思路:
解决迷宫求解的问题,从入口出发,顺某一方向向前探索,若能走通,则继续往前走;否则沿原路退回,换一个方向再继续探索,直至所有可能的通路都探索到为止。为了保证在任何位置上都能沿原路退回,所以需要用一个后进先出的结构来保存从入口到当前位置的路径。因此,在求迷宫通路的算法中要应用“栈”的思想假设“当前位置”指的是“在搜索过程中的某一时刻所在图中某个方块位置”,则求迷宫中一条路径的算法的基本思想是:若当前位置“可通”,则放入“当前路径”,并继续朝“下一位置”探索,即切换“下一位置”为“当前位置”,如此重复直至到达出口;若当前位置“不可通”,则应顺着“来向”退回到“前一通道块”,然后朝着除“来向”之外的其他方向继续探索;若该通道块的四周4个方块均“不可通”,则应从“当前路径”上删除该通道块。所谓“下一位置”指的是当前位置四周4个方向(上、下、左、右)上相邻的方块。假设以栈Stack记录“当前路径”,则栈顶中存放的是“当前路径上最后一个通道块”。由此,“放入路径”的操作即为“当前位置入栈”;“从当前路径上删除前一通道块”的操作即为“出栈”。
代码块
maze.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
#define N 10
struct pos
{
size_t _row;
size_t _col;
};
stack <pos> minstack;
void GetMaze(int arr[][N],int size)
{
FILE* f = fopen("MAP.txt","r");
if (NULL == f){
cout << "打开文件失败" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
for (int j = 0; j < size;){
char ch = fgetc(f);
if (ch == EOF){
cout << "读取地图失败" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
if (ch == '1' || ch == '0'){
arr[i][j] = ch - '0';
++j;
}
}
}
fclose(f);
}
bool CheckIsAccess(int arr[][N],pos next)
{
assert(arr);
if((next._row>=0)&&(next._row<=N)&&(next._col>=0)&&(next._col<=N)&&arr[next._row][next._col]==0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void PrintMaze(int arr[][N],int size)
{
for (int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<size;j++)
{
cout<<arr[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
bool MazePath(int arr[][N],pos entry,stack<pos>& path)
{ //找到通路
path.push(entry);
arr[entry._row][entry._col] = 2;
while (!path.empty())
{
pos cur = path.top();
pos next = cur;
if (cur._row == N - 1 || cur._row == 0 || cur._col == N - 1 ){ //更新最短路径
if (minstack.empty())
minstack = path;
else if (path.size() < minstack.size()){
minstack = path;
path.pop();
continue;
}
}
//上
next._row -= 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(arr,next)){
path.push(next);
arr[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
//下
next._row += 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(arr,next)){
path.push(next);
arr[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
//左
next._col -= 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(arr,next)){
path.push(next);
arr[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
next = cur;
//右
next._col += 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(arr,next)){
path.push(next);
arr[next._row][next._col] = 2;
continue;
}
path.pop();
}
if (path.empty()) //判断是否找完所有路径
return true;
return false;
}
测试代码块:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <assert.h>
#include "maze.h"
using namespace std;
#define N 10
int main(){
int mazeMap[N][N] = { 0 };
GetMaze(mazeMap,N);
PrintMaze(mazeMap,N);
stack<pos> path;
pos entry = {2,0}; //定义迷宫入口
bool ret = MazePath(mazeMap,entry,path);
if (ret){
PrintMaze(mazeMap,N);
while (!minstack.empty()){
cout << "<" << minstack.top()._row << "," << minstack.top()._col << ">" << endl;;
minstack.pop();
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
地图文件
map.txt
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1
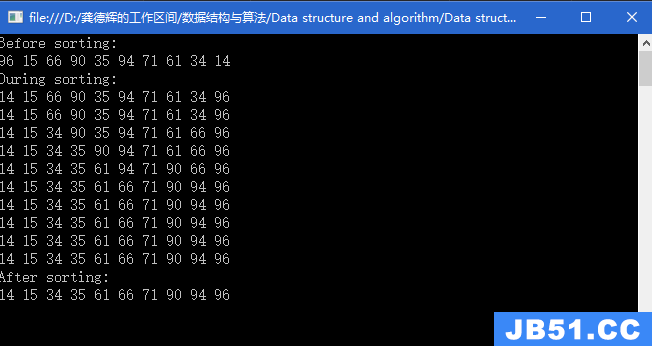
运行结果图