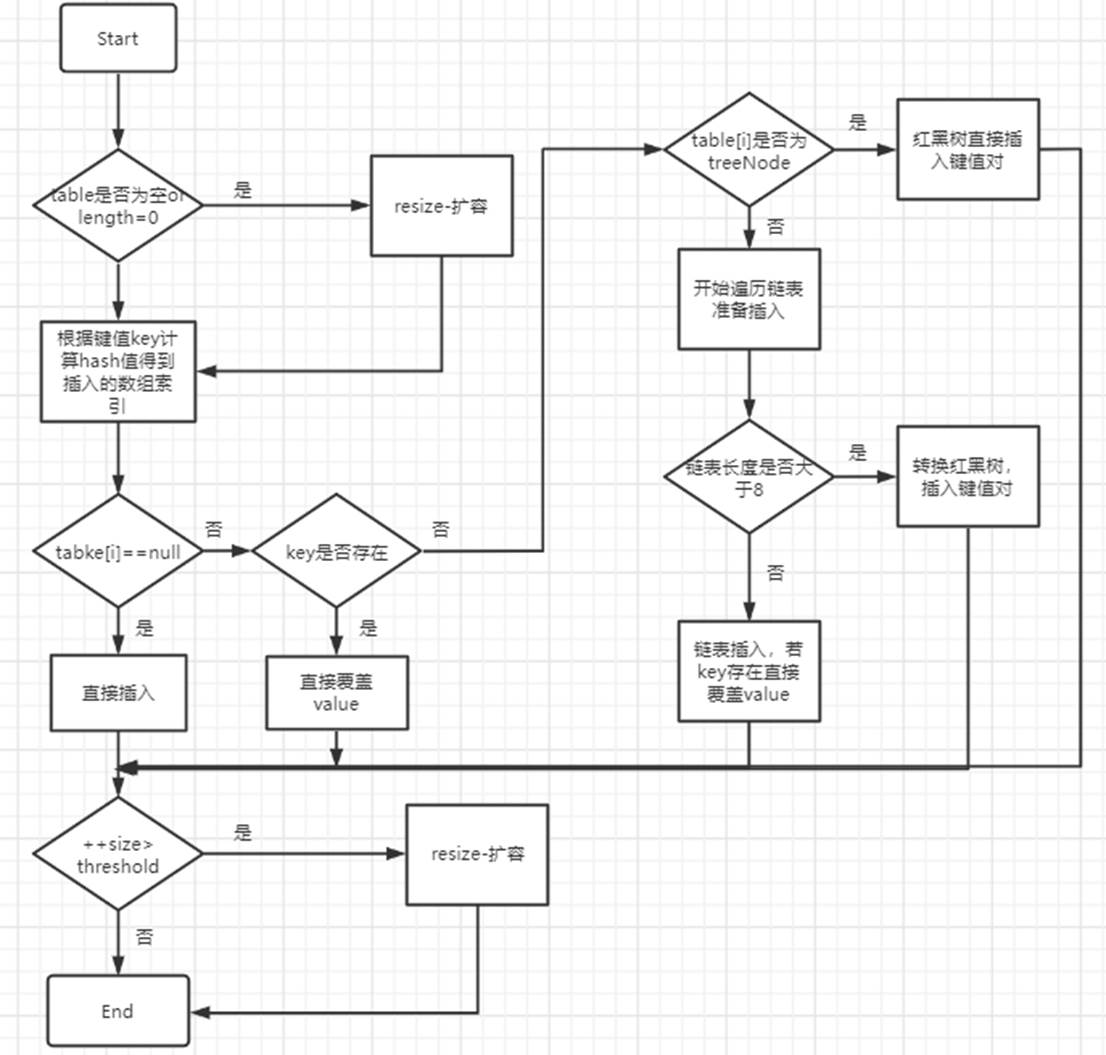
Bootstrap
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The Bootstrap class loader loads the basic runtime classes provided by the JVM,plus any classes from JAR files present in the system extensions directory. It is parent to the System class loader. To add JAR files to the system extensions,directory,see .
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
System
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The System class loader loads Application Server launch classes. It is parent to the Shared Chain class loader. It is created based on the system-classpath attribute of the java-config element in the domain.xml file. In the Admin Console,select the Application Server component,the JVM Settings tab,and the Path Settings tab,then edit the System Classpath field. See and java-config in Sun Java System Application Server Platform Edition 9 Administration Reference.
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
Shared Chain
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The Shared Chain class loader loads most of the core Application Server classes. It is parent to the MBean class loader and the Common class loader. Classes specified by the classpath-prefix and classpath-suffixattributes of the java-config element in the domain.xml file are added to this class loader. In the Admin Console,then edit the Classpath Prefix or Classpath Suffix field.
The environment classpath is included if env-classpath-ignored="false" is set in the java-configelement.
Use classpath-prefix to place libraries ahead of Application Server implementation classes in the shared chain. The classpath-prefix is ideal for placing development and diagnostic patches. Use classpath-suffix to place libraries after implementation classes in the shared chain.
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
MBean
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The MBean class loader loads the MBean implementation classes. See .
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
Common
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The Common class loader loads classes in the domain-dir/lib/classes directory,followed by JAR files in thedomain-dir/lib directory. It is parent to the Connector class loader. No special classpath settings are required. The existence of these directories is optional; if they do not exist,the Common class loader is not created. See .
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
Connector
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The Connector class loader is a single class loader instance that loads individually deployed connector modules,which are shared across all applications. It is parent to the LifeCycleModule class loader and the Application class loader.
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
LifeCycleModule
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The LifeCycleModule class loader is created once per lifecycle module. Each lifecycle-module element’sclasspath attribute is used to construct its own class loader. For more information on lifecycle modules,see.
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
Application
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The Application class loader loads the classes in a specific enabled individually deployed module or Java EE application. One instance of this class loader is present in each class loader universe; see . The Application class loader is created with a list of URLs that point to the locations of the classes it needs to load. It is parent to the Web class loader.
The Application class loader loads classes in the following order:
Classes specified by the library-directory element in the application.xml deployment descriptor or the –-libraries option during deployment; see
-
Classes specified by the application's or module's location attribute in the domain.xml file,determined during deployment
-
Classes in the classpaths of the application's sub-modules
-
Classes in the application's or module's stubs directory
The location attribute points to domain-dir/applications/j2ee-apps/app-name or domain-dir/applications/j2ee-modules/module-name.
The stubs directory is domain-dir/generated/ejb/j2ee-apps/app-name or domain-dir/generated/ejb/j2ee-modules/module-name.
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
Web
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The Web class loader loads the servlets and other classes in a specific enabled web module or a Java EE application that contains a web module. This class loader is present in each class loader universe that contains a web module; see . One instance is created for each web module. The Web class loader is created with a list of URLs that point to the locations of the classes it needs to load. The classes it loads are in WEB-INF/classes or WEB-INF/lib/*.jar. It is parent to the JSP Engine class loader.
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="left" valign="top">
JSP Engine
</td>
<td align="left" valign="top">
The JSP Engine class loader loads compiled JSP classes of enabled JSP files. This class loader is present in each class loader universe that contains a JSP page; see . The JSP Engine class loader is created with a list of URLs that point to the locations of the classes it needs to load.
</td>
</tr>
figure shows the class loader runtime hierarchy." src="https://www.jb51.cc/res/2019/02-12/10/bd2c580bc4a140bea1360f03be6b322c.gif" alt="figure shows the class loader runtime hierarchy.">