Flask 蓝图的基本使用
Flask 中使用蓝图,提供了模块化管理程序路由的功能,使程序结构更加清晰。
1. 蓝图简介
随着 Flask 程序越来越复杂,需要对程序进行模块化的处理,蓝图 (Blueprint) 是 Flask 程序的模块化处理机制,它是一个存储视图方法的集合,Flask 程序通过 Blueprint 来组织 URL 以及处理请求。
Flask 的 Blueprint 具有如下属性:
2. 基本用法
2.1 功能概述
程序将 /news/society/ 和 /news/tech/ 的相关功能组成一个蓝图 news;程序将 /products/car/ 和 /products/baby/ 的相关功能组成一个蓝图 products。
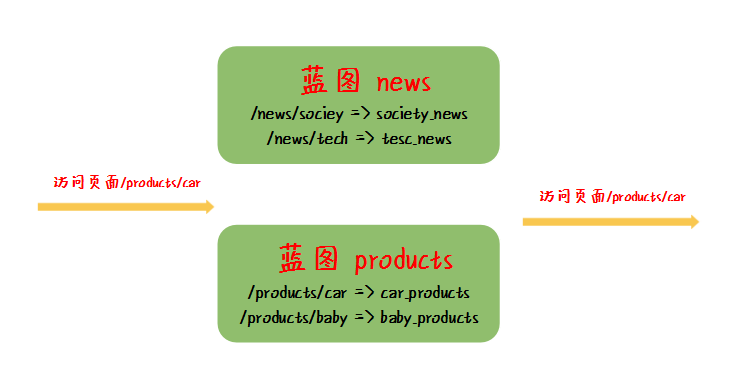
假设访问的页面路径是 /products/car,Flask 框架在蓝图 news 和蓝图 products 中查找匹配该页面路径的路由,发现在蓝图 products 中,存在和路径 /products/car 相应的处理函数 car_products,最后将请求转发给函数 car_products 处理。
-
app.py,程序的主文件; -
news.py,实现蓝图 news; -
products.py,实现蓝图 products。
2.2 主程序 app.py
首先编写主程序 app.py:
from flask import Flask
import news
import products
app = Flask(__name__)
app.register_blueprint(news.blueprint)
app.register_blueprint(products.blueprint)
app.run(debug = True)
在第 2 行,导入模块 news.py,在 news.py 中定义了一个蓝图对象 news.blueprint;在第 3 行,导入模块 products.py,在 products.py 中定义了一个蓝图对象 products.blueprint。
2.3 蓝图 news.py
from flask import Blueprint
blueprint = Blueprint('news', __name__, url_prefix='/news')
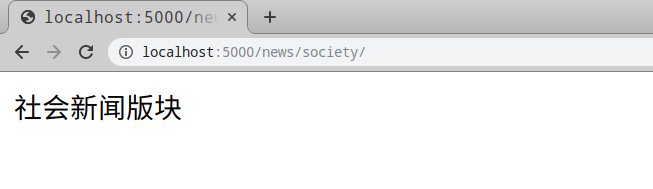
@blueprint.route("/society/")
def society_news():
return "社会新闻版块"
@blueprint.route("/tech/")
def tech_news():
return "IT 新闻板块"
在第 3 行,创建一个蓝图对象,它包含 3 个参数:
在第 5 行,将路径 /society/ 和函数 society_news 关联;在第 9 行,将路径 /tech/ 和函数 tech_news 关联。注意:页面的绝对路径是 /news/society/ 和 /news/tech/,因为蓝图的 url_prefix 设置为 news,在蓝图内部,页面的相对路径是 /society/ 和 /tech/。
2.4 蓝图 products.py
编写 products.py,实现页面 /products/car 和 /products/baby 的功能:
from flask import Blueprint
blueprint = Blueprint('products', __name__, url_prefix='/products')
@blueprint.route("/car")
def car_products():
return "汽车产品版块"
@blueprint.route("/baby")
def baby_products():
return "婴儿产品版块"
在第 3 行,创建一个名为 ‘products’ 的蓝图,该蓝图中页面的 URL 前缀为 /products;在第 5 行,将路径 /car/ 和函数 car_products 关联;在第 9 行,将路径 /baby/ 和函数 baby_products 关联。
注意:页面的绝对路径是 /products/car/ 和 /product/baby/,因为蓝图的 url_prefix 等于 products,在蓝图内部,页面的相对路径是 /car/ 和 /baby/。
2.5 运行程序
在浏览器中,访问 http://localhost:5000/news/society/, 显示如下:
2.6 源代码下载
3. 更具扩展性的架构
3.1 概述
在这种架构中,程序完全不具备扩展性。在初学 Flask 时,使用的例子都是这种类型。
在这种架构中,程序具备一定的扩展性:
第 2 小节的程序采用的就是这种架构,程序包含 2 个蓝图: news 和 products,由 3 个文件构成:app.py、news.py、products.py,其中 news.py 实现新闻版块,products.py 实现产品版块。
3. 使用一个独立的目录实现蓝图
在这种架构中,程序的扩展性最好:
3.2 模板文件寻找规则
3.3 静态文件寻找规则
4. 具有扩展性的架构的例子
4.1 目录结构
本节通过实例讲解如何规划目录、使得程序具有良好的扩展性。程序的功能与第 2 小节相同,包含 2 个蓝图:news 和 products,程序的目录结构如下:
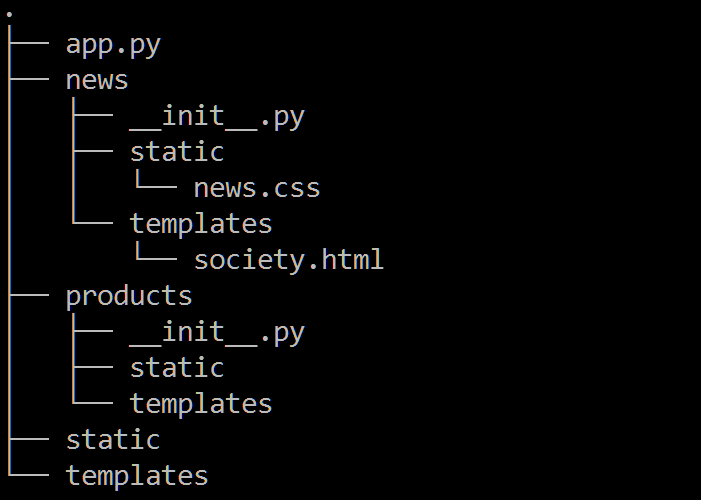
项目的目录的功能描述如下:
4.2 实现 app.py
首先实现主程序 app.py:
from flask import Flask
import news
import products
app = Flask(__name__)
app.register_blueprint(news.blueprint)
app.register_blueprint(products.blueprint)
app.run(debug = True)
在第 2 行,导入模块 news.py,在 news.py 中定义了一个蓝图对象 news.blueprint;在第 3 行,导入模块 products.py,在 products.py 中定义了一个蓝图对象 products.blueprint。
4.3 实现 news/__init.py__
和蓝图 news 相关的所有文件均放置在项目的 news 目录下,在主程序中导入蓝图 news.py 时,会执行 news/__init.py__:
from flask import Blueprint, render_template
blueprint = Blueprint('news', __name__, url_prefix='/news', template_folder='templates', static_folder='static')
@blueprint.route("/society/")
def society_news():
return render_template('society.html')
@blueprint.route("/tech/")
def tech_news():
return "IT 新闻板块"
在第 3 行,创建一个名为 ‘news’ 的蓝图:
在第 7 行,调用 render_template (‘society.html’) 渲染模板文件 society.html,根据模板文件的查找规则,最终在 ‘项目目录 /news/templates’ 目录下找到模板文件。
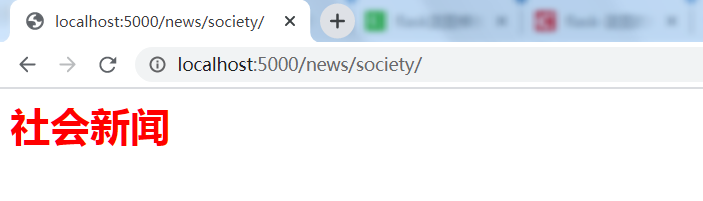
4.4 实现 news/templates/society.html
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{ url_for('news.static',filename='news.css')}}">
<h1>社会新闻</h1>
在模板文件中引用了静态文件 news.css。{{url_for (‘news.static’,filename=‘news.css’) }} 的输出为 news/static/news.css,其中 news.static 表示蓝图 news 的 static 目录。
4.5 实现 news/static/news.css
h1 {
color: red;
}
4.6 实现 products/__init.py__
和蓝图 products 相关的所有文件均放置在项目的 products 目录下,在主程序中导入蓝图 products.py 时,会执行 products/__init.py__:
from flask import Blueprint
blueprint = Blueprint('products', __name__, url_prefix='/products')
@blueprint.route("/car")
def car_products():
return "汽车产品版块"
@blueprint.route("/baby")
def baby_products():
return "婴儿产品版块"
在第 3 行,创建一个名为 ‘products’ 的蓝图:
4.7 运行程序
在浏览器中,访问 http://localhost:5000/news/society/, 显示如下: