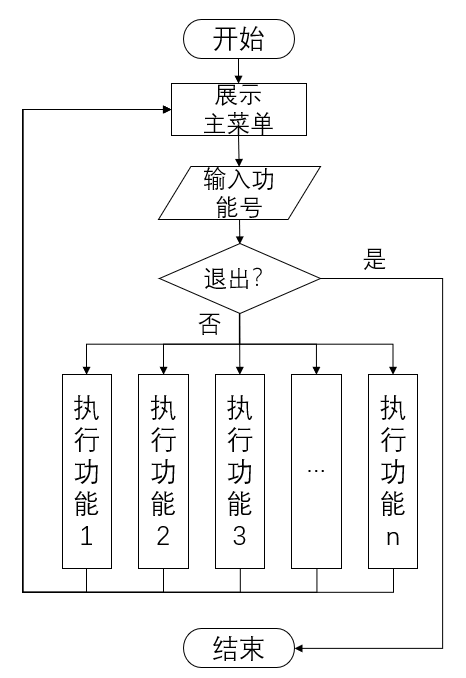
我是新增的
python.我必须首先在cpp代码中初始化一个cpp类实例,然后将此cpp实例传递给python代码,使用python类实例来调用它(cpp实例).我已经尝试过
Python / C API的方式,但失败了,所以我不知道如何传递一个c类的实例到一个python类.
以下是我的代码,从boost python演示中更改.
在main.cpp
#include <python2.6/Python.h>
#include <boost/python.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace boost::python;
using namespace std;
class World
{
private:
string name;
public:
void set(string name)
{
this->name = name;
}
void greet()
{
cout << "hello,I am " << name << endl;
}
};
typedef boost::shared_ptr< World > world_ptr;
BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE(hello)
{
class_<World>("World")
.def("greet",&World::greet)
.def("set",&World::set)
;
register_ptr_to_python<world_ptr>();
};
int main()
{
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");
world_ptr worldobjectPtr (new World);
worldobjectPtr->set("C++!");
try
{
inithello();
PyObject* pModule =PyImport_ImportModule("python");
PyObject* pDict = PyModule_GetDict(pModule);
PyObject* pClassHelloPython = PyDict_GetItemString(pDict,"Person");
PyObject* pInstanceHelloPython = PyInstance_New(pClassHelloPython,NULL,NULL);
PyObject_CallMethod(pInstanceHelloPython,"sayHi",NULL);
worldobjectPtr->greet();
PyObject_CallMethod(pInstanceHelloPython,"greetReset","O",worldobjectPtr);
worldobjectPtr->greet();
}
catch (error_already_set)
{
PyErr_Print();
}
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
在python.py
class Person:
def sayHi(self):
print 'hello from python'
def greetReset(self,instance):
instance.set('Python')
在上面的代码中,我想将worldobjectPtr传递给pInstanceHelloPython,因此,pInstanceHelloPython可以将worldobjectPtr->名称设置为Python.但我只是不知道该怎么做.谢谢你的耐心提前!
解决方法
通过boost :: python :: ptr将对象指针传递给python.这将阻止python解释器复制:
#include <boost/python.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace boost::python;
using namespace std;
class World
{
private:
string name;
public:
void set(string name) {
this->name = name;
}
void greet() {
cout << "hello,I am " << name << endl;
}
};
typedef boost::shared_ptr< World > world_ptr;
BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE(hello)
{
class_<World>("World")
.def("greet",&World::greet)
.def("set",&World::set)
;
};
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
Py_Initialize();
try {
PyRun_SimpleString(
"class Person:\n"
" def sayHi(self):\n"
" print 'hello from python'\n"
" def greetReset(self,instance):\n"
" instance.set('Python')\n"
);
world_ptr worldobjectPtr (new World);
worldobjectPtr->set("C++!");
inithello();
object o_main
= object(handle<>(borrowed(PyImport_AddModule("__main__"))));
object o_person_type = o_main.attr("Person");
object o_person = o_person_type();
object o_func1 = o_person.attr("sayHi");
o_func1();
object o_func2 = o_person.attr("greetReset");
o_func2(boost::python::ptr(worldobjectPtr.get()));
worldobjectPtr->greet();
}
catch (error_already_set) {
PyErr_Print();
}
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}