介绍
Realm 是一个 MVCC (多版本并发控制)数据库,由Y Combinator公司在2014年7月发布一款支持运行在手机、平板和可穿戴设备上的嵌入式数据库,目标是取代sqlite。
Realm 本质上是一个嵌入式数据库,他并不是基于sqlite所构建的。它拥有自己的数据库存储引擎,可以高效且快速地完成数据库的构建操作。和sqlite不同,它允许你在持久层直接和数据对象工作。在它之上是一个函数式风格的查询api,众多的努力让它比传统的sqlite 操作更快 。
详细介绍(如果进不去,看这个也行)
优势
如果在在使用它时候,连它的优势在哪都不知道的话就有点说不过去了。
- 易用
Ream 不是在sqlite基础上的ORM,它有自己的数据查询引擎。并且十分容易使用。 - 快速
由于它是完全重新开始开发的数据库实现,所以它比任何的ORM速度都快很多,甚至比SLite速度都要快。 - 跨平台
Realm 支持 iOS & OS X (Objective‑C & Swift) & Android。我们可以在这些平台上共享Realm数据库文件,并且上层逻辑可以不用任何改动的情况下实现移植。 - 高级
Ream支持加密,格式化查询,易于移植,支持JSON,流式api,数据变更通知等高级特性 - 可视化
Realm 还提供了一个轻量级的数据库查看工具,在Mac Appstore 可以下载“Realm browser”这个工具,开发者可以查看数据库当中的内容,执行简单的插入和删除数据的操作。(windows上还不清楚)
条件
- 目前不支持
Android以外的Java - Android Studio >= 1.5.1
- 较新的Android SDK版本
- JDK version >=7.
- 支持API 9(Android 2.3)以及之后的版本
使用
不介绍了,看代码了。
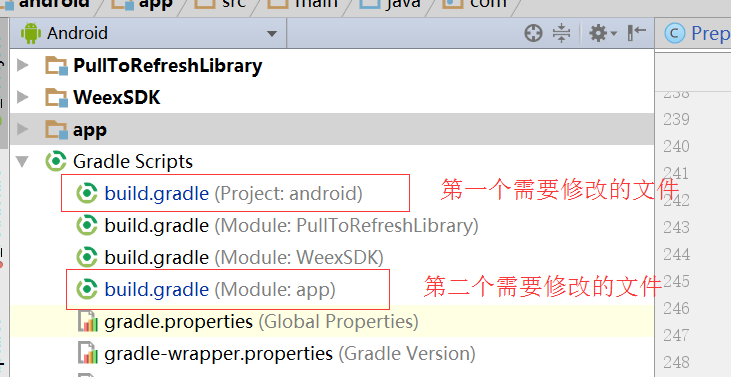
- 加入依赖
在project的build中加入依赖
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath "io.realm:realm-gradle-plugin:2.2.1"
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

在module中加入
apply plugin: 'realm-android'
- 1
- 1

创建model
创建一个User类,需要继承RealmObject。支持public, protected和 private的类以及方法
public class User extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
除了直接继承于RealmObject来声明 Realm 数据模型之外,还可以通过实现 RealmModel接口并添加 @RealmClass修饰符来声明。
@RealmClass
public class User implements RealmModel {
...
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 支持的属性
boolean,byte,short,int,long,float,double,String,Date和,byte[],RealmObject,RealmList<? extends RealmObject>
还支持Boolean,Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Float和Double
Tip:整数类型short、int和long都被映射到 Realm 内的相同类型(实际上为 long ) @PrimaryKey——表示该字段是主键
使用过数据库的同学应该看出来了,PrimaryKey就是主键。使用@PrimaryKey来标注,字段类型必须是字符串(String)或整数(byte,short,int或long)以及它们的包装类型(Byte,Short,Integer, 或Long)。不可以存在多个主键,使用字符串字段作为主键意味着字段被索引(注释@PrimaryKey隐式地设置注释@Index)。
@PrimaryKey
private String id;
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
@required——表示该字段非空
在某些情况下,有一些属性是不能为null的。使用@required可用于用于强行要求其属性不能为空,只能用于Boolean,Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Float,Double,String,byte[]和Date。在其它类型属性上使用@required修饰会导致编译失败。
Tip:基本数据类型不需要使用注解@required,因为他们本身就不可为空。
@required
private String name;
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
@Ignore
private String name;
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
@Index——添加搜索索引
为字段添加搜索索引,这样会使得插入的速度变慢,数据量也变得更大。不过在查询速度将变得更快,建议只在优化读取性能的特定情况时添加索引。支持索引:String,byte,short,int,long,boolean和Date字段。
> **注意**:如果你创建Model并运行过,然后修改了Model。那么就需要升级数据库,否则会抛异常。升级方式后面会提到
### **初始化**
使用默认配置
```java
Realm.init(this);
Realm mRealm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这时候会创建一个叫做 default.realm的Realm文件,一般来说,这个文件位于/data/data/包名/files/。通过realm.getPath()来获得该Realm的绝对路径。
注意:模拟器上运行时,
Realm.getDefaultInstance()抛出异常,真机上没问题(不止何故)
当然,我们还可以使用RealmConfiguration来配置Realm
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder()
.name("myrealm.realm") //文件名
.schemaVersion(0) //版本号
.build();
Realm realm = Realm.getInstance(config);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
创建非持久化的Realm,也就是保持在内存中,应用关闭后就清除了。
RealmConfiguration myConfig = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.name("myrealm.realm")//保存在内存中
.inMemory() .build();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
Builder.name: 指定数据库的名称。如不指定默认名为default。Builder.schemaVersion: 指定数据库的版本号。Builder.encryptionKey: 指定数据库的密钥。Builder.migration: 指定迁移操作的迁移类。Builder.deleteRealmIfMigrationNeeded: 声明版本冲突时自动删除原数据库。Builder.inMemory: 声明数据库只在内存中持久化。build: 完成配置构建。
关闭Realm
记得使用完后,在onDestroy中关闭Realm
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// Close the Realm instance.
realm.close();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
增
写入操作需要在事务中进行,可以使用executeTransaction方法来开启事务。
- 使用
executeTransaction方法插入数据
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
User user = realm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("Gavin");
user.setAge(23);
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
在execute方法中执行插入操作
注意:如果在UI线程中插入过多的数据,可能会导致主线程拥塞。
- 使用
copyToRealmOrUpdate或copyToRealm方法插入数据
当Model中存在主键的时候,推荐使用copyToRealmOrUpdate方法插入数据。如果对象存在,就更新该对象;反之,它会创建一个新的对象。若该Model没有主键,使用copyToRealm方法,否则将抛出异常。
final User user = new User();
user.setName("Jack");
user.setId("2");
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
realm.copyToRealmOrUpdate(user);
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 如果你用的是这样的
modle
public class User2 extends RealmObject {
public String name;
public int age;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
就这样写
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
User2 user = realm.createObject(User2.class);
user.name = "Micheal";
user.age = 30;
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 如果User还有其他属性是,比如养了只
Dog:
public class Dog extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private int age;
//getters and setters
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
对应的User属性中加入Dog类
public class User extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private int age;
private Dog dog;
//getters and setters
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
如果你养了不止一只,你养了二哈、阿拉撕家…那你就要用到RealmList了。在User中加入该属性
private RealmList<Dog> dogs;
- 1
- 1
插入数据
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
User user = realm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("Gain");
user.setAge(23);
Dog dog1 = realm.createObject(Dog.class);
dog1.setAge(1);
dog1.setName("二哈");
user.getDogs().add(dog1);
Dog dog2 = realm.createObject(Dog.class);
dog2.setAge(2);
dog2.setName("阿拉撕家");
user.getDogs().add(dog2);
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
mRealm.beginTransaction();//开启事务
User user = mRealm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("Gavin");
user.setId("3");
mRealm.commitTransaction();//提交事务
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
在插入前,先调用beginTransaction(),完成后调用commitTransaction()即可。
注意:在UI和后台线程同时开启创建write的事务,可能会导致ANR错误。为了避免该问题,可以使用
executeTransactionAsync来实现。
RealmAsyncTask transaction = mRealm.executeTransactionAsync(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
User user = realm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("Eric");
user.setId("4");
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
还可以加入监听
RealmAsyncTask transaction = mRealm.executeTransactionAsync(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
User user = realm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("Eric");
user.setId("4");
}
}, new Realm.Transaction.OnSuccess() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
//成功回调
}
}, new Realm.Transaction.OnError() {
@Override
public void one rror(Throwable error) {
//失败回调
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
注意:如果当Acitivity或Fragment被销毁时,在OnSuccess或OnError中执行UI操作,将导致程序奔溃 。用RealmAsyncTask .cancel();可以取消事务
在onStop中调用,避免crash
public void onStop () {
if (transaction != null && !transaction.isCancelled()) {
transaction.cancel();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- JSON
Realm还是个很nice的功能就是将Json字符串转化为对象,厉害了我的Realm
(直接借用官方的例子)
// 一个city model
public class City extends RealmObject {
private String city;
private int id;
// getters and setters left out ...
}
// 使用Json字符串插入数据
realm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
realm.createObjectFromJson(City.class, "{ city: \"copenhagen\", id: 1 }");
}
});
// 使用InputStream插入数据
realm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
try {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("path_to_file"));
realm.createallFromJson(City.class, is);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
Realm 解析 JSON 时遵循如下规则:
- 使用包含空值(null)的 JSON 创建对象:
- 对于非必须(可为空值的属性),设置其值为 null;
- 对于必须(不可为空值的属性),抛出异常;
- 使用包含空值(null)的 JSON 更新对象:
- 对于非必须(可为空值的属性),设置其值为 null;
- 对于必须(不可为空值的属性),抛出异常;
- 使用不包含对应属性的 JSON: * 该属性保持不变
查
查找操作就比插入方便多了,并不需在事务中操作,直接查询即可。
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class).findAll();
- 1
- 1
这里使用RealmResults来接受查询到的结果,突然出现的RealmResults可能会让人懵逼。看看他的源码,发现RealmResults继承了AbstractList,而AbstractList又实现了List接口。好吧,原来实现了我们熟悉的List接口。
public final class RealmResults<E extends RealmModel> extends AbstractList<E>
- 1
- 1
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E>
- 1
- 1
注意:
RealmResults虽然实现了List接口,不过有很多方法是不能用的。比如add、addAll、remove、clear等,调用后会直接抛异常。不过也不用当心误用这些方法,因为它们都被标记为@Deprecated了。
findAllAsync——异步查询
当数据量较大,可能会引起ANR的时候,就可以使用findAllAsync
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "Gavin")
.findAllAsync();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
值得注意的是,这里并不会马上查到数据,是有一定延时的。也就是说,你马上使用userList的时候,里面是没有数据的。可以注册Realmchangelistener监听器,或者使用isLoaded()方法,判断是否查询完成
if (result.isLoaded()) {
// 完成查询
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
User user2 = mRealm.where(User.class).findFirst();
- 1
- 1
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "Gavin").findAll();
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
如果User中还有Dog属性,希望根据Dog的条件来获取用户:
例:查询dogs.name为二哈的User
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("dogs.name", "二哈").findAll();
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
得到有养有dogs.name为”二哈”的用户列表(这里的dogs是User表中的属性名)
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "Gavin").findAll();
RealmResults<User> userList = user5.where()
.equalTo("dogs.name", "二哈").findAll();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
上面先找到name为“Gavin”的User列表,然后再得到的结果中查询dogs.name为“二哈”
觉得这样写太麻烦?我也是这样想的,所以还可以这样写
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "Gavin")
.equalTo("dogs.name", "二哈")
.findAll();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
是不是很清爽~~~
-
更多查询条件
上面就展示了equalTo的用法。当然,查询还有更多的用法,我就不一一示例了。已知的方法如下:sum():对指定字段求和。average():对指定字段求平均值。min(): 对指定字段求最小值。max(): 对指定字段求最大值。count : 求结果集的记录数量。findAll(): 返回结果集所有字段,返回值为RealmResults队列findAllSorted(): 排序返回结果集所有字段,返回值为RealmResults队列between(),greaterThan(),lessthan(),greaterThanorEqualTo()&lessthanorEqualTo()equalTo()¬EqualTo()contains(),beginsWith()&endsWith()isNull()&isNotNull()isEmpty()&isNotEmpty() -
RealmQuery以及or的使用
在使用where()方法时,能得到一个RealmQuery对象,使用方法如下:
例:查询name为“Gavin”和“Eric”的用户
RealmQuery<User> query = mRealm.where(User.class);
query.equalTo("name", "Gavin");
query.or().equalTo("name", "Eric");
RealmResults<User> userList = query.findAll();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
这种情况下就要用到or()方法
这么一大串,你又觉得麻烦了?没事,继续简化。
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "Gavin")
.or().equalTo("name", "Eric")
.findAll();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Tip:查询的时候你不用当心得到的RealmResults为null。如果查询的结果为空,那么RealmResults的size为0
- 排序
查询结束后,还可以进行排序,就像这样:
RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class) .findAll();
userList = result.sort("age"); //根据age,正序排列
userList = result.sort("age", Sort.DESCENDING);//逆序排列
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
RealmResults<User> results = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
long sum = results.sum("age").longValue();
long min = results.min("age").longValue();
long max = results.max("age").longValue();
double average = results.average("age");
long matches = results.size();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
改
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
//先查找后得到User对象
User user = mRealm.where(User.class).findFirst();
user.setAge(26);
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
修改也是需要在事务中操作。
使用查询语句得到数据,然后将内容改了即可。
删
- 使用
deleteFromrealm()
//先查找到数据
final RealmResults<User> userList = mRealm.where(User.class).findAll();
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
userList.get(0).deleteFromrealm();
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 使用
deleteFromrealm(int index)
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
userList.deleteFromrealm(0);
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 更多方法:
userList.deleteFirstFromrealm(); //删除user表的第一条数据
userList.deleteLastFromrealm();//删除user表的最后一条数据
results.deleteallFromrealm();//删除user表的全部数据
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
版本升级
当数据结构发生变化是,需要升级数据库。对于Realm来说,数据库升级就是迁移操作,把原来的数据库迁移到新结构的数据库。(体验:略麻烦)
- 例1:
User类发生变化,移除age,新增个@required的id字段。User版本:version 0
String name;
int age;
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
User版本:version 1
@required
String id;
String name;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
创建迁移类CustomMigration,需要实现RealmMigration接口。执行版本升级时的处理:
/**
* 升级数据库
*/
class CustomMigration implements RealmMigration {
@Override
public void migrate(DynamicRealm realm, long oldVersion, long newVersion) {
RealmSchema schema = realm.getSchema();
if (oldVersion == 0 && newVersion == 1) {
RealmObjectSchema personSchema = schema.get("User");
//新增@required的id
personSchema
.addField("id", String.class, FieldAttribute.required)
.transform(new RealmObjectSchema.Function() {
@Override
public void apply(DynamicReal
mObject obj) {
obj.set("id", "1");//为id设置值
}
})
.removeField("age");//移除age属性
oldVersion++;
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
使用Builder.migration升级数据库,将版本号改为1(原版本号:0)。当Realm发现新旧版本号不一致时,会自动使用该迁移类完成迁移操作。
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder()
.name("myrealm.realm") //文件名
.schemaVersion(1)
.migration(new CustomMigration())//升级数据库
.build();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 例2:加入
Dog类,User中加入Dog集合。User版本:version 1
@required
String id;
String name;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
User版本:version 2
@required
private String id;
private String name;
private RealmList<Dog> dogs;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Dog类
public class Dog extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private int age;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
在迁移类CustomMigration中,继续添加处理方法。
if (oldVersion == 1 && newVersion == 2) {
//创建Dog表
RealmObjectSchema dogSchema = schema.create("Dog");
dogSchema.addField("name", String.class);
dogSchema.addField("age", int.class);
//User中添加dogs属性
schema.get("User")
.addRealmListField("dogs", dogSchema)
.transform(new RealmObjectSchema.Function() {
@Override
public void apply(DynamicRealmObject obj) {
//为已存在的数据设置dogs数据
DynamicRealmObject dog = realm.createObject("Dog");
dog.set("name", "二哈");
dog.set("age", 2);
obj.getList("dogs").add(dog);
}
});
oldVersion++;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 更多用法——
RealmObjectSchema
例:取消id必填:
personSchema.setNullable("id", true):
- 1
- 1
例:移除id字段
personSchema.removeField("id");
- 1
- 1
例:重命名
personSchema..renameField("id", "userId");
- 1
- 1
String id = obj.getString("id");
- 1
- 1
例:为字段设置值
obj.setString("name", "Gavin");
obj.setInt("id", 1);
obj.setLong("id", 1);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
疑问:我在debug时发现这样的数据,如图:
userList
什么,dogs、id、name的值怎么都是null?这~~
开始我还以为升级时数据丢失,不过在图中userList第0条数据的右边看到了我的数据,于是我展开了里面的内容,如图:展开后的userListg
好吧,他并不是我想象中的那种存法,我已经不知道他内部是怎么实现的了。(还望大神赐教)
加密
(官方原文)
Realm 文件可以通过传递一个512位(64字节)的密钥参数给 Realm.getInstance().encryptionKey() 来加密存储在磁盘上。
byte[] key = new byte[64];
new SecureRandom().nextBytes(key);
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder()
.encryptionKey(key)
.build();
Realm realm = Realm.getInstance(config);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
保证了所有永久性存储在磁盘上的数据都是通过标准 AES-256 加密的。每次创建新的 Realm 实例的时候,都需要提供相同的密钥。
参考 examples/encryptionExample。这个例子演示了如何通过 Android KeyStore 来安全地存储密钥。
适配器(Adapter)
(官方原文)
Realm提供了一些抽象的工具类来方便地将 OrderedRealmCollection
(RealmResults和 RealmList 都实现了这个借口)展示到UI控件上。
你需要在 app 的 build.gradle中添加额外的依赖以使用这些适配器。
dependencies {
compile 'io.realm:android-adapters:1.4.0'
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
Intents
(官方原文)
你不可以直接通过 intent传递 RealmObject,建议你只传递RealmObject的标识符。举个常用例子,假如你的对象拥有一个主键,请通过intent 的 bundle 来传递这个主键的值。
// Assuming we had a person class with a @PrimaryKey on the 'id' field ...
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(), ReceivingService.class);
intent.putExtra("person_id", person.getId());
getActivity().startService(intent);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
在接受方(Activity、Service、IntentService、broadcastReceiver及其它)从 bundle中解析出这个主键然后打开Realm 查询得到这个 RealmObject。
// in onCreate(), onHandleIntent(), etc.
String personId = intent.getStringExtra("person_id");
Realm realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
Person person = realm.where(Person.class).equalTo("id", personId).findFirst();// do something with the person ...
realm.close();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
可以参考 threading example 中的 Object Passing部分。该示例展示了在安卓开发中常用的如何传递 id 并且得到对应的 RealmObject。
RxJava
对于这么火的RxJava,Realm又怎么会放过他。
Realm 包含了对 RxJava 的原生支持。如下类可以被暴露为一个 Observable:Realm, RealmResults, RealmObject, DynamicRealm 和 DynamicRealmObject。
(直接用一个官方的例子)
Realm realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
GitHubService api = retrofit.create(GitHubService.class);
realm.where(Person.class).isNotNull("username").findAllAsync().asObservable()
.filter(persons.isLoaded)
.flatMap(persons -> Observable.from(persons))
.flatMap(person -> api.user(person.getGithubUserName())
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe(user -> showUser(user));
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
这里使用asObservable轻松转换成RxJava中的Observable,使用.filter(persons.isLoaded)来判断是否已查询完成。到这里,熟悉RxJava的同学应该已经看明白了~~。可能还有人会一脸懵逼,->? 这是什么鬼?哈哈,这叫Lambda,有时间可以去看看。
也许还有很多同学不了解RxJava,这里极力推荐给 Android 开发者的 RxJava 详解。
终于写完了~~~说好易用的,没想到内容居然这么多。
源码地址
参考资料
官方文档
GitHub
Realm for Android快速入门教程
Android开发笔记(八十五)手机数据库Realm
在Android加入和使用Realm
Android 进阶之第三方库的介绍 Realm [一] 基础用法