问题描述
假设uint是我的定点平台上最大的整数类型,我有:
uint func(uint a,uint b,uint c);
需要返回近似的a * b / c。
c的值大于a的值和b的值。
因此我们可以肯定地知道a * b / c的值将适合uint。
但是,a * b本身的值溢出了uint的大小。
因此,计算a * b / c的值的一种方法是:
return a / c * b;
甚至:
if (a > b)
return a / c * b;
return b / c * a;
但是,c的值大于a的值和b的值。
所以上面的建议只会返回零。
我需要按比例减少a * b和c,但同样-问题是a * b溢出。
理想情况下,我将能够:
- 将
a * b替换为uint(-1) - 将
c替换为uint(-1) / a / b * c。
但是无论我如何对表达式uint(-1) / a / b * c进行排序,都会遇到问题:
-
uint(-1) / a / b * c由于uint(-1) / a / b被截断为零 -
uint(-1) / a * c / b由于uint(-1) / a * c溢出 -
uint(-1) * c / a / b由于uint(-1) * c溢出
我如何解决这种情况才能找到a * b / c的良好近似值?
编辑1
当最大整数类型为_umul128时,平台上没有uint64之类的东西。我最大的类型是uint,并且我不支持任何更大的类型(既不在硬件级别,也不在某些预先存在的标准库中)。
我最大的类型是uint。
编辑2
针对众多重复的建议和评论:
我手头没有一些“较大类型”,可以用来解决此问题。这就是为什么该问题的开头声明是:
假设
uint是我的定点平台上最大的整数类型
我假设在SW层(通过某些内置的标准库)或在HW层上都没有其他类型。
解决方法
需要返回
a * b / c的良好近似值
我最大的类型是uint
a和b都小于c
this 32-bit problem上的变化:
Algorithm: Scale a,b to not overflow
SQRT_MAX_P1 as a compile time constant of sqrt(uint_MAX + 1)
sh = 0;
if (c >= SQRT_MAX_P1) {
while (|a| >= SQRT_MAX_P1) a/=2,sh++
while (|b| >= SQRT_MAX_P1) b/=2,sh++
while (|c| >= SQRT_MAX_P1) c/=2,sh--
}
result = a*b/c
shift result by sh.
对于n位的uint,我希望结果正确至少约n/2个有效数字。
可以利用a,b小于SQRT_MAX_P1中的较小者来改善情况。如果感兴趣的话,稍后再介绍。
示例
#include <inttypes.h>
#define IMAX_BITS(m) ((m)/((m)%255+1) / 255%255*8 + 7-86/((m)%255+12))
// https://stackoverflow.com/a/4589384/2410359
#define UINTMAX_WIDTH (IMAX_BITS(UINTMAX_MAX))
#define SQRT_UINTMAX_P1 (((uintmax_t)1ull) << (UINTMAX_WIDTH/2))
uintmax_t muldiv_about(uintmax_t a,uintmax_t b,uintmax_t c) {
int shift = 0;
if (c > SQRT_UINTMAX_P1) {
while (a >= SQRT_UINTMAX_P1) {
a /= 2; shift++;
}
while (b >= SQRT_UINTMAX_P1) {
b /= 2; shift++;
}
while (c >= SQRT_UINTMAX_P1) {
c /= 2; shift--;
}
}
uintmax_t r = a * b / c;
if (shift > 0) r <<= shift;
if (shift < 0) r >>= shift;
return r;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
uintmax_t a = 12345678;
uintmax_t b = 4235266395;
uintmax_t c = 4235266396;
uintmax_t r = muldiv_about(a,b,c);
printf("%ju\n",r);
}
具有32位数学运算的输出(精确答案为12345677)
12345600
具有64位数学运算的输出
12345677
这是另一种使用递归和最小逼近的方法来实现高精度的方法。
首先提供代码,然后在解释下方
。代码:
uint32_t bp(uint32_t a) {
uint32_t b = 0;
while (a!=0)
{
++b;
a >>= 1;
};
return b;
}
int mul_no_ovf(uint32_t a,uint32_t b)
{
return ((bp(a) + bp(b)) <= 32);
}
uint32_t f(uint32_t a,uint32_t b,uint32_t c)
{
if (mul_no_ovf(a,b))
{
return (a*b) / c;
}
uint32_t m = c / b;
++m;
uint32_t x = m*b - c;
// So m * b == c + x where x < b and m >= 2
uint32_t n = a/m;
uint32_t r = a % m;
// So a*b == n * (c + x) + r*b == n*c + n*x + r*b where r*b < c
// Approximation: get rid of the r*b part
uint32_t res = n;
if (r*b > c/2) ++res;
return res + f(n,x,c);
}
说明:
The multiplication a * b can be written as a sum of b
a * b = b + b + .... + b
Since b < c we can take a number m of these b so that (m-1)*b < c <= m*b,like
(b + b + ... + b) + (b + b + ... + b) + .... + b + b + b
\---------------/ \---------------/ + \-------/
m*b + m*b + .... + r*b
\-------------------------------------/
n times m*b
so we have
a*b = n*m*b + r*b
where r*b < c and m*b > c. Consequently,m*b is equal to c + x,so we have
a*b = n*(c + x) + r*b = n*c + n*x + r*b
Divide by c :
a*b/c = (n*c + n*x + r*b)/c = n + n*x/c + r*b/c
The values m,n,r can all be calculated from a,b and c without any loss of
precision using integer division (/) and remainder (%).
The approximation is to look at r*b (which is less than c) and "add zero" when r*b<=c/2
and "add one" when r*b>c/2.
So now there are two possibilities:
1) a*b = n + n*x/c
2) a*b = (n + 1) + n*x/c
So the problem (i.e. calculating a*b/c) has been changed to the form
MULDIV(a1,b1,c) = NUMBER + MULDIV(a2,b2,c)
where a2,b2 is less than a1,b2. Consequently,recursion can be used until
a2*b2 no longer overflows (and the calculation can be done directly).
我已经建立了一种可以解决O(1)复杂性(无循环)的解决方案:
typedef unsigned long long uint;
typedef struct
{
uint n;
uint d;
}
fraction;
uint func(uint a,uint b,uint c);
fraction reducedRatio(uint n,uint d,uint max);
fraction normalizedRatio(uint a,uint scale);
fraction accurateRatio(uint a,uint scale);
fraction toFraction(uint n,uint d);
uint roundDiv(uint n,uint d);
uint func(uint a,uint c)
{
uint hi = a > b ? a : b;
uint lo = a < b ? a : b;
fraction f = reducedRatio(hi,c,(uint)(-1) / lo);
return f.n * lo / f.d;
}
fraction reducedRatio(uint n,uint max)
{
fraction f = toFraction(n,d);
if (n > max || d > max)
f = normalizedRatio(n,d,max);
if (f.n != f.d)
return f;
return toFraction(1,1);
}
fraction normalizedRatio(uint a,uint scale)
{
if (a <= b)
return accurateRatio(a,scale);
fraction f = accurateRatio(b,a,scale);
return toFraction(f.d,f.n);
}
fraction accurateRatio(uint a,uint scale)
{
uint maxVal = (uint)(-1) / scale;
if (a > maxVal)
{
uint c = a / (maxVal + 1) + 1;
a /= c; // we can now safely compute `a * scale`
b /= c;
}
if (a != b)
{
uint n = a * scale;
uint d = a + b; // can overflow
if (d >= a) // no overflow in `a + b`
{
uint x = roundDiv(n,d); // we can now safely compute `scale - x`
uint y = scale - x;
return toFraction(x,y);
}
if (n < b - (b - a) / 2)
{
return toFraction(0,scale); // `a * scale < (a + b) / 2 < MAXUINT256 < a + b`
}
return toFraction(1,scale - 1); // `(a + b) / 2 < a * scale < MAXUINT256 < a + b`
}
return toFraction(scale / 2,scale / 2); // allow reduction to `(1,1)` in the calling function
}
fraction toFraction(uint n,uint d)
{
fraction f = {n,d};
return f;
}
uint roundDiv(uint n,uint d)
{
return n / d + n % d / (d - d / 2);
}
这是我的考试:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
uint a = (uint)(-1) / 3; // 0x5555555555555555
uint b = (uint)(-1) / 2; // 0x7fffffffffffffff
uint c = (uint)(-1) / 1; // 0xffffffffffffffff
printf("0x%llx",func(a,c)); // 0x2aaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
return 0;
}
您可以按以下方式取消主要因素:
uint gcd(uint a,uint b)
{
uint c;
while (b)
{
a %= b;
c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return a;
}
uint func(uint a,uint c)
{
uint temp = gcd(a,c);
a = a/temp;
c = c/temp;
temp = gcd(b,c);
b = b/temp;
c = c/temp;
// Since you are sure the result will fit in the variable,you can simply
// return the expression you wanted after having those terms canceled.
return a * b / c;
}

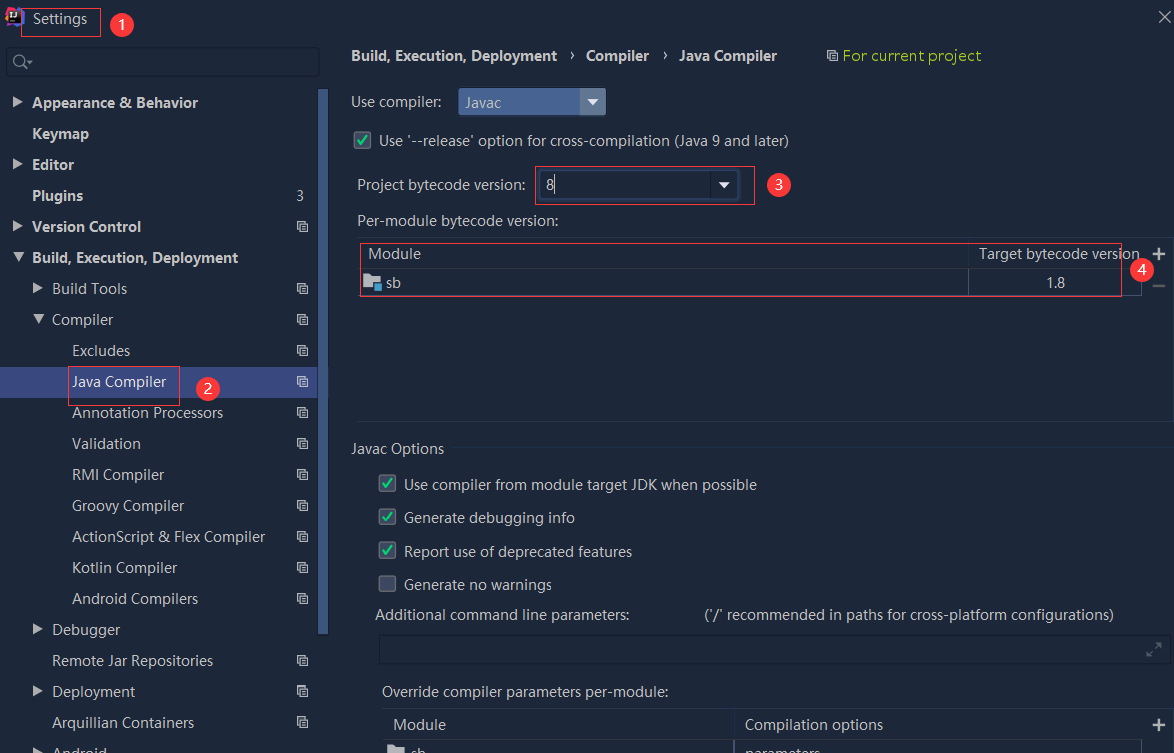 依赖报错 idea导入项目后依赖报错,解决方案:https://blog....
依赖报错 idea导入项目后依赖报错,解决方案:https://blog....
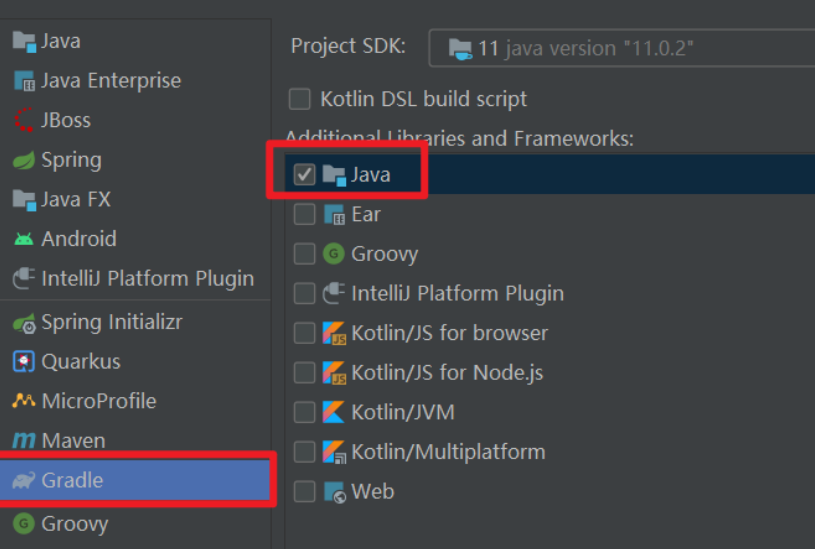 错误1:gradle项目控制台输出为乱码 # 解决方案:https://bl...
错误1:gradle项目控制台输出为乱码 # 解决方案:https://bl...