题目链接:http://www.spoj.com/problems/COT/en/
——————————————————————————————————————
COT - Count on a tree
#tree
You are given a tree with N nodes.The tree nodes are numbered from 1 to N.Each node has an integer weight.
We will ask you to perform the following operation:
u v k : ask for the kth minimum weight on the path from node u to node v
Input
In the first line there are two integers N and M.(N,M<=100000)
In the second line there are N integers.The ith integer denotes the weight of the ith node.
In the next N-1 lines,each line contains two integers u v,which describes an edge (u,v).
In the next M lines,each line contains three integers u v k,which means an operation asking for the kth minimum weight on the path from node u to node v.
Output
For each operation,print its result.
Example
Input:
8 58 5
105 2 9 3 8 5 7 7
1 2
1 3
1 4
3 5
3 6
3 7
4 8
2 5 1
2 5 2
2 5 3
2 5 4
7 8 2
Output:
2
8
9
105
7
Submit solution!
——————————————————————————————————————
题目大意:
就是求在树上 (u,v)的路上的第K小的权值
解题思路:
首先对于求第K小的问题 我们可以用主席树搞,没有问题,
但是对于一个树形结构,我们需要将其转化为线性,然后需要树剖才能做.
然后考虑链上的第k值怎么维护,
发现如果树剖计算的话 维护不了啊
因为(u,v)的路 可能在很多个链上,那么不能对每个求第K值,这样明显是错误的啊,
然后我们知道主席树其实就是维护了一个前缀和
那么我们可以对每一个节点到根节点建立前缀和,就能找任意一个节点到根节点的第K值,
那么根据主席树的性质,我们就能够计算(u,v)的路上的第K值了
只要在查询的时候稍改变一下就行了
cnt = sum[ls[u]]+sum[ls[v]]-sum[ls[lca(u,v)]]-sum[ls[fa[lca(u,v)]]];
不理解其实可以将主席树画出来 思考下 挺好理解的.
附本题代码
——————————————————————————————————————
#pragma comment(linker,"/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long int LL;
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch = getchar();
while('0'>ch||ch>'9'){if('-'==ch)f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while('0'<=ch&&ch<='9'){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
#define abs(x) ((x>0)?x:(-x))
/********************************/
const int N = 100000+7;
int n,m,w[N],b[N];
struct node{
int to,next;
}G[N<<1];
int head[N],tot;
/** ChairTree begin */
int rt[N],ls[N*20],rs[N*20],sum[N*20],chairtree,siz;
void build(int &rt,int l,int r){
rt=++chairtree;
sum[rt]=0;
if(l>=r)return ;
int m =((r-l)>>1)+l;
build(ls[rt],l,m);
build(rs[rt],m+1,r);
}
void update(int& rt,int r,int last,int pos){
rt=++chairtree;
ls[rt]=ls[last];
rs[rt]=rs[last];
sum[rt]=sum[last]+1;
if(l>=r) return ;
int m=((r-l)>>1)+l;
if(pos<=m) update(ls[rt],ls[last],pos);
else update(rs[rt],r,rs[last],pos);
}
int query(int rt,int lca,int flca,int k){
if(l>=r) return l;
int m=((r-l)>>1)+l;
int cnt=sum[ls[rt]]+sum[ls[last]]-sum[ls[lca]]-sum[ls[flca]];
if(k<=cnt) query(ls[rt],ls[lca],ls[flca],k);
else query(rs[rt],rs[lca],rs[flca],k-cnt);
}
void dfs(int rt,int r){
int m = ((r-l)>>1)+l;
printf("%d",sum[rt]);
if(l>=r) return ;printf("( ");
dfs(ls[rt],m);printf("_%*d,",2,ls[rt]);
dfs(rs[rt],r);printf("_%*d )",rs[rt]);
}
/**
ChairTree end
*/
void add(int u,int v){
G[++tot].to=v,G[tot].next=head[u],head[u]=tot;
G[++tot].to=u,G[tot].next=head[v],head[v]=tot;
}
int dep[N],fa[N],sz[N],son[N];
void dfs1(int u,int f,int d){
dep[u]=d,fa[u]=f,sz[u]=1,son[u]=0;
for(int i=head[u],to;i;i=G[i].next){
to=G[i].to;
if(to==f)continue;
dfs1(to,u,d+1);
sz[u]+=sz[to];
if(sz[son[u]]<sz[to])son[u]=to;
}
}
int tree[N],top[N],pre[N],cnt;
void dfs2(int u,int tp){
top[u]=tp,tree[u]=++cnt,pre[tree[u]]=u;
update(rt[u],1,siz,rt[fa[u]],w[u]);
if(!son[u])return;
dfs2(son[u],tp);
for(int i=head[u],to;i;i=G[i].next){
to=G[i].to;
if(to==fa[u]||to==son[u])continue;
dfs2(to,to);
}
}
int Lca(int x,int y){
int fx=top[x],fy=top[y];
while(fx!=fy){
if(dep[fx]<dep[fy])swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy);
x=fa[fx],fx=top[x];
}
if(dep[x]>dep[y])swap(x,y);
return x;
}
int main(){
n=read(),m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) w[i]=read(),b[i]=w[i];
for(int i=1;i< n;i++) add(read(),read());
fa[1]=0;
sort(b+1,b+n+1);
siz = unique(b+1,b+n+1)-(b+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) w[i]=lower_bound(b+1,b+siz+1,w[i])-b;
build(rt[0],siz);
dfs1(1,0,1),dfs2(1,1);
while(m--){
int u,v,k;
u=read(),v=read(),k=read();
int lca=Lca(u,v);
printf("%d\n",(b[query(rt[u],rt[v],rt[lca],rt[fa[lca]],k)]));
}
return 0;
}

 匿名组 这里可能用到几个不同的分组构造。通过括号内围绕的正...
匿名组 这里可能用到几个不同的分组构造。通过括号内围绕的正...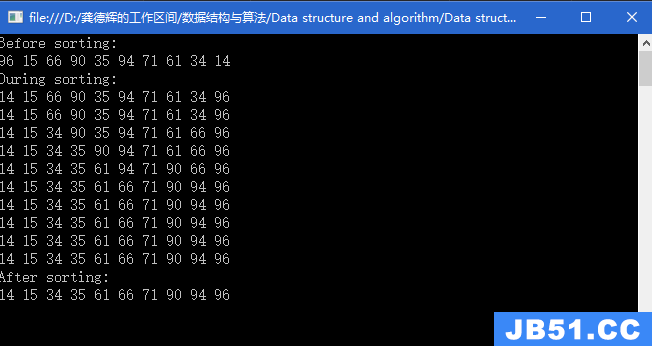 选择排序:从数组的起始位置处开始,把第一个元素与数组中其...
选择排序:从数组的起始位置处开始,把第一个元素与数组中其...